![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
bone |
-C.T. with few cells, abundance of mineralized intercellular matrix, C.T. periosteal covering, vascular -nutrients do not diffuse through matrix -capable of remodelling and changing shape due to pressures and stress |
|
|
functions of bone |
-support -protection of the viscera and brain -assistant in movement -storage of minserals (calcium and phosphate) -production of blood cells in bone marrow |
|
|
osteocytes |
-maintenance cells of bone -surrounded by the matrix inside lacunae -has numerous processes that extend from the cell to form a network of canals to allow nutrients to pass through the matrix |
|
|
lamellae |
layers of tissue in bone |
|
|
long bones |
bones that are tubular in shape |
|
|
short bones |
bones that are more cuboidal in shape |
|
|
flat bones |
bones that are flat, mainly the cranial bones |
|
|
irregular bones |
bone classification of various shapes |
|
|
sesamoid bones |
bones within a tendon |
|
|
cortical bone |
compact outer layer of bone, major supportive structure in long bones |
|
|
medullary bone |
inner layer of bone made of thin plates |
|
|
spongy bone |
inner region of long bones formed from thin plates of osseous tissue surrounded by the numerous interconnecting spaces of the marrow cavity -nutrients can diffuse to osteocytes without need for canals |
|
|
periosteum |
a layer of dense irregular C.T. that covers the external surface of bone |
|
|
Sharpey's fibers |
bundles of collagen fibers that bind the periosteum to the bone surface |
|
|
functions of the periosteum |
-attachment site for ligaments and tendons -contains blood vessels that penetrate the bone -osteoblasts within it contribute to the appositional growth -necessary for repair of fractures |
|
|
endosteum |
-a single layer of cells that covers the internal surface of bone -either osteoblasts or osteoprogenitor cells -major function is growth and repair |
|
|
canaliculi |
small channels within the bone matrix formed by cell processes -run aroundward from the center of a osteon perpendicular to the long bone |
|
|
osteoid |
organic component of the bone matrix secreted by cells prior to mineralization -40% of bone weight -mostly type I collagen -main GAG: chondroitin sulfate -gives flexibility |
|
|
hydroxyapatite |
-main inorganic component of bone -40% bone weight -crystalline structure of calcium, phosphate, and hydroxyl ions -gives rigidity |
|
|
Haversian systems (osteons) |
-found in compact bone -consist of several layers of osseous tissue encircling a central blood vessel -form cylinders running parallel to the long axis of the bone |
|
|
cementing line |
transparent line surrounding a Haversion system -mark position of bone formation and resorption |
|
|
Volkmann's (perforating) canals |
blood vessel canals that join the surface vessels of the periosteum to the vessels of the Haversian system and join adjacent Haversian systems -run perpendicular to the length of bone |
|
|
outer circumferential lamellae |
several concentric layers of osseous tissue that form the outer perimeter of the long bone |
|
|
inner circumferential lamellae |
concentric layers of bone that form the inner perimeter of long bone |
|
|
Interstitial lamellae |
irregular wedges of lamellar bone that are located in between adjacent Haversian systems |
|
|
structure of flat bone |
-similar to long bone -cotical bone forms flattened plates -spongy bone in between cortical bone called diploe -covered by periosteum |
|
|
trabeculae |
thin plates of bone in spongy bone |
|
|
spicules |
small spinous processes in spongy bone |
|
|
osteoblasts |
matrix forming cells of the bone -located on inner and outer surfaces in C.T. -turn into osteocytes as they are surrounded by bone matrix |
|
|
osteoid seam |
layer of newly formed bone matrix |
|
|
osteoclasts |
large multinucleated cells that are derived from monocytes in the blood -located on bone surfaces -reabsorb bone |
|
|
marrow cavity |
spaces between the trabeculae of spongy bone |
|
|
hemopoietic tissue |
undifferentiated cells that become either blood or bone |
|
|
red marrow |
marrow actively forming blood cells |
|
|
yellow marrow |
marrow that is mostly fat |
|
|
primary bone |
immature bone -first boen to appear in the embryo and during fracture repair -more cellular than secondary bone -less mineralized -unorganized collagen |
|
|
secondary bone |
-most bone in adults -mature bone -collagen bundled in parallel lamellae -lamellar bone |
|

|
flat bones |
|
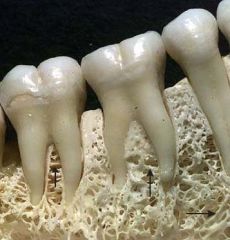
|
trabeculae |
|
|
cementing line |
|
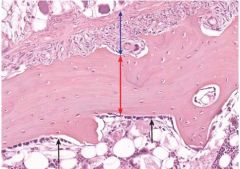
black arrows |
endosteum |
|
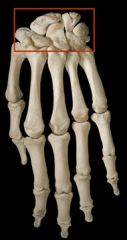
|
short bones |
|
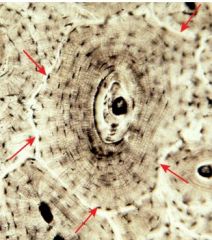
|
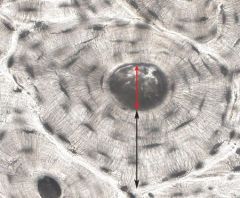
Haversian system red arrow-Haverisan canal black arrow-lamallae |
|

|
long bone |
|
|
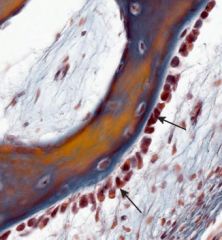
osteoblasts |
|
|
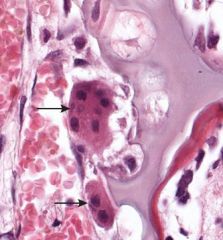
osteoclasts |
|
|
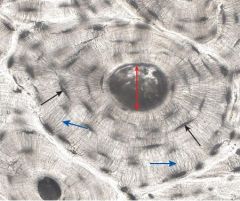
osteocytes (black arrows) canciculli (blue arrows) |
|
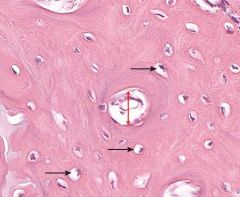
|
black arrows - osteocytes in lacunae |
|
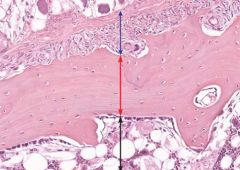
|
periosteum (blue) cortical bone (red) medullary cavity (black) |
|
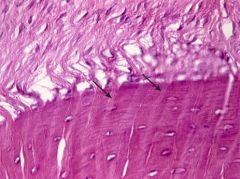
|
Sharpey's fibers |
|
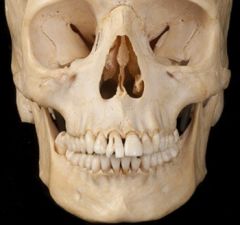
|
irregular bones |
|
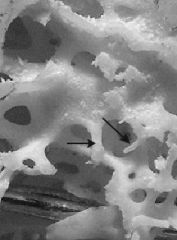
|
spicule |
|
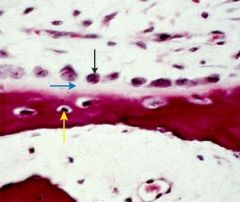
|
trabecular bone yellow-osteocyte black-osteoblasts blue-osteoid |
|
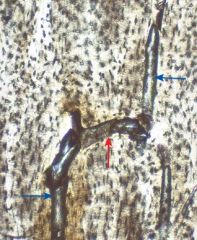
|
Volkmann's canal (red) Haversian canal (blue) |

