![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Areal RF equation |

IDF |
|
|
Saturation pressure |
Pressure if water vapour in equilibrium with its liquid |
|
|
Relative humidity |
vapour pressure of air : saturation vapour pressure |
|
|
ed |
Vapour pressure of air |
|
|
es |
Saturation vapour pressure |
|
|
Equation for relative humidity |
RH= ed/es * 100 |
|
|
What does saturated vapour pressure change with |
Temperature |
|
|
Dew point temperature does cold or hot air hold less water vapour |
When moist air below the saturation vapour content at one temperature is cooled until the saturation vapour content at a lower temp is reached |
|
|
Does cool or hot air hold more water vapour |
Warm |
|
|
How do clouds form above land |
Land is warm and hot air rises. Dry air expands as it rises and cools. Stops when is it the same temp as surrounding air |
|
|
How do clouds form over water does cold or warm air have a higher dew point temp |
Cooling of moist air can cause it to reach dew point temples condenses |
|
|
Does cold or warm air have a higher saturation vapour pressure consensati |
Warm |
|
|
CCN |
Cloud condensation nuclei. Water vapour condenses on aerosols to make cloud |
|
|
How does rain form from Warm clouds |
Collision and coalescence Water droplets are large enough to overcome air currents |
|
|
how does rain form in Cold clouds |
Ice crystals attract water vapour |
|
|
How does precipitation occur |
Water vapour goes up and droplets form on aerosols. Get bigger with condensation, get heavy. Some get smaller via evaporation and repeat the process but others get bigger via aggregation and fall |
|
|
Hygroscopic particle |
Something that attracts water from surroundings |
|
|
Non recording gauge |
Uses a measuring cylinder |
|
|
Tipping bucket rain gauge |
Tips certain amounts out and use an electric signal for recording |
|
|
Weighing rain gauge |
Records a trace on the drum chart with weight of water collected. Has a pen inside |
|
|
What are some problems when using a rain gauge |
Wind/aerodynamics Evaporation Splashing Locations |
|
|
Methods for areal average rainfall estimates |
Arithmetic average Thiessen polygon method Isohyetal method |
|
|
Thiessen polygon method |
Rain gauges are set up and separated. The rainfall for each polygon is the rainfall in mm*area of the polygon |
|
|
Isohyetal method |
Lines of equal rainfall |
|
|
Isohyet |
Line of equal rainfall |
|
|
How else can rainfall be measured |
Radar Satellites |
|
|
Return period equation |
T= 1/exceedance probability |
|
|
Convective precipitation which |
Warm moist air rises, condensation and thunderstorms |
|
|
Return period of 10 years |
T=1/P T=1/10 T=0.1 T=10% |
|
|
DDF |
Depth duration frequency curve. Lines connect rain data in the same storm |
|
|
What do each of the curves on a DDF curve represent what |
Return period |
|
|
What are PMPs used for |
Probably maximum precipitation. Used an inputs for models used to estimate design storms ie dam spillways, drainage structures, land use for flooding management |
|
|
Adiabatic lapse rate |
Explains how cooling occurs as vapour rises up in atmosphere and temperature subsequently drops |
|
|
Vapour pressure vs air temp graph |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Which precipitation type is caused by earths hot surface |
Convective |
|
|
Orographic precipitation |
Horizontal air currents are forced to rise over natural barriers. |
|
|
Rainshadow effect |
Moist rain does not make it over natural barriers |
|
|
Cold front |
advancing Cold front forces hot air to rise, causes rapid cooling and intense but short rainfall |
|
|
Warm front |
Advancing Warm air rises up over cold air, gradual cooling. Moderate but long rainfall |
|
|
Frontal precipitation |
Rain resulting from meeting or warm and cold air currents |
|
|
What is air movement affected by |
Coriolis affect and friction |
|
|
Vapour pressure vs air temp graph |
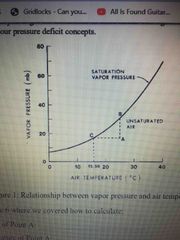
Back (Definition) |

