![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Patterns of Inheritance |
Patterns that of how certain genes are passed from one generation to the next |
1. The 3:1 ratio of smooth and wrinkled peas 2. Comparing my features to those of my grandparents you might be able to see some patterns of inheritance |
|
|
Allele |
Different forms of genes that lead to slightly different characteristics |

2. All people have the chromosomes, but different alleles
|
|
|
Homologous Chromosome |
Two chromosomes of a pair that code for the same genes |

2. Homologous chromosomes line up together in meiosis |
|
|
Dominant |
Traits that are always expressed in an individual if they are present |
1. The trait for yellow embryos in peas 2. If a dominant and recessive trait are given to an individual the dominant one will be expressed |
|
|
Recessive |
Traits that are expressed if there are no dominant traits |
1. The trait for green embryos in peas 2. A person needs to have two repressive traits in order for the trait to be expressed |
|
|
Principle of Segregation |
Principle that states each gamete only receives one allele for a trait |
1. A gamete for an egg embryo receiving a constricted pod trait 2. Mendel might not have developed his principle of segregation if he'd tested snapdragons |
|
|
Gene |
A segment of DNA that codes for a particular product |
1. Gene for Zellweger Syndrome 2. The products genes code for are proteins that serve a particular function in the cell |
|
|
Genotype |
Genetic makeup |

2. Genotypes consist of the dominant or recessive form of the alleles recieved |
|
|
Phenotype |
How the genotype of each individual is expressed |
1. A person whose genotype codes for brown hair with a widows peak 2. Phenotypes are only used to describe observable characteristics |
|
|
Homozygous |
Genotypes where the alleles are the same |
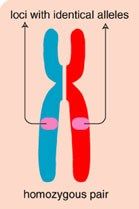
2. If an has a recessive trait that means its genotype is homozygous
|
|
|
Heterozygous |
Genotypes with different alleles |
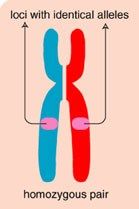
2. Organisms in the F1 generation have heterozygous genotypes |
|
|
Principle of Independent Assortment |
Principle that states alleles divide among gametes independently of different alleles |
1. An allele for a constricted pod an an allele for a wrinkled seed dividing among gametes independently 2. Genes of the same chromosome may be a slight exception to the principle of independent assortment |
|
|
Incomplete Dominance |
Traits that when expressed are a mixture of the two alleles received from parents |
1. A pink snapdragon offspring from red and white snapdragon parents 2. Incomplete dominance provided evidence for the blended theory of inheritance |
|
|
Codominance |
Traits that equally express both alleles received from each parent |
1. An AB blood type 2. Codominant phenotypes express all of both genes as opposed to some of each |
|
|
Multiple Alleles |
Genes that have more than 2 alleles they can code for |
1. Genes for blood type 2. Since some genes have multiple alleles the variety of characteristics and organism might have grows even more |
|
|
Polygenic Inheritance |
Inheritance of characteristics controlled by multiple alleles |
2. The more genes you have with multiple alleles the greater your polygenic inheritance
|
|
|
Linked Genes |
Genes found on the same chromosome |
1. The glucokinase and hepatic growth factor genes 2. Alleles of linked genes often are exchanged between homologous chromosomes in crossing over |
|
|
X-Linked Genes |
Genes that are only found on the X chromosome |

2. Even if X linked genes are recessive they are still always expressed on males |
|
|
Nondisjunction |
When homologous chromosomes stay together in meiosis instead of going o separate gametes |
1. When a gamete has 3 chromosomes 2. Nondisjunction can create XXY cells |
|
|
Multifactorial/Quantatitative Traits |
Traits that are affected by multiple genes and environmental factors |
1. Eye color 2. Because most traits are mutlifactoral/quantatitive traits they cannot be studied by just examining the genome |

