![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Classifying Matter |
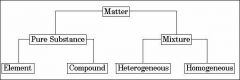
|
|
|
What does 2n^2 represent? |
The number of electrons per energy level. n=energy level. |
|
|
What does the row (period) of the periodic table tell you? |
Outside energy level of the electrons |
|
|
What does the Group A number on the periodic table tell you? |
The electrons configuration of the valence electrons. |
|
|
How do you find the Average atomic mass? |
Mass Of Isotope 1 X % Isotope 1/ mass of Isotope 2 X % Isotope 2 |
|
|
What are Physical Properties? |
Characteristics of the substance (a description to identify the substance) -States of matter (solid, liquid, gas) -Colour -Hardness -Solubility -Density -Boiling & Melting points -Odour |
|
|
What are chemical Properties? What are the 5 ways to identify a chemical reaction? |
Chemical Properties are characteristics when 2 or more substances react, or don't react. You can identify chemical reactions if there is: -A new colour -Light or heat produced or absorbed -Solid precipitate -Gas Forms -Changes are very hard to reverse |
|
|
What was Dalton's model for the atom? |
-The billiard ball -Atoms were invisible -Different Atoms had different properties -Molecules were compound Atoms in whole ratios |
|
|
What is Thompsons atomic theory? |
Through experiments with cathode rays he discovered the electrons. -Milliken discovered the charges of the atom -Raisin bun: Bread is positive matter, raisins are negative electrons |
|
|
What was Rutherford's discovery about the atom? |
Gold foil experiments found that small positive particles were widely spread throughout the foil. This did not agree with uniform distribution of mass and charge. Model- Atoms have a positive nucleus |
|
|
What discovery did Bohr have for the model of the atom? |
-Discovered the neutron -Found protons and neutrons make up atomic mass -1 proton/Neutron= 1 Atomic Unit -Electrons mass is too small to change overall mass |
|
|
What is the Law of Definite Composition? |
-Elements combine in a characteristic mass ratio -Each atom has a particular combining capacity |
|
|
What is the Law of Multiple Proportions? |
-If the same elements combine to form different compounds, the ratio of elements is single and constant -There may be more than one mass ratio. Some elements have more than one combining capacity. |
|
|
What is the Law of Conservation Of Mass? |
-Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed, simply rearranged and remain constant in a chemical reaction. |
|
|
What are the 4 quantum numbers? |
-n= energy level -L = Orbital Type -ML= Orbital Orientation -MS= Electron spins |
|
|
What are the 4 orbital types? |
-S orbital--L=0 (2 electrons max) -P orbital--L=1 (6 electrons max) -D orbital--L=2 (10 electrons max) -F orbital--L=3 (14 electrons max) |
|
|
What are the orbital Orientations? |
-S orbital- ML=0 -P orbital- ML= -1,0,1 -D orbital- ML= -2, -1, 0, 1, 2 -F orbital- ML= -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3 |
|
|
What are the possible Electron spins? |
The electrons spins can either be -MS= 1/2 clockwise ⬆ -MS= -1/2 counterclockwise ⬇ |
|
|
Who is the ♞? |
BAMAN |
|
|
What is ENC? |
-The overall strength of the positive nucleus. Two factors effect ENC: 1:Size of the charge (# of protons) 2: Electron shielding Trend: -ENC increases from left to right -ENC decreases down a column |
|
|
What are diatomic elements? |
HON Halogens Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, (Group 7A) |
|
|
What are the prefixes? |
1-Mono 2-Di 3-Tri 4-Tetra 5-Penta 6-Hexa 7-Hepta 8-Octa 9-Nano 10-Deca |
|
|
What is the Periodic Law? |
The periodic table organizes the known elements into terms of increasing number of protons |
|
|
What is Atomic Radius? |
The size of the atom Atomic Radius Trends: -Left to right- Atomic Radius decreases -Top to bottom- Atomic Radius increases |
|
|
What is Ionizing Energy? |
The energy required to make an electron move from an Atom -I.E. increases from left to right -I.E. decreases from top to bottom |
|
|
What is Electronegativity? |
Electronegativity is the measure of the attraction and atom has on its electrons -E.N increase from left to right -E.N decreases from top to bottom |
|
|
What is Reactivity? |
How likely or vigorously an Atom will react with other substances METALS: -Reactivity decreases from left to right -Reactivity increases from top to bottom NON METALS: -Reactivity increases from left to right -Reactivity decreases from top to bottom |
|
|
What is Melting Point? |
The point at which a substance is at its max temperature while still being solid Metals: -Melting Point increases from left to right - Melting point increases from top to bottom |
|
|
What are properties of ionic substances? |
-Solid at room temperature -Extremely high Melting points -Hard and brittle |
|
|
What are the Types of Covalent bonds? |
TWO SIDED SHARING: -Single Bond: One Electron pair or two electrons shared between Atoms -Double Bond: Two Electron pairs or 4 electrons shared between Atoms -Triple Bond: Three Electron pairs or 6 electrons shared between atoms |
|
|
What is a Co-ordinate Covalent bond? |
A single bond where one atom donates two electrons to be shared between two Atoms. (Single sided sharing) |
|
|
What is a polyatomic ion? |
A group of Atoms held together by Covalent bonds where the central atom has a charge "Many atom ion" |
|
|
What Is VSEPR Theory? |
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Electron pairs and bonding Atoms will be as far apart from each other as possible around a central atom in space |
|
|
What are the Parent VSEPR families? |
-Linear Family: 360÷2=180° apart -Planar Triangle Family (Flat Trigonal Planar) 360÷3= 120° apart -Tetrahedral Family: 109.5° apart |
|
|
What is Metallic Bonding? |
Bonding between two metals -Delocalized electrons -Create alloys |
|
|
What are properties of metals? |
-Good conductors of heat and electricity -Shiny and reflective -Solid at room Temperature -Emit photoelectric effect (Electron emission caused by heat or light) |
|
|
What are properties of Alloys |
-Harder than metals -Higher Melting and boiling points than metals -Mixtures of elements that have metallic properties E.g. Brass= Copper +Zinc |
|
|
What are interstitial Alloys? |
Formed when the interces (holes) in the closest packed metal structure are filled by small atoms |
|
|
What are Properties of Covalent substances? |
-Low Melting and boiling points -Polar have strong intermolecular forces -Have a wide variety of properties, for example some conduct electricity when dissolved in water while some don't. |
|
|
What are Binary Compounds? |
Compounds made of two different elements. Least electronegative first, most electronegative last |
|
|
What are the different naming systems? |
-Multiple Valence naming system: Use ic/ous to indicate charge. Use Latin names where possible. -Roman Numeral Method: And Roman Numeral is placed in brackets after the English name to indicate multiple valence charge. -Prefix Method:Use prefixes to indicate that number of Atoms in the chemical formula |
|
|
What are hydrates? |
Crystals that have water trapped inside their structure. Heat releases the water. |
|
|
What does "Thio" mean? |
-To replace one Oxygen atom with a sulfur. This is possible because they both have the same bonding due to their same number of valence electrons. |
|
|
What are Peroxides? |
-Peroxide means to add one more oxygen. Magnesium oxide = MgO Magnesium Peroxide= MgO2 |
|
|
What are Binary Acids? |
Acids that contain ONLY Hydrogen and one other element other than oxygen |
|
|
How do you Forms a Base? |
Metal Oxide + Water= Base |
|
|
How do you form an Acid? |
Nonmetal Oxide + Water= Acid |
|
|
What is a Synthesis Reaction? |
A reaction that involves the direct combination of two or more substances to form one new Substance. X + Y= XY |
|
|
What is a decomposition Reaction? |
A reaction breaking a single react ant into simpler products XY= X+Y |
|
|
What is an Oxidation Reaction? |
The combination of an element and Oxygen. Metal + Oxygen = Metal Oxide Nonmetal + Oxygen= Nonmetal Oxide |
|
|
How do you form a Binary Compound? |
Metal + Nonmetal = Binary Compound |
|
|
What are combustion Reactions? |
Fuel + O2 = CO2 + H2O Reactions that require Oxygen and always produces H2O and CO2. How to balance: 1. C's 2. H's 3. O's |
|
|
What are single displacement Reactions? |
One element replaces another in a compound. This can only happen if the element that is replacing the old one is more reactive than the one it is replacing. (See activity series for reactivity) |
|
|
What are double Displacement Reactions? |
Positive ions switch negative partners. 2 new compounds form. See Solubility rules to see if it is (S) or (aq). |
|
|
What are Neutralization Reactions? |
Acid + Base= Ionic Salt + Water |
|
|
What are Exothermic Reactions? |
Reactions involving heat being produced |
|
|
What are Endothermic Reactions? |
Reactions involving heat being absorbed |
|
|
What are the Types of Radioactive Decay? |
Alpha Particle Emissions= (2/2He) Beta Particle Emissions= (0/-1e) Gamma Ray Emission = (0/0 gamma ray) |
|
|
What is Nuclear Fusion? |
A reaction which 2 or more atomic nucleus come close enough and form one nuclei and particles. |
|
|
What is Nuclear Fission? |
Nuclear reaction or Radioactive Decay where the nucleus splits into smaller parts. It releases free neutrons, gamma rays, and lots of energy. |
|
|
What is a solute? |
What dissolves. The smaller amount |
|
|
What is a solvent? |
What the solute dissolves into. The larger amount. |
|
|
What is % composition by mass? |
Mass Element/Mass Compound ×100% |
|
|
What is % Yeild? |
Actual Yeild/ Theoretical Yeild ×100% |
|
|
What is % Error? |
Actual Yeild/Theoretical Yeild ×100%. *Always positive. |

