![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What causes groundwater to have more than 1000 mg/L of an element? |
Encountered highly soluble material been concentrated by evapotranspiration been geothermally heated been polluted |
|
|
What parameters measured? |
Chemical Physical Biological Radiological |
|
|
How are parameters measured? |
Temperature Conductivity pH and Eh major cations and anion minor ions trace elements silica Alkalinity total dissolved solids hardness Natural organic carbon (total and dissolved) Turbidity Dissolved gasses (O2, CO2, CH4, Rn) |
|
|
What is the importance of measuring temperature? |
Describing concentration -temperature dependent units( eg molarity based on volumes; M=mol/L) -not temperature dependent units ( eg molality based on masses; m=mol/kg)
determines rate of chemical reactions -rates double for each 10 degree C rise in temp |
|
|
What is the importance of measuring conductivity? |
Ability of water to conduct electricity directly proportional to the amount of ions (dissolved solids)
can estimate TDS from conductivity |
|
|
What is the importance of measuring pH? |
logarithmic scale so apparently small changes aren't really small
not the same as acidity -ph only one part of total acidity
rate of many geochemical reactions are pH dependent -eg carbonate and silicates dissolve at low ph |
|
|
What is the importance of measuring Alkalinity? |
One of the most important characteristics
resists acidity, which is very toxic
a proxy measure of bicarbonate in most cases
at great depths caused by HS- where there is no oxygen
pH < 4.5 no alkalinity
pH 4.5-8.0 alkalinity dominated by bicarbonate ions HCO3-
pH 8.5 - 11.0 alkalinity dominated by carbonate ions (CO3)2-
pH > 11 alkalinity dominated by hydroxide ions OH- |
|
|
What is the importance of measuring Eh? |
sometimes called redox potential
measure of status of redox reactions
hard to measure in the field -conditions rapidly change from reducing to oxidizing during sample transport to the lab |
|
|
What is the importance of measuring Hardness? |
Reflection of the concentration of Ca2+ and Mg2+
total hardness (TH) is calculated according to the formula
TH(meq/L) as CaCO3 = 2.5[Ca2+] + 4[Mg2+]
[ ] is the concentration in meq/L
temporary hardness: present until temperature rise causes precipitation of Ca2+ and Mg2+ and hardness is eliminated -why kettles get limes scale
permanent hardness present always regardless of temperature |
|
|
What is temporary hardness? |
present until temperature rise causes precipitation of Ca2+ and Mg2+ and hardness is eliminated -why kettles get lime scale |
|
|
What is premanent hardness? |
present always regardless of temperature |
|
|
What are the ways to plot parameters? |
Contour elements on a map Stiff diagrams ion balance or collins diagram (bar graphs) pie graphs or charts piper diagram durov diagram schoeller diagram radial plot box and whisker plot |
|
|
what are stiff diagrams? |
developed by H.A Stiff in 1951
useful to compare overall water chemistry from one area with another
must use same species, order, scale
shows cations and anions on separate sides of diagram
Often used on maps
polygonal shapes made by 3-4 parallel horizontal axes on either side of a vertical zero axis
Cations are plotted on the left side one to each horizontal axis
anions are plotted on the right side |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of stiff diagrams? |
Advantages can help visualize ionically related waters from which a flow path can be determined if the flow path is known to show how the ionic composition changes over space and/or time
disadvantage only on analysis per plot |
|
|
what are piper diagrams? |
Cations and anions shown by separate ternary plots
apexes of the cation plot are Ca, Mg and Na + K
apexes of the anion plot are (SO4)2-, Cl- and (CO3)2- + HCO3-
Two ternary plots then projected onto a diamond a - a matrix transformation of anions and cations |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of piper diagrams? |
advantages many analyses plotted on same diagram can classify by hydrochemical facies can be used to identify mixing of waters can track changes through space and time
disadvantages concentrations are renormalized not useful where oter cations or anions are significant |
|
|
What are Durov diagrams? |
useful for categorizing water "types"
Compars percentage of each major ion as a fracion of the total cations or anions
shows precentage of each cation to cation sum in one triangle and percentage of each anion to anion sum in the other triangle
particularly useful for identifying chemical similarities among subgroups
eliminates some shortcomings of hill and piper diagrams
expanded durov diagram very similar to piper diagram, except it shows ions as a percentage of total ions rather than percentage of separate cations and anions |
|
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of durov diagrams? |
Advantages particularly useful for identifying chemical similarities among subgroups
eliminates some shortcomings of hill and piper diagrams
Disadvantages for some types of groundwater, piper and durov diagrams do not show enough detail to discriminate between similar waters (eg saline water) hounslow diagrams more useful
|
|
|
What is a box and whisker plot? |
represents basic statistical information eg minimum, maximum, median, upper and lower quartiles and mean
multiple plots can be connected to show variance over time or compared with other sites to show differences
more conclusions can be drawn than for simple time series |
|
|
What is NAPLs? |
Non-aquesoud phase liquids
|
|
|
What are the three plumes of NAPLs? |
Vapour immiscible liquid dissolved |
|
|
What are the characteristics of LNAPLs? |
Lighter than water
"float" at the water table
give rise to associated vapour phase and dissolved phase |
|
|
What are the characteristics of DNAPLs? |
Heavier than water
"sink" to bottom of aquifers
can also give rise to dissolved phase |
|
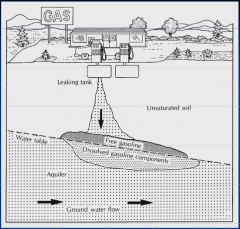
Which NAPL? |
Light NAPL |
|
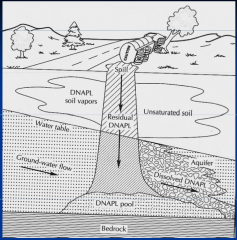
Which NAPL? |
Dense NAPL |
|
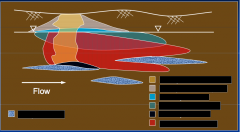
|
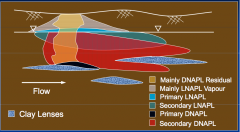
|
|
|
How large of a contaminant plume will will 10 000 L & 15 000 L of contaminant affect? |
10 000 L = 6 000 000 L 15 000 L = 40 000 000 L |
|
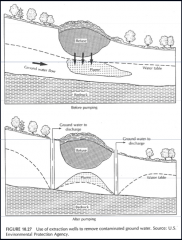
Problems with Extractions wells ? |
For a 100 000 L at 5ppm spill you have to pump 2 e^9 L
No aquifer is perfectly homogeneous and NAPL will stay in low permeability areas
remediation nearly impossible in fine grained, low (or variable) conductivity sediments |
|
|
What is a PRB? |
permeable reactive barrier (passive reactive barrier or permeable reactive treatment walls)
it is a permeable subsurface barrier containing a reactive material (eg granular iron) constructed across the path of a contaminant plume |
|
|
what are the six major categories of contaminants |
radionuclides trace metals nutrients other inorganics organics biological |
|
|
what are the pollution limits? |
allowable limit
recommended limit
mandatory limit |
|
|
how do dissolved organics move? |
mobility proportional to solubility (high solubility high mobility) |
|
|
how do NAPL organics move? |
dependent on density (0.8 -1.6x water)(density is a function of chloride) porous or fractured system pure vs dissolved phases
|
|
|
what are the three main groups of organic compounds in crude oil and crude oil products? |
alkanes (butane, hexane, cyclohexane, ect) alkenes (ethene, propene, ect) |
|
|
what are the three fractions of the distillation of crude oil? |
gasolines
middle distillates
Residual products |
|
|
What are PCBs? why are they dangerous? |
....... |
|
|
What are 3 main sources of bio contaminants? |
......... |
|
|
What are 3 important bio contaminants? |
......... |

