![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
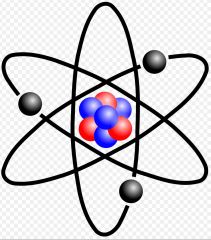
Atom
|
The smallest part of an element that retains the properties of that element
|
Ex: hydrogen The atom hydrogen, has 1 proton, 1 electron, and 0 neutrons.
|
|
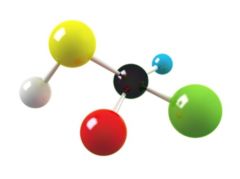
Molecule
|
The smallest unit of a compound; composed of atoms covalently bonded together
|
Ex: water Molecules are made up of two or more elements.
|
|
Element
|
A substance composed of atoms that are chemically identical. Found on the periodic table.
|
Ex: Boron Boron is an element on the periodic table.
|
|
|
Proton
|
A partial with a positive charge found in the nucleus of an atom
|
Ex: positive Chlorine has 7 protons
|
|
|
Hydrogen bond
|
Weak attraction between hydrogen atoms and oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine atoms. Holds the strands of DNA in their double helix
|
Ex: chloroform Chloroform is a hydrogen bond between a carbon molecule and a hydrogen molecule.
|
|
|
pH scale
|
A scale from 0-14 testing the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. Number less than 7 is acidic and greater than is basic
|
Ex: black coffee-4 acidic. Black coffee is a 4 on the pH scale.
|
|
|
Acid
|
pH scale less than 7, more dissolved hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions
|
Ex: battery acid Battery acid is a 0 on the pH scale, very acidic.
|
|
|
Base
|
pH greater than 7, reflecting more dissolved hydroxide ions than hydrogen ions
|
Ex: sodium hydroxide Sodium hydroxide is very basic, it is a 14 on the pH scale
|
|
|
Organic compounds
|
Carbon atoms bond with hydrogen and usually oxygen
|
Ex: acetamide Acetamide has carbon and hydrogen molecules, just what organic compounds are made of.
|
|
|
Macromolecules
|
Large complex molecules
|
Ex: backbone of large complex molecules. Macromolecules are just big molecules.
|
|
|
Carbohydrates
|
Organic compound made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, with the hydrogen and oxygen atoms in a 2:1 ratio
|
Ex: sugar All known types of living cells contain carbohydrates.
|
|
|
Lipids
|
Long term storage of energy and carbon. Do not dissolve in water because they are nonpolar. It is a nutrient and not a polymer
|
Ex: fats and oils Lipids are not a fixed ratio.
|
|
|
Proteins
|
Most structural materials and enzymes in a cell are proteins. Composed of one or more polypeptide chains of amino acids.
|
Ex: skin, hair Proteins (enzymes) most important role is to assist in many reactions occurring in cells.
|
|
|
Nucleic acids
|
Macromolecules that dictate the sequence of amino acids, source of genetic information in chromosomes.
|
Ex: DNA Nucleic acids are made of nucleotides.
|
|
|
Electron
|
A negatively charged particle that is on the outer shell of the nucleus
|
Ex: Hydrogen has 1 electron
|
|
|
Monosaccharides
|
Single sugar, simplest carbohydrates
|
Ex: glucose. Monosaccharides are the building blocks of disaccharides.
|
|
|
Fatty acids and glycerol
|
Building blocks of lipids, make up simple fats most common in our diet
|
Ex: fat in steak Fatty acids and glycerol are building blocks of lipids.
|
|
|
Amino acids
|
Small molecules that contain hydrogen , oxygen , carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur atoms that make proteins
|
Ex: alanine Alanine is an amino acid that makes up a protein.
|
|
|
Nucleotides
|
Small units of Nucleic acids, connected to form long chains
|
Ex: DNA Nucleotides are building blocks of Nucleic acids.
|
|
|
Disaccharide
|
Two simple sugar molecules
|
Ex: sucrose(table sugar) If you have two monosaccharides, it makes one disaccharide.
|
|
|
Polysaccharides
|
Several glucose molecules that bond
|
Ex: starch Many monosaccharides makes polysaccharides.
|
|
|
Polypeptide
|
Long chain of amino acids
|
Ex: glucagon A polypeptide forms a protein the length or the chain determines what kind of protein.
|
|
|
Peptide bond
|
Covalent bonds formed between two amino acids
|
Ex: polypeptide A polypeptide is is a long chain of peptide bonds.
|
|
|
DNA
|
Contains deoxyribose, hereditary material of most organisms, four nitrogen-containing bases
|
Ex: double helix DNA is the biological information of a person.
|
|
|
Gene
|
Physical unit of hereditary, specifications that goes from one generation to the next. A segment of DNA
|
Ex: DNA Genes are something you get passed down from your parents.
|
|
|
Neutron
|
A particle that has no charge(neutral) that is in the nucleus
|
Ex: no charge Hydrogen has 0 neutrons.
|
|
|
Ion
|
An atom or molecule that has gained or loss electrons giving it a positive or negative charge
|
Ex: aluminum An ammonium ion is formed together with amine.
|
|
|
Isotope
|
An atom that has the same properties as the elemental form of the substance but has more or less neutrons
|
Ex: Carbon Isotopes of hydrogen, having one extra neutron.
|
|
|
Ionic bond
|
Bond between a negatively charged atom and positively charged atom
|
Ex: NaCl Sodium chloride is an ionic bond.
|
|
|
Covalent bond
|
A chemical bond between two atoms sharing electrons
|
Ex: carbon dioxide Carbon and oxygen share electrons to make a covalent bond.
|
|
|
Polar covalent bond
|
The shared electrons spend a greater amount of time closer to the oxygen nucleus than the hydrogen nucleus
|
Ex: H2O When electrons are unequally shared they make a polar covalent bond.
|
|
|
Law of Conservation of Matter
|
Law stating that matter cannot be created or destroyed
|
Ex: ice cube that melts into a liquid then heated to a gas. Oxidation is an example of the Law of Conservation of Matter
|
|
|
Activation energy
|
Amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction
|
Ex: boiling water To boil water you must heat it first, showing activation energy.
|
|
|
Proton
|
A partial with a positive charge found in the nucleus of an atom
|
Ex: Chlorine has 7 protons
|
|
|
Hydrogen bond
|
Weak attraction between hydrogen atoms and oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine atoms. Holds the strands of DNA in their double helix
|
Ex: chloroform Chloroform is a hydrogen bond between a carbon molecule and a hydrogen molecule.
|
|
|
pH scale
|
A scale from 0-14 testing the concentration of hydrogen ions in solution. Number less than 7 is acidic and greater than is basic
|
Ex: black coffee-4 acidic. Black coffee is a 4 on the pH scale.
|
|
|
Acid
|
pH scale less than 7, more dissolved hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions
|
Ex: battery acid Battery acid is a 0 on the pH scale, very acidic.
|
|
|
Base
|
pH greater than 7, reflecting more dissolved hydroxide ions than hydrogen ions
|
Ex: sodium hydroxide Sodium hydroxide is very basic, it is a 14 on the pH scale
|
|
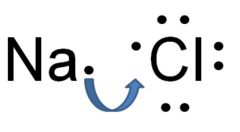
Ionic bond
|
Bond between a negatively charged atom and positively charged atom
|
Ex: NaCl Sodium chloride is an ionic bond.
|
|
|
Macromolecules
|
Large complex molecules
|
Ex: backbone of large complex molecules. Macromolecules are just big molecules.
|
|
|
Carbohydrates
|
Organic compound made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, with the hydrogen and oxygen atoms in a 2:1 ratio
|
Ex: sugar All known types of living cells contain carbohydrates.
|
|
|
Lipids
|
Long term storage of energy and carbon. Do not dissolve in water because they are nonpolar. It is a nutrient and not a polymer
|
Ex: fats and oils Lipids are not a fixed ratio.
|
|
|
Proteins
|
Most structural materials and enzymes in a cell are proteins. Composed of one or more polypeptide chains of amino acids.
|
Ex: skin, hair Proteins (enzymes) most important role is to assist in many reactions occurring in cells.
|
|
|
Nucleic acids
|
Macromolecules that dictate the sequence of amino acids, source of genetic information in chromosomes.
|
Ex: DNA Nucleic acids are made of nucleotides.
|
|
|
Electron
|
A negatively charged particle that is on the outer shell of the nucleus
|
Ex: negative Hydrogen has 1 electron
|
|
|
Monosaccharides
|
Single sugar, simplest carbohydrates
|
Ex: glucose. Monosaccharides are the building blocks of disaccharides.
|
|
|
Fatty acids and glycerol
|
Building blocks of lipids, make up simple fats most common in our diet
|
Ex: fat in steak Fatty acids and glycerol are building blocks of lipids.
|
|
|
Amino acids
|
Small molecules that contain hydrogen , oxygen , carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur atoms that make proteins
|
Ex: alanine Alanine is an amino acid that makes up a protein.
|
|
|
Nucleotides
|
Small units of Nucleic acids, connected to form long chains
|
Ex: DNA Nucleotides are building blocks of Nucleic acids.
|
|
|
Disaccharide
|
Two simple sugar molecules
|
Ex: sucrose(table sugar) If you have two monosaccharides, it makes one disaccharide.
|
|
|
Polysaccharides
|
Several glucose molecules that bond
|
Ex: starch Many monosaccharides makes polysaccharides.
|
|
|
Polypeptide
|
Long chain of amino acids
|
Ex: glucagon A polypeptide forms a protein the length or the chain determines what kind of protein.
|
|
|
Peptide bond
|
Covalent bonds formed between two amino acids
|
Ex: polypeptide A polypeptide is is a long chain of peptide bonds.
|
|
|
DNA
|
Contains deoxyribose, hereditary material of most organisms, four nitrogen-containing bases
|
Ex: double helix DNA is the biological information of a person.
|
|
|
Gene
|
Physical unit of hereditary, specifications that goes from one generation to the next. A segment of DNA
|
Ex: DNA Genes are something you get passed down from your parents.
|
|
|
Neutron
|
A particle that has no charge(neutral) that is in the nucleus
|
Ex: Hydrogen has 0 neutrons.
|
|
|
Ion
|
An atom or molecule that has gained or loss electrons giving it a positive or negative charge
|
Ex: aluminum An ammonium ion is formed together with amine.
|
|
|
Isotope
|
An atom that has the same properties as the elemental form of the substance but has more or less neutrons
|
Ex: Carbon Isotopes of hydrogen, having one extra neutron.
|
|
|
Ionic bond
|
Bond between a negatively charged atom and positively charged atom
|
Ex: NaCl Sodium chloride is an ionic bond.
|
|
|
Covalent bond
|
A chemical bond between two atoms sharing electrons
|
Ex: carbon dioxide Carbon and oxygen share electrons to make a covalent bond.
|
|
|
Polar covalent bond
|
The shared electrons spend a greater amount of time closer to the oxygen nucleus than the hydrogen nucleus
|
Ex: H2O When electrons are unequally shared they make a polar covalent bond.
|
|
|
Law of Conservation of Matter
|
Law stating that matter cannot be created or destroyed
|
Ex: ice cube that melts into a liquid then heated to a gas. Oxidation is an example of the Law of Conservation of Matter
|
|
|
Activation energy
|
Amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction
|
Ex: boiling water To boil water you must heat it first, showing activation energy.
|
|
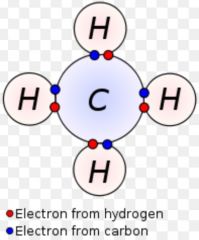
Covalent bond
|
A chemical bond between two atoms sharing electrons
|
Ex: carbon dioxide Carbon and oxygen share electrons to make a covalent bond.
|

