![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What does hetrotrophs mean. |
Ingest food |
Food contains energy that human cells require. |
|
|
Define nutrition |
The materials (food) that are required for cells to function |
|
|
|
Ingestion |
Taking food into the mouth |
|
|
|
Digestion |
Breaking down of food into smaller molecules to easily diffuse through the membrane of cells that line the digestive tract. The molecules then diffuse into the blood. |
|
|
|
Mechanical digestion |
Pieces of food are broken down into smaller particles of food. (Does not result in smaller molecules of food) occurs in mouth (teeth) stomach (stomach muscles) |
|
|
|
Chemical digestion |
Food molecules are broken down into smaller molecules. So that large food molecules can be absorbed through thevcell membrane and into the blood. |
Occurs with the assistance of digestive enzymes. Chem digestion in mouth stomach and small intestine. |
|
|
Protease |
Gastric glands release pepsin in the stomach
Pancreas release trypsin in duodenum |
Pepsin -gastric Trypsin -pancake |
|
|
Lipase |
Released by pancreas to duodenum to break down lipids |
Lipids |
|
|
Amylases |
Break down of carbohydrates. |
|
|
|
Nucleases |
Released by pancreas to the duodenum to Breakdown nucleic acids. |
|
|
|
Function of salivary amylase |
Start the Digestion of carb starch & lubricates food jnto bolus so its easy to swallow and doesnt damage oesophagus |
|
|
|
Pharynx |
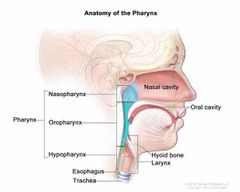
A pathway for both food and air that we breath |
|
|
|
Epiglottis |
A flap in the throat that Prevent food from entering the lung. by closing the opening of trachea when we we swallow |
|
|
|
Peristalsis muscle structure. |

The process of moving food through the esophagus by waves of muscular contractions is called Peristalsis |
|
|
|
Photo |

By Smooth muscles that surround the digestive tract that contract and relax to push food through |
|
|
|
Function of hcl |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What structure of the stomach controls how much chyme passes through the small intestine? |
Pyloric sphincter ( contact and relax) maximising digestion and absorption in small intestine. Too much food = wouldnt difest properly |
|
|
|
Duodenum |
Where most digestion takes place |
|
|
|
Duodenum |
Where most digestion takes place |
|
|
|
Ileum |
Where most absorption takes placeb |
|
|
|
Gall bladder |
Where bile is stored after being produced by liver. G.bladder releases bile into duodenum |
|
|
|
Gall bladder |
Where bile is stored after being produced by liver. G.bladder releases bile into duodenum |
|
|
|
Functions of bile |
Emulsifies fats (break fats down in to smaller particles) = creating larger surface area = allows enzyme lipase to be more effective in the breakdown of large fat molecules. |
|
|
|
Gall bladder |
Where bile is stored after being produced by liver. G.bladder releases bile into duodenum |
|
|
|
Functions of bile |
Emulsifies fats (break fats down in to smaller particles) = creating larger surface area = allows enzyme lipase to be more effective in the breakdown of large fat molecules. |
|
|
|
Is bile alkaline or acidic? |
Bile is alkaline. This helps Neutralise stomach acid in Duodenum |
|

