![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
sebaceous glands are what kind of glands?
|
Holocrine secretion — the entire cell disintegrates to secrete its substances. They can be simple OR compound alveolar glands
|
|
|
mitotically active layer of epidermis
|
stratum germinativum = stratum basale + stratum spinosum
|
|
|
part of epidermis located on top of basement membrane
|
stratum basale
|
|
|
Merocrine
|
Merocrine glands - cells secrete their substances by exocytosis , form vesicles, so NO part of gland is damages or lost unlike apocrine and holocrine (e.g., mucous and serous glands). Also called "eccrine."
|
|
|
Sweat Gland.
|
Apocrine Sweat Gland. A class of large sweat gland, usually located in the groin and armpits, that produces odoriferous secretions.
|
|
|
In hypodermis, adipose tissue is present either in the form of small clusters or large mass of fat called _________
|
panniculus adiposus - large mass of fat in hypodermis
|
|
|
pilosebaceous unit
|
consists of hair shaft, hair follicle, sebaceous gland which makes sebum, and erector pili muscle which causes the hair to stand up when it contracts.
|
|
|
produces the hair itself
|
hair follicle, sac sac from which hair grows and into which sebaceous (oil) glands open. Follicle is lined by cells derived from epidermal (outside) layer of skin.
|
|
|
3 layers of hair shaft
which layer contains the pigment |
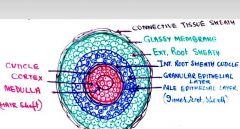
cuticle- single layer of flat ker. cells
cortex - dense keratinized, CONTAINS PIGMENT medulla - loose center, cuboital or flat Surrounded by hair follicle (internal and external root sheath) |
|
|
2 layers of Dermis (what made of?)
|
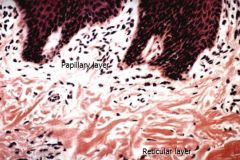
Papillary layer: Loose connective tissue.
Reticular layer: Dense irregular connective tissue |
|
|
subcutis
|
aka hypodermis
It consist of loose arrangement of collagen and elastic fibers. Adipose tissue is present either in the form of small clusters or large mass of fat called panniculus adiposus. |
|
|
subcutis
|
aka hypodermis
It consist of loose arrangement of collagen and elastic fibers. Adipose tissue is present either in the form of small clusters or large mass of fat called panniculus adiposus. |
|
|
what type of gland (structurally) is mammary gland?
|
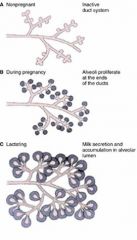
compound tubular acinar, lots of branching and duct
i believe its a merocrine gland? |
|
|
Oxytocin causes ___________ to contract and release milk into ________
|
myoepithelial cells to contract, lumen of alveoli
|
|
|
Where are merocrine sweat glands found?
|
foot pad of dog and cat
|
|
|
another word for 'sweat' gland
|
sudoriferous
|
|
|
Epithelium lining ducts of mammary gland?
(hint: must know names of 2 sinuses) |
Interlobular duct (str. cuboidal)
Intralobular (simple cuboidal) Lactiferous sinus (stratified cuboidal) – where milk stored Teat sinus (after Lact.sinus) and papillary duct (final openings) - both are stratified squamous. |
|
|
Bovine planum nasolabiale
Carpal glands of swine. Foot pad of dogs and cats, Have what type of glands? |
merocrine sweat glands
|
|
|
Layers of epidermis from outer to inner?
|
Stratum disjunctum
Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum Spinosum Stratum basale |
|
|
what layers of epidermis contain melanocytes?
|
stratum basale and spinosum
|
|
|
only present in non-hairy skin (footpad)
|
Stratum lucidum
|
|
|
3 layers of hoof (hard keratin corneal horn)
|
stratum externum
stratum medium stratum internum -primary lamina -secondary lamina -laminar column |
|
|
sebacious gland - what type gland?
|
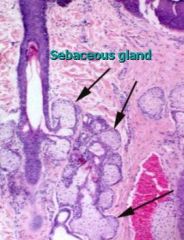
simple OR compound alveolar gland
-associated with hair follicles. -duct empty into hair folllicle thr. pilosebacious canal |
|
|
Responsible for pig (color) of eye
|
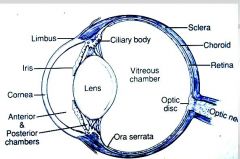
Iris, forms circular band around lens
|
|
|
Anterior portion of fibrous tunic?
Posterior portion of fibrous tunic? |
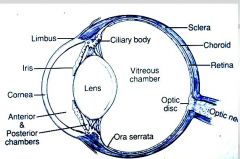
cornea
sclera |
|
|
Sclera structure?
|
on posterior surface of eye
white layer of dense irregular connective tissue. Bundles of collagen fibers having few elastic fibers |
|
|
cornea of fibrous tunic consists of 5 layers
|
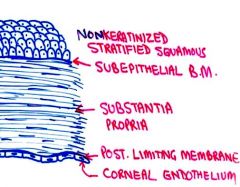
Cornea: is composed of:
1. Anterior epithelium (nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium) 2. Subepithelial Basement membrane 3. Substantia propria: collagen fiber layers or lamellae. 4. Posterior limiting membrane (highly refractile thick BM. 5. Posterior epithelium (corneal endothelium) a simple squamous epithelium |
|
|
The _______ is highly vascularized layer of the eye ball.
In the dorsal half of the fundus of the eye ball, the ______ have a light-reflecting area known as ________. |
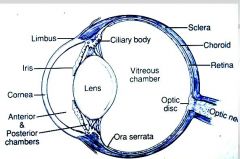
choroid (of vascular tunic)
choroid tapetum lucidum |
|
|
ciliary body is _______ continuation of the _______ in the _________ tunic.
|
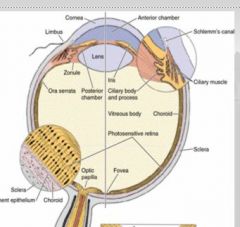
ciliary body is rostral continuation
of choriod in VASCULAR TUNIC |
|
|
vascular tunic comprised of
|
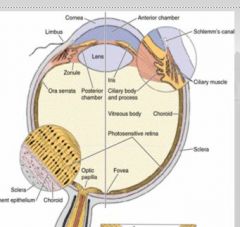
choroid - vascularized, composed of a dense network of blood vessels embedded in the heavily pigmented connective tissue. (which has tapetum lucidum on dorsal surface)
The ciliary body is the rostral continuation of the choroid. The iris is composed of highly vascularized connective tissue and pigmented epithelium. |
|
|
Layers of Nervous Tunic (retina)
|
The retina is composed of:
1. Pigment epithelium 2. Photoreceptive layer (rods and cones) 3. External limiting membrane 4. Outer nuclear layer 5. Outer plexiform layer 6. Inner nuclear layer 7. Inner plexiform layer 8. Ganglionic cell layer - MPN 9. Optic nerve fiber layer 10. Internal limiting membrane |
|
|
differentiate between different colors
|
cones
|
|
|
work during night (dark)
|
rods
|
|
|
affected by cataracts
|
lens
|
|
|
lacrimal gland
~identify the types of secretion these glands produce, particularly how vary betw. species |
compound tubulo-alveolar gland
predom. serous in ruminants, serous iin cats and S/M in dogs |
|
|
Middle Ears
|
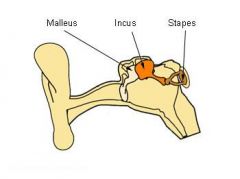
Auditory ossicles (malleus, incus and stapes),
Tympanic cavity Auditory tube. |
|
|
Name 2 Main Parts of Inner ear:
(don't need to go into too much detail b/c IE is incredibly complicated) ~must say what flows through these |
Bony labyrinth: is filled with perilymph.
Membranous labyrinth: is filled with endolymph. (containing sensory mechanisms - hearing and balance) |
|
|
3 structures responsible for balance
>For Vestibular (balancing) mechanism |
Crista ampullaris
Macula utriculi Macula sacculi |
|
|
Structures in IE responsible for balance
|
The vestibular system is dedicated to
Crista ampullaris Macula utriculi Macula sacculi |
|
|
cochlea is dedicated to
|
HEARING
|
|
|
Structures in IE responsible for hearing
|
Spiral organ (organ of Corti) of hearing
|
|
|
bony labyrinth
|
or osseous labyrinth of INNER EAR, is the network of passages with bony walls lined with periosteum. The membranous labyrinth runs inside of the bony labryinth
(i don't know of any unique function bony labryinth has, BUT i contains perilymph while membranous labr. contains endolymph) |
|
|
name 3 membranes of organ of corti
|
tectorial membranne
vestibular membrane basilar membrane TVB (B for best) |
|
|
3 Auditory ossicles of middle ear?
|
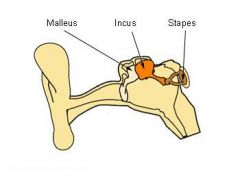
malleus, incus and stapes
|

