![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
matter
|
anything that has mass and takes up space.
|
|
|
Elements
|
are the basic building blocks of matter that cannot be broken down by chemical means.
|
|
|
Atoms
|
are the smallest units of an element that retain the elements physical and chemical properties. These bond together to Form molecules.
|
|
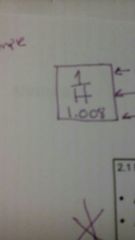
atomic symbol
|

|
|
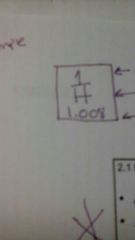
Atomic mass
|

|
|
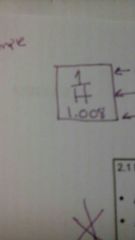
Atomic number
|

|
|
|
Neutrons
|
neutrons are neutral (uncharged)
|
|
|
Protons
|
protons are positively charged +
|
|
|
What makes up the nucleus?
|
neutrons and protons make up the nucleus.
|
|
|
What orbit around the nucleus?
|
Electrons are negatively (-) charged and orbit around the nucleus.
|
|
|
Isotopes
|
Isotopes are atoms that have the same atomic number but a different atomic mass because the number of neutrons differ.
|
|
|
Radioisotopes
|
Radioisotopes are useful in dating old objects imaging body organs and tissue through X-Rays, and killing cancer cells.
|
|
|
How is radiation harmful?
|
Radiation can be harmful by damaging cells and DNA and/or causing cancer.
|
|
|
Molecules
|
*They are made of atoms that are bonded together.
* Can be made of the same atom or different atoms. |
|
|
Ionic Bonds
|
*Atoms in this type of bond donate or take on electrons.
*Results in a stable outer shell. *Occur between particles that are changed (ions) |
|
|
Covalent Bonds
|
*Atoms in this type of bond share electrons.
*Result in a stable outer shell |
|
|
What is the pH scale?
|
*A measure of hydrogen ion (H+) concentration
*Working scale is between 0 and 14 with 7 being neutral. *A pH below 7 is acidic and above 7 is basic. *The concentration of hydrogen ions between each whole number changes by a factor of 10. |
|
|
Dehydration reaction
|
The removal of water that allows subunits to link together into larger molecules.
|
|
|
Hydrolysis reaction
|
The addition of water that breaks larger molecules into their subunits.
|
|
|
What organic molecules are found in living organisms?
|
1. Carbohydrates
2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic acids |
|
|
What are carbohydrates?
|
*Made of subunits called monosaccharides.
*Made of C, H, and O in which the H and O atoms are in a 2:1 ratio *Function as short-and long-term energy storage. *Found as simple and complex forms |
|
|
What are simple carbohydrates. ?
|
*Monosaccharides- 1 carbon ring as found in glucose.
*Disaccharide- 2 carbon rings as found in maltose. |
|
|
What are complex carbohydrates?
|
*Polysaccharides are made of many carbon rings.
*Glycogen is the storage form in animals. *Starch is the storage form in plants. |
|
|
What are lipids.
|
*Molecules that do not dissolve in water.
*Used as energy molecules. *Found in cell membranes *Found as fats and oils, phospholipids, and steroids |
|
|
How are fats and oils different?
|
Fats:
*usually animal origin *Solid at room temperature *Function for long-term energy storage, insulation from heat loss, and cushion for organs |
|
|
How are fats and oils different?
|
Oils
*Usually plant origin *Liquid at room temperature |
|
|
What is the structure of fats and oils?
|
A glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acid tails
|
|
|
Understanding fats when reading a nutrition label
|
*Recommendation for total amount of fat for 2,000 calorie diet is 65g.
*Be sure to know how many servings there are. *A % DV of 5% or less is low and 20% or more is high. *Try to stay away from Trans fats |
|
|
What is the structure of a phospholipid?
|
*The structure is similar to a triglyceride.
*One fatty acid is replaced by a polar phosphate group. *Phospholipids are the primary components of cellular membranes. |
|
|
What is a steroid?
|
*A steroid is a lipid.
*The structure is four fused carbon rings. *Examples are cholesterol and sexton hormones. |
|
|
What are proteins?
|
*Made of subunits called amino acids.
*Important for diverse functions in the body including hormones, enzymes, antibodies, and transport. *Can denature: undergo a change in shape that causes loss of function. |
|
|
What are the 4 levels of protein organization.?
|
*Primary- the linear order of amino acids
*Secondary- localized folding into pleated sheets and helices *Tertiary- the 3-D shape of the entire protein in space. *Quaternary- combination of more than one polypeptide *All proteins have primary, secondary, and tertiary structure, while only a few have quaternary structure. |
|
|
What are nucleic acids?
|
*Made of nucleotides subunits
*Function in the cell to make proteins *Include RNA and DNA |
|
|
What are the 5 bases found in nucleotides?
|
*Adenine (A) and guanine (G) are double purine
*Cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U) are single-ringed pyrimidines. *In DNA, A pairs with Tandy G pairs with C. |
|
|
Summary of DNA & RNA structural differences
|
DNA
*Sugar is deoxyribose *Bases include A, T, C and G *Double-stranded |
|
|
Summary of DNA and RNA structural differences
|
RNA
*Sugar is ribose *Bases include A, U, C, and G *Single-stranded |
|
|
Summary of the macromolecules: organic molecules
|
Carbohydrates:
example: monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides Functions: immediate energy and stored energy; structural molecules |
|
|
Summary of the macromolecules : organic molecules
|
Lipids:
example: fats, oils, phospholipids, steroids functions: long-term energy storage; membrane components |
|
|
Summary of the macromolecules : organic molecules
|
Proteins:
example: structural enzymatic, carrier, hormonal contractile functions: support metabolic, transport, regulation, motion |
|
|
Summary of the macromolecules : organic molecules
|
Nucleic acids
example: DNA, RNA functions: storage of genetic information |
|
|
What are properties of water?
|
*Water is liquid at room temperature.
*Liquid water does not change temperature quickly. *Water has a high heat of evaporation,. *Frozen water is less dense than liquid water. *Molecules of water cling together. *Water is a solvent for polar molecules. |
|
|
What bond holds water molecules together?
|
*Hydrogen bonds occur between a hydrogen in a covalent bond and a negatively charged atoms.
*These are relatively weak bonds. |
|
|
Acids and Bases
|
*Acids are substances that dissociate and release hydrogen ions (H+)
*Bases are substances that take up hydrogen ions (H+) or release hydroxide ions (OH-) |

