![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
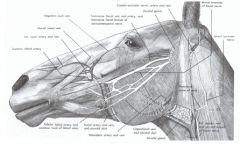
What are the 4 salivary glands of the ox and horse?
|
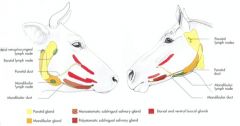
Parotid salivary gland (with Parotid duct)
Mandibular salivary gland Buccal salivary glands (ventral and dorsal) Sublingual salivary gland (will not see superficially) |
|
|
T/F - the parotid duct of the goat and sheep are variable
|
True. The parotid duct may course along the ventral border of the mandible or across the masseter m.
|
|
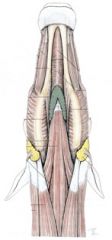
What are the two structures of the horse head seen here (in green and yellow)?
|
Green is the mandibular lnn.
Yellow is the parotid salivary gland. |
|
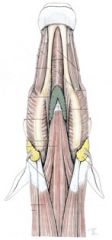
can you name these horse lymph nodes?
|
bueno
|
|
|
What structures does the parotid ln drain in the ox head? What does it drain to?
|
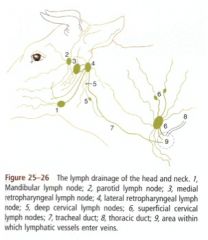
Afferents come from many of the superficial structures of the head
Efferents course to the lateral retropharyngeal ln. |
|
|
What ox lymph nodes drain to the lateral retropharyngeal ln.? Where does it then drain to?
|
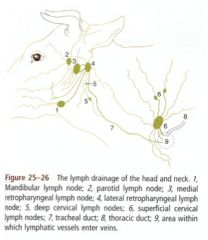
Afferents come from structures of the oral cavity, salivary glands and muscles of the neck
Efferents form the tracheal trunk |
|
|
What are the nerves in the horse that can be damaged by the buckle of their halter? This nerve must also be protected in lateral recumbency.
|
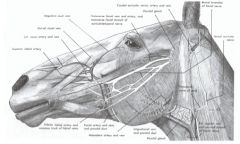
The dorsal and ventral buccal branches of the facial n.
|
|
|
In the horse, what does the auriculotemporal n. divide into?
What do they course with? |
Divides into two branches:
Transverse facial br. courses with the transverse facial vessels Larger br. joins with the dorsal buccal br. of facial n. Both brs. supply sensory innervation to the skin of the cheek |
|
|
In the horse, what does auriculopalpebral n. divide into?
|
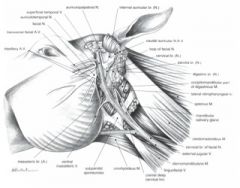
Rostral auricular brs. innervate rostral auricular mm.
Zygomatic br. gives rise to palpebral brs. that innervate orbicularis oculi, levator anguli oculi medialis, and levator nasolabialis mm. Zygomatic br. courses over the zygomatic arch |
|
|
What is the difference in the location of dorsal and ventral buccal brs of facial n. between the horse and ox?
|
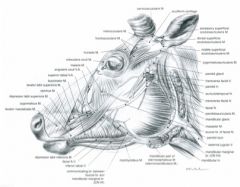
The horse facial n. branches both course over the masseter, closer together than the ox, in which the ventral buccal br. is along the ventral border of masseter m. (shown)
|
|
|
What is the pathway back to a CN from zygomatic n.?
|
Zygomatic n. branches off of auriculopalpebral n. which branches off of CN VII.
|
|
|
What nerve supplies sensory innervation to the bovine horn?
What is this nerve a branch of? |
The cornual n
Branch of the zygomaticotemporal n. of ophthalmic division of trigeminal n. |
|
|
What is a cornual nerve block in the ox? Where is it performed?
|
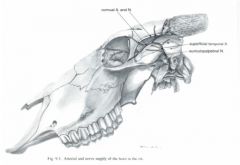
The cornual nerve block is used in dehorning to block innervation to the bovine horn.
Cornual nerve is blocked midway between the lateral canthus of the eye and the base of the horn just ventral to the temporal line |
|
|
What is the innervation of the caprine horn? What is the blocking procedure necessary to dehorn goats?
|
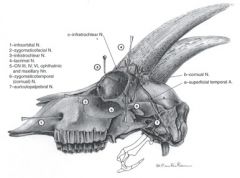
Cornual nerve
Branch of ophthalmic division of trigeminal nerve Blocked midway between the lateral canthus of the eye and base of the horn Infratrochlear nerve Branch of ophthalmic division of trigeminal nerve Blocked midway between the medial canthus of the eye and base of the horn |
|
|
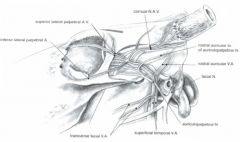
Facial a. of the horse has a deep branch and many superficial branches. What are they?
|
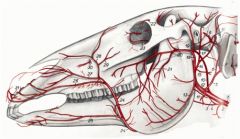
Deep is sublingual a.
Superficial branches are: Inferior labial a. (25) Superior labial a. (26) Lateral nasal a. (27) Dorsal nasal a. (28) Angularis oculi a. (29) |
|
|
What are the palpable arteries in the head of the horse?
|
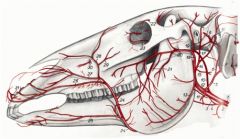
Facial a. (24)
Transverse facial a. (20) Masseteric a. (13) |
|
|
What is the first branch off of external carotid a. in the horse? What does external carotid a. branch into at the end?
|
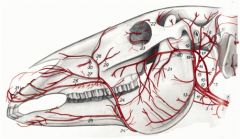
The first branch is linguofacial trunk
External carotid a. (12) finally branches into superficial temporal a. and maxillary a. |
|
|
In the ruminant, what is sublingual a. a branch off of?
|
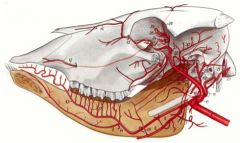
Sublingual a. (9) comes off of Lingual a. (8), not Facial a (6), as it is in the dog and horse.
|
|
|
In ruminants, where does the dorsal nasal a. artery branch from?
|
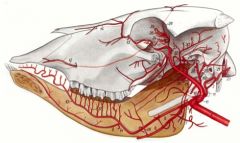
Dorsal nasal a (14) comes from the maxillary a (31) in ruminants, instead of off of facial (6) as it does in horses.
|
|
|
Which artery is important in dehorning in the ox?
|
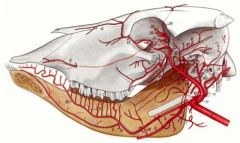
The superficial temporal a (18), which gives branches to transverse facial a (26, as in horses), rostral auricular a (20) and then cornual a (23).
|
|
|
Do small ruminants have a facial a.?
|
No. The job is done by transverse facial a.
|
|
|
Where does the sublingual a. branch off of in the caprine and sheep?
|
From the lingual a., as in the bovine.
|
|
|
Where does dorsal nasal a. branch from in the goat?
|
From Superficial temporal a., not from malar a., as in the bovid.
|
|
|
Does the ovine dorsal nasal a. more resemble the bovine or the caprine?
|
The bovine. The ovine dorsal nasal a. comes from malar a. like the bovine. The caprine dorsal nasal a. comes from superficial temporal a.
|
|
|
The horse has three facial venous sinuses. What are they? What role does the masseter m. play in relation to them?
|
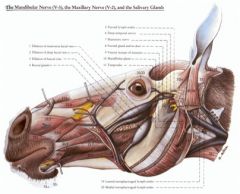
Transverse facial v. - Between facial v. and superficial temporal v.
Deep facial v. - Between facial v. and cavernous venous sinus in the cranial cavity, caudal to the orbital fissure Buccal v. - Between facial v. and superficial temporal v. Masseter m. pumps blood to prevent stagnation |
|
|
What structures course together along the ventral border of the mandible in the horse?
|
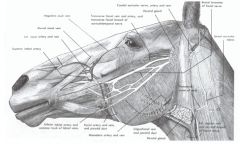
Facial a
Facial v Parotid duct |
|
|
In the ox, what structures course together along the ventral border of the mandible?
|
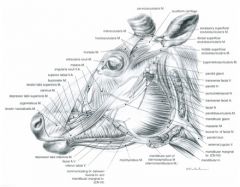
In the ox, the facial artery, facial vein, parotid duct and ventral buccal branch of facial nerve course together along the ventral border of the mandible
|
|
|
In the small ruminant, what structures course along the ventral border of the mandible?
|
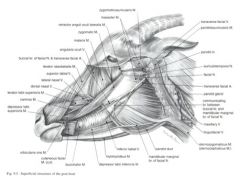
In the small ruminant, the facial vein courses along the ventral border of the mandible
The parotid duct and ventral buccal branch are variable in position |

