![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Prefrontal Cortex: Location and Function |
Location: outer layers of brain
Function: planning, selecting and coordinating thoughts ("executive functions") |
|
|
Auditory Cortex: Location and Function |
Location: on temporal lobe Function: conscious processing of sounds |
|
|
Amygdala: Location and Function |
Location: limbic system Function: linked to emotion |
|
|
Hippocampus: Location and Function |
Location: limbic system Function: linked to memory |
|
|
Corpus Callosum |
Long, thick band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right sides of the brain (allowing communication between them) |
|
|
Thalamus |
Relays messages between lower brain centers and cerebral cortex |
|
|
Hypothalamus |
Controls maintenance functions such as eating; helps govern endocrine system; linked to emotion and rewards |
|
|
Pituitary |
Master endocrine gland |
|
|
Visual Cortex: Location and Function |
Location: on occipital lobe Function: conscious processing of sights |
|
|
Spinal Cord |
Pathway for neural fibers traveling to and from brain; controls simple reflexes |
|
|
Cerebellum |
Coordinates voluntary movement and balance |
|
|
Cerebral Cortex: Location and Function |
Location: outer layers of brain Function: ultimate control and information-processing center |
|
|
What happens when the prefrontal cortex matures? |
-Sleep becomes more regular.
-Emotions become more nuanced and responsive.
-Temper tantrums subside.
-Uncontrollable laughter and tears are less common. |
|
|
Which part of the brain grows rapidly during early childhood? |
Corpus callosum |
|
|
What is the name of the long, thick band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right sides of the brain? (Makes communication between the two brain hemispheres more efficient.) |
Corpus callosum |
|
|
What is lateralization? |
The specialization in certain function by a dominant side of the brain (left or right). |
|
|
What are axons? |
Fibers through which impulses are passed from neuron to neuron. |
|
|
Why is it important for the corpus callosum to mature? |
Because both sides of the brain are usually involved in every skill: logic (left brain) without emotion (right brain) is bad and vise versa. (Brain balance is crucial!) |
|
|
What is myelination and when is it most apparent? |
The process by which axons become coated with myelin, a fatty substance that speeds the transmission of nerve impulses from neuron to neuron; during early childhood. |
|
|
Name the major system for emotions. |
Limbic system |
|
|
Emotional expression and regulation advance during early childhood because of which three parts of the limbic system? |
The amygdala, hippocampus and hypothalamus. |
|
|
Compare and contrast Piaget and Vygotsky with respect to thinking in early childhood. |
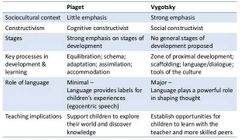
|

