![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
83 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
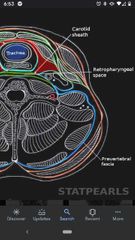
Prevertebral fascia |
Surrounds the posterior part of the neck, which contains the cervical VT and the muscles that move it. |
|
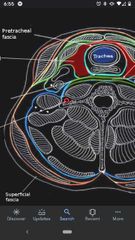
Pretracheal fascia |
Surrounds the anterior part of the neck. |
|
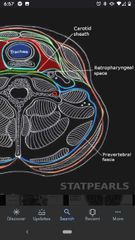
Retropharyngeal space |
The point of separation between the prevertebral and pretracheal fascia. A potential space, referred as the "danger space", because infections spread into this space and pass into the mediastinum. |
|
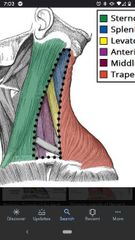
Borders of the posterior triangle |
Anteriorly by the posterior border of the SCM, posteriorly by superior border of the trapezius, inferiorly by the clavicle. |
|
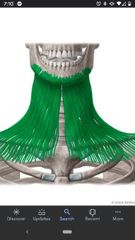
Platysma muscle |
Superior Att: mandible, skin of the cheek, angle of the mouth, & orbicularis oris muscle. Inferior Att: superficial fascia of the deltoid & pectoral regions. Actions: tenses the skin of the neck, depresses the mandible. Innervation: cervical branch of Facial nerve (CN VII) |
|
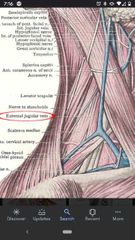
External jugular vein |
Begins posterior to the angle of the mandible and crosses the superficial surface of the SCM. Drains into the subclavian vein. |
|
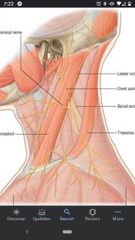
Cutaneous branches of cervical plexus (Erb's point) |
Lesser occipital nerve (C2), great auricular nerve (C2, C3), transverse cervical nerve (C2, C3), supraclavicular nerves (C3, C4) |
|
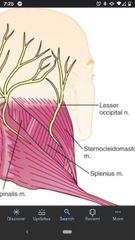
Lesser occipital nerve (C2) |
Parallels the posterior border of the SCM as it passes superiorly. Supplies the scalp that is immediately posterior to the ear. |
|
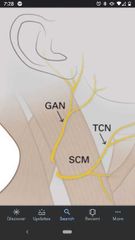
Great auricular nerve (C2, C3) |
Crosses the superficial surface of the SCM parallel to the external jugular vein. Supplies the skin of the lower part of the ear, skin of parotid gland, & skin from mandible to mastoid process. |
|
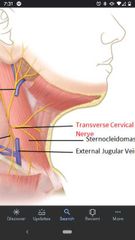
Transverse cervical nerve (C2, C3) |
Runs transversely across SCM and neck. Supplies the skin of the anterior triangle of the neck. |
|
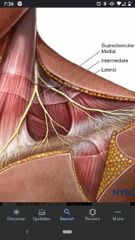
Supraclavicular nerves (C3, C4) |
Pass inferiorly to innervate the skin over the shoulder. Has medial, intermediate, and lateral branches. |
|
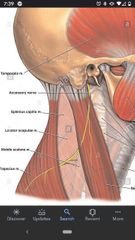
Spinal accessory nerve (CN XI) |
Innervates the SCM and trapezius muscle, DOES NOT originate from cervical plexus. |
|
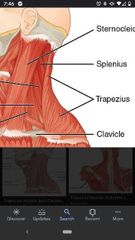
Trapezius muscle |
Superior Att: superior nuchal line, external occipital protuberance, ligamentum nuchae, SP C7- T12. Inferior Att: lateral third of clavicle and acromion and spine of scapula. Actions: rotates, elevates (superior part) retracts (middle part) and depresses (inferior part) the scapula. Innervation: spinal accessory nerve (CN XI) |
|
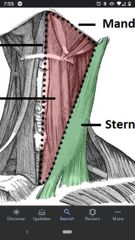
Sternocleidomastoid (SCM) |
Superior Att: mastoid process, lateral half of superior nuchal line. Inferior Att: sternal head & clavicular head. Actions: laterally flexes the head and rotates face to opposite side (unilateral), extends head (bilateral). Innervation: spinal accessory nerve (CN XI) |
|
Borders of anterior triangle |
Medially by medial plane of neck, laterally by the anterior border of SCM, superiorly by inferior border of mandible. |
|

Divisions of anterior triangle |
Divided by digastric and omohyoid muscles. Muscular triangle, carotid triangle, submandibular, & submental triangle. |
|
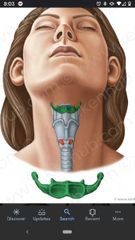
Hyoid bone |
Does not articulate with any other bone. At the angle between the floor of the mouth and the superior end of the neck. |
|
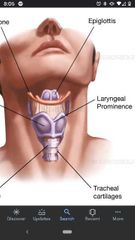
Laryngeal prominence |
On thyroid cartilage, known as Adam's apple. An extension of cartilage marking the location of vocal cords. |
|
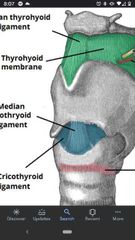
Thyrohyoid membrane |
Stretches between thyroid cartilage and hyoid bone. |
|
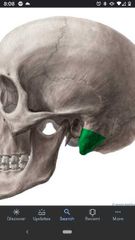
Mastoid process |
On the temporal bone. SCM superiorly attaches here. |
|
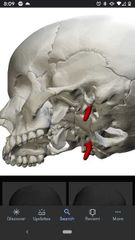
Styloid process |
On the temporal bone. |
|
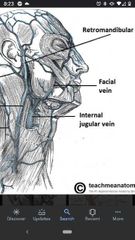
Retromandibular vein |
Joins the external jugular vein superiorly. |
|
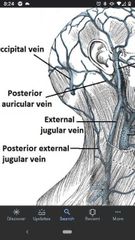
Posterior auricular vein |
Joins the external jugular vein superiorly. |
|
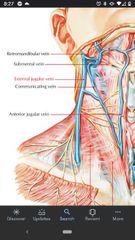
Communicating vein |
Connects the common facial vein with the anterior jugular vein along the anterior border of the SCM. |
|
|
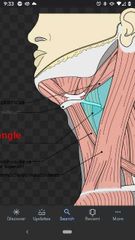
Contents of the Muscular triangle |
Infrahyoid muscles, the thyroid gland, and the parathyroid glands |
|
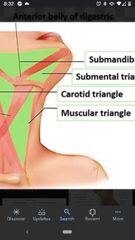
Boundaries of muscular triangle |
Bounded medially by the median plane of neck, superolaterally by the superior belly of omohyoid muscle, and inferolaterally by the anterior border of SCM. |
|
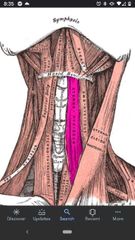
Sternohyoid muscle |
Superior Att: body of hyoid bone. Inferior Att: posterior surface of manubrium. Actions: depresses the hyoid Innervation: Ansa cervicalis (C1-C3). |
|
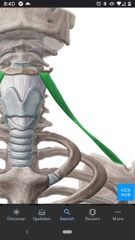
Omohyoid muscle |
Superior Att: inferior border of hyoid bone. Inferior Att: superior border of scapula near suprascapular notch Actions: depresses and retracts the hyoid. Innervation: Ansa cervicalis (C1-C3) |
|
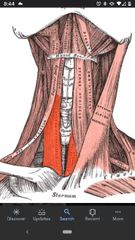
Sternothyroid muscle |
Superior Att: oblique line of thyroid cartilage. Inferior Att: posterior surface of manubrium. Actions: depresses thyroid cartilage and larynx. Innervation: Ansa cervicalis (C1-C3) |
|
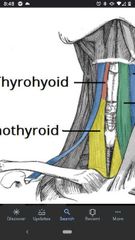
Thyrohyoid muscle |
Superior Att: inferior border of body and greater horn of hyoid. Inferior Att: oblique line of thyroid cartilage. Actions: depresses hyoid & elevates the thyroid cartilage and larynx. Innervation: C1 via hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) |
|
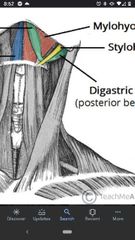
Digastric muscle |
Superior Att: digastric fossa of mandible (anterior belly) Inferior Att: mastoid process (posterior belly) Actions: elevates hyoid and depresses mandible. Innervation: trigeminal nerve (CN V3), Facial nerve (CN VII) |
|
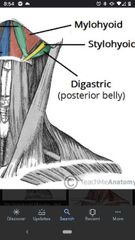
Stylohyoid muscle |
Superior Att: styloid process. Inferior Att: body of hyoid Actions: elevates hyoid Innervation: Facial nerve (CN VII) |
|
Mylohyoid muscle |
Superior Att: mylohyoid line of mandible (lateral attachment) Inferior Att: hyoid bone and mylohyoid raphe Actions: supports the floor of the oral cavity Innervation: trigeminal nerve (CN V3) |
|
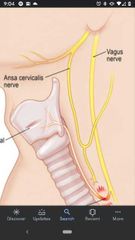
Ansa cervicalis |
Innervates 3/4 infrahyoid muscles. Superior branch (C1), inferior branch (C2, C3) |
|
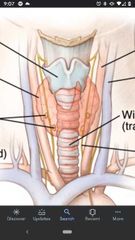
Thyroid gland |
Located at vertebral levels C5-T1. Has a right and left lobe connected by the isthmus which crosses the anterior surface of tracheal rings 2 & 3. |
|
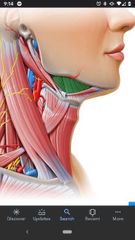
Contents of Submandibular triangle |
Submandibular gland, facial artery & vein, stylohyoid muscle, part of hypoglossal nerve, & lymph nodes. |
|
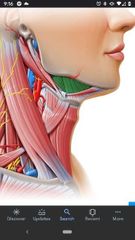
Boundaries of submandibular triangle |
Superiorly by inferior border of mandible, anteroinferiorly by anterior belly of digastric muscle, posteroinferiorly by the posterior belly of digastric muscle |
|
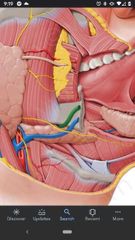
Facial artery/vein |
Cross over the margin of the body of mandible. Artery is more tortuous than vein and courses more anteriorly. |
|
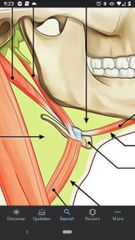
Intermediate tendon |
The two bellies of digastric muscle attach to each other by this tendon. |
|
Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) |
Courses lateral to the carotid arteries. Enters submandibular triangle deep to the posterior belly of digastric and mylohyoid muscle, then enters floor of mouth. |
|
Submental triangle |
Contents are the submental lymph nodes. Bounded inferiorly by hyoid bone and anterior bellies of right and left digastric muscles. |
|
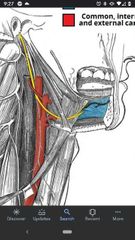
Carotid triangle |
Contents are the carotid arteries (common, internal, & external), part of hypoglossal nerve (CN XII), & branches of vagus nerve (CN X). |
|
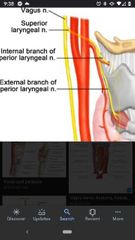
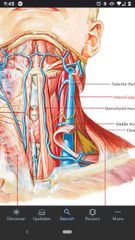
Internal branch of superior laryngeal nerve |
Supplies sensory fibers to mucosa of the larynx above the level of the vocal cords. |
|
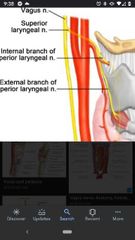
External branch of superior laryngeal nerve |
Joins the the internal branch to form the superior laryngeal nerve |
|
Superior laryngeal nerve |
Formed by the internal and external branches. |
|
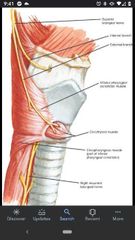
Cricothyroid muscle |
Innervated by the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve |
|
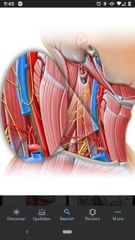
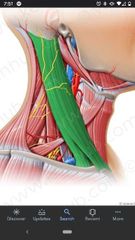
Carotid sheath |
Contains common carotid artery, internal carotid artery, internal jugular vein, and vagus nerve (CN X). |
|
Internal jugular vein |
Located lateral to the common carotid. |
|
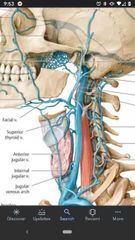
Tributaries of the internal jugular vein |
Common facial vein, superior thyroid vein, and middle thyroid vein |
|
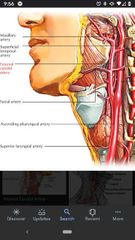
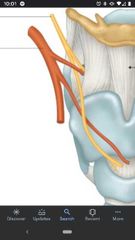
External carotid artery |
Superior bifurcation of the common carotid artery. |
|
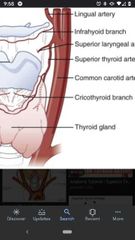
Superior thyroid artery |
Arises from the anterior surface of the external carotid artery. |
|
Superior laryngeal artery |
A branch of the superior thyroid artery, which pierces the thyroid membrane together with the internal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. |
|
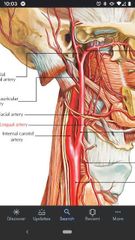
Lingual artery |
Located superior to the superior thyroid artery off the anterior surface of the external carotid artery. |
|
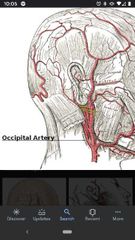
Occipital artery |
On the posterior surface of the external carotid artery. Supplies blood to part of the scalp. |
|
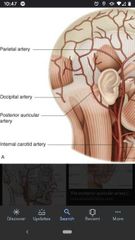
Posterior auricular artery |
Located superior to the origin of the occipital artery |
|
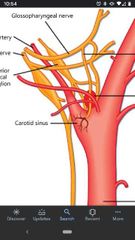
Carotid sinus |
A dilation of the internal carotid artery near it's origin. Walls contain baroreceptors that monitor blood pressure. Innervated glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) and vagus nerve (CN X). |
|
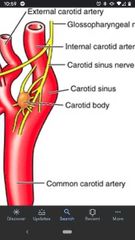
Carotid body |
Located on the medial aspect of the carotid bifurcation. A small mass of nerve tissue that contains chemoreceptors to monitor changes in O2 & CO2 concentration of the blood. Innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) and the vagus nerve (CN X). |
|
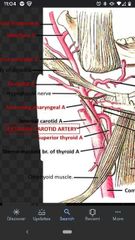
Ascending pharyngeal artery |
Arises from medial surface of the external carotid artery, close to the bifurcation of common carotid artery. |
|
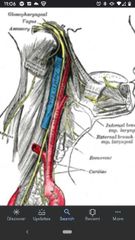
Vagus nerve (CN X) |
Within the carotid sheath where it lies between and posterior to the common carotid artery and the internal jugular vein. |
|
|
6 branches of the External carotid artery in the Carotid triangle. |
1) superior thyroid artery 2) superior laryngeal artery 3) lingual artery 4) facial artery 5) occipital artery 6) posterior auricular artery |
|
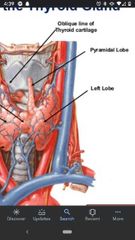
Pyramidal lobe of Thyroid gland |
Extends superiorly from the isthmus. Remnant of embryonic development, shows the route of descent of the thyroid gland. |
|
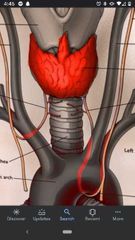
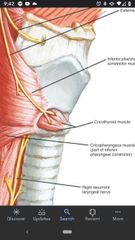
Left/right recurrent laryngeal nerves |
Pass posterior to the lobes of the thyroid gland in the groove between the trachea and esophagus. |
|
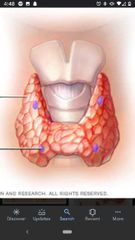
Parathyroid glands |
Darker in color and harder in structure than the thyroid gland. Usually 1-3 on each side of gland. Play an important role Ca2+ metabolism. |
|
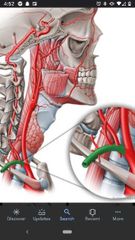
Subclavian artery |
On the right side it is a branch of the brachiocephalic trunk, but on the left side it is a branch of the aortic arch. Has 3 parts. |
|
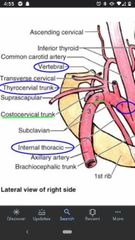
1st part of the subclavian artery |
Vertebral artery, internal thoracic artery, & thyrocervical trunk. Origin to the medial border of the anterior scalene muscle. |
|
Vertebral artery |
Passes superiorly between anterior scalene and longus colli muscles until it enters the transverse foramen of vertebra C6. |
|
Internal thoracic artery |
Arises from the anteroinferior surface of the subclavian artery and passes inferiorly to supply the anterior thoracic wall. |
|
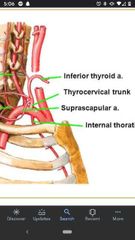
Thyrocervical trunk |
Arises from the anterosuperior surface of the subclavian artery. |
|
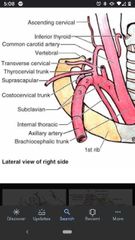
What are the 3 branches of the thyrocervical trunk? |
Transverse cervical artery, suprascapular artery, inferior thyroid artery. |
|
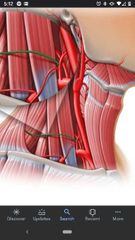
Transverse cervical artery |
Branches off the thyrocervical trunk. Runs deep to omohyoid muscle and supplies the trapezius. |
|
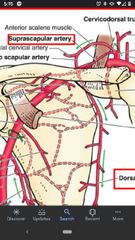
Suprascapular artery |
Branches off the thyrocervical trunk. Passes superiorly to the transverse scapular ligament, supplies the supraspinatus & infraspinatus muscles. |
|
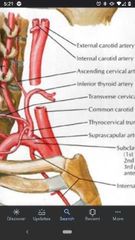
Inferior thyroid artery |
Branches off the thyrocervical trunk, which passes medially towards the thyroid gland. |
|
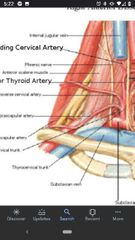
Ascending cervical artery |
Branch off the inferior thyroid artery. |
|
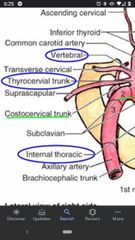
2nd part of the subclavian artery |
Lies posterior to the anterior scalene muscle and has one branch, Costocervical trunk. |
|
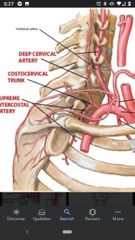
Costocervical trunk |
The only branch point off the 2nd part of the subclavian artery. Arises from the posterior surface and divides into the deep cervical artery & supreme Intercostal artery. |
|
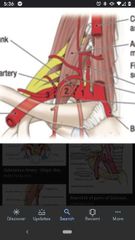
3rd part of the subclavian artery |
Has one branch, the dorsal scapular artery. Between the lateral border of the anterior scalene muscle and the lateral border of the 1st rib. |
|
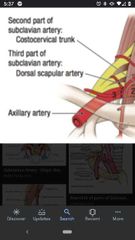
Dorsal scapular artery |
Passes superior to the middle trunk of the brachial plexus to supply the rhomboid muscles and levator scapulae. |
|
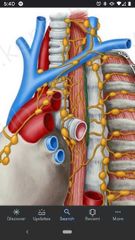
Thoracic duct |
On the left side ascends from thorz into the neck. Joins the venous system near the left venus angle (junction of the left internal jugular vein & the left subclavian vein). |
|
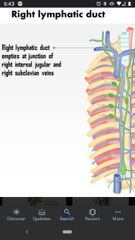
Right lymphatic duct |
Drains into the right venus angle (junction of the right subclavian vein & the right internal jugular vein). |
|
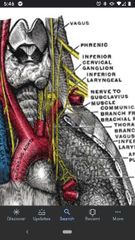
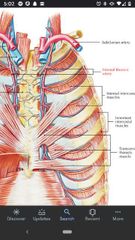
Phrenic nerve |
Crosses the anterior surface of the anterior scalene muscle. Arises from C3-C5 and innervates the diaphragm. |
|
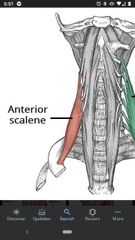
Anterior scalene muscle |
Superior Att: TP of C4-C6. Inferior Att: 1st rib Actions: flexes neck, elevates 1st rib during inspiration. Innervation: anterior Rami C4-C6. |
|
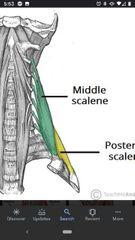
Middle scalene muscle |
Superior Att: posterior tubercles of TP of C2-C7. Inferior Att: 1st rib Actions: flexes neck & elevates 1st rib during inspiration. Innervation: anterior Rami C2-C6 |
|
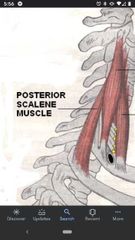
Posterior scalene muscle |
Superior Att: posterior tubercles of TP of C4-C6. Inferior Att: 2nd rib Actions: flexes neck laterally, elevates 2nd rib during inspiration. Innervation: anterior Rami C7-C8. |

