![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Adductors of the hip |
Adductor Magnus Adductor Longus Adductor brevis Pectineus Gracilis |
|
|
|
Flexors of the hip |
Psoas major Iliacus Tensor fasciale latae |
|
|
|
Extensors of the hip |

Gluteus Maximus Hamstring Bicep femoris |
|
|
|
Abductors of the hip |
Gluteus max and minimus Tensor fasciae latae |
|
|
|
Femur |
Longest bone in body Structural support of thigh |
|
|
|
External Rotators of the hip |
Piriformis Quadratus femoris Obturator internus Obturator externus Gemellus superior Gemellus inferior |
|
|
|
Acetabulum |
The illum, pubis and ischium meet at the acetabulum, which creates a socket for the head of the femur |
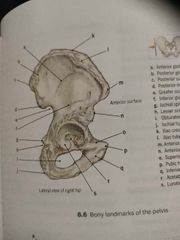
R |
|
|
Ischail tuberosity |
Lower half of the ischial body is the ischial tuberosity |

J |
|
|
Illiac crest |
The rounded edge of the superior border of the ilium |

K |
|
|
Anterior superior illiac spine |
The most anterior point of the iliac crest |
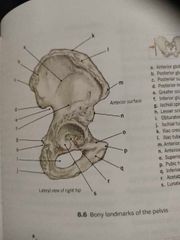
K |
|
|
Posterior superior illiac spine |

D |
|
|
|
Anterior inferior illac spine |

N |
|
|
|
Obturator foramen |
A protective passageway for nerves and blood vessels of the leg |

I |
|
|
Pelvis and hip (label) |
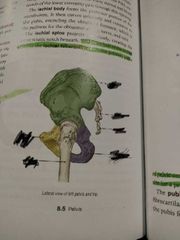
|
|
|
|
What 2 bones is the pelvis (pelvic girdle) formed of |
Two hip coxal bones |
|
|
|
What is the three hip portions |
Ilium, pubis and ischium |
|
|
|
TFL- tensor fasciae latae |
Originates at the illiac crest. Movement- flex, internally rotate and abduct |
|
|
|
Where does the sternum connect to |
The vertebrae |
|
|
|
Where is the sternum |
At the front of the body |
|
|
|
What articular surfaces connect to the sternocostal joint |
Manubrim, body of sternum and xphiod process |
|
|
|
How many ribs connect to the sternum |
7 pairs also known as true ribs |
|
|
|
What joint is in the sternum |
Sternocostal |
|
|
|
Trunk rotation muscles |
External and internal oblique, multifidi, rotatores |
|
|
|
Trunk flexion |
External and internal oblique, transverse abdominus |
|
|
|
Trunk extension |
Llicostas Longissimus Spinae Erector spinae group |
|
|
|
Internal rotation |
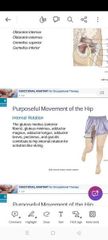
|
|
|
|
Posterior pelvic tilt |
Backward rotation of pelvis Flattens lumbar spine Increases thoracic flexion |
|
|
|
Anterior pelvic tilt |
Forward rotation of pelvis Increases lumbar lordosis Increases ext of upper trunk |
|
|
|
What plane is pelvic tilt |
Sagittal plane Pelvis tilts anterior and posterior |
|
|
|
Pelvic rotation plane |
Transverse plane position Rotation of one side of pelvis |
|
|
|
What plane obliquity in |
Frontal plane One side of pelvis is superior or inferior to other |
|
|
|
Incontinence |
Result of pelvic floor weakness |
|
|
|
Where is a proximal hip fracture |
Femoral neck Or intertrochanteric (between great and lesser than trochanter |
|
|
|
THA meaning |
Total hip arthroplasty Replaces femoral head and acetabulum |
|
|
|
Hemiarthroplasty |
Replaces femoral head |
|
|
|
Hip precautions |
Hip rotation Adduction and flexion beyond a certain point |
|
|
|
Weight shifting |
Shifting weight from one leg to another Helps positioning and movement of body |
|
|
|
Bones of the lower leg |
Femur Tibia Patella Fibia Bones of the foot |
|
|
|
Attachment sites for hip bones |
Posterior attachment at the sacrum Anterior attachment at the pubic symphysis |
|
|
|
Where is the sacrum located |
Between 5th lumbar vertebrae and coccyx 5 sacral vertebrae |
|
|
|
What does the sacroiliac joint do |
Stabiliszes pelvis under strain of opposing forces |
|
|
|
What joint is the SI |
Synovial with very limited rotation |
|
|
|
What movements does the hip joint do |
Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, external and internal rotation |
|

