![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
list the normal functions of the liver
|
amino acid, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism
plasma protein and enzyme synthesis production of bile detoxification storage of proteins, glycogen, vitamins (fat soluble A, D, E, K) and metals immune functions |
|
|
gross anatomy of the liver
|
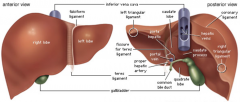
about 1.5 kg
covered by dense irregular connective tissue 4 lobes 2 principle - right and left divided by falciform ligament (a fold of the parietal peritoneum) 2 others on left lobe quadrate (inferior) and caudate (posterior) |
|
|
what is the portal triad?
|
portal triad = hepatic artery, portal vein, bile duct (or branches thereof)
|
|
|
describe the basic histology of the liver
|
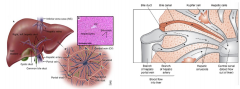
made up of functional units called lobules (6 sided structures composed of hepatocytes) arranged around central veins
hepatocytes have three types of surface - sinusoidal, intercellular and canalicular blood passes through large endothelium-lined spaces called sinusoids, rather than capillaries endothelium of sinusoid is fenestrated and lacks complete basement membrane sinusoids contain Kupffer cells/reticuloendothelial cells (specialised macrophages) between sinusoidal cells and hepatocytes lies the space of Disse/perisinusoidal space containing blood plasma microvilli from hepatocytes extend into this space for absorption of proteins and other plasma components |
|
|
vasculature of the liver
|
hepatic artery (30-40% blood supply), O2 rich from aorta
portal vein (60-70% blood supply), nutrient rich from GI tract |
|
|
parenchymal cells of the liver
|
hepatocytes
- 70% of liver - regenerative - perform major functions of the liver Kupffer/reticuloendothelial cells - break down RBCs by phagocytosis into - heme - converted to bilirubin - globin - recycled - iron - reused perisinusoidal (fat- storing) cells liver-associated lymphocytes |
|
|
connective tissue in the liver
|
- liver capsule
- portal tracts - parenchymal reticulin |
|
|
contents and purpose of bile
|
Bile contains
- water - electrolytes - phospholipids - bile salts/acids - bile pigments - cholesterol - bilirubin Bile needed for fat absorption, and is a mechanism to remove waste and cholesterol |
|
|
fate of RBCs
|
about 126 days old, RBCs are phagocytosed and haemoglobin is broken down into
- heme - converted to bilirubin and bound to albumin - globin - broken down into amino acids and recycled - iron - bound by transferrin and returned to iron stores in liver and bone marrow unconjugated bilirubin (bound to albumin) is water insoluble and cannot be removed by the body released from albumin in sinusoidal tissue and conjugated - attached to glucuronic acid molecules expelled into intestines degraded by intestinal bacteria to form urobilinogen 80% of urobilinogen is oxidised to stercobilin and excreted in the faeces 20% of urobilinogen is recycled by the liver or excreted in the urine |
|
|
3 causes of jaundice
|
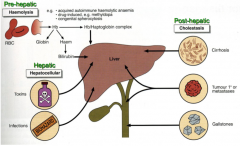
pre-hepatic - haemolysis
hepatic - hepatocellular post-hepatic - cholestasis |
|
|
biliary system
|

|
|
|
what affects the rate of bile secretion and storage?
|
hepatocytes continuously release bile but production and secretion increase when portal blood contains more bile acids - thus, as digestion and absorption continue, bile secretion increases
in fasting state, bile is stored and concentrated (x5) in the gall bladder bile release stimulated by - parasympathetic impulses along vagus nerve - stimulate production of bile - fatty acids and amino acids in duodenum (chyme) stimulate release of enteroendocrine cells such as CCK which causes contraction of the wall of the gall bladder, and relaxation of sphincter of Oddi |
|
|
carbohydrate metabolism in the liver
|
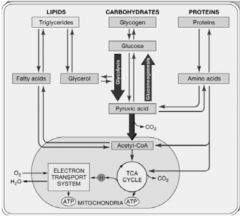
storage - converting glucose to glycogen when blood glucose levels are high
release - glycogenolysis, breaking down glycogen to glucose when blood glucose is low gluconeogenesis - synthesis of glucose from other sources, e.g. lactate, pyruvate, glycerol, alanine conversion of other sugars such as fructose and galactose to glucose |
|
|
lipid metabolism in the liver
|
mitochondrial ß oxidation of short chain fatty acids to generate ATP
synthesis of fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids and lipoproteins |
|
|
protein metabolism in the liver
|
hepatocytes deaminate (remove the amino group) from amino acids so they can be used for ATP production, or converted to carbohydrates or fats
the resulting toxic ammonia is then converted into the less toxic urea and excreted in the urine hepatocytes also synthesise most plasma proteins, e.g. alpha and beta globulins, albumin, prothrombin and fibrinogen - these are used as a measure of hepatic synthetic function |
|
|
biotransformation in the liver
|
Phase 1 reactions
- in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum mediated by cytochrome P450 to produce hydroxylated or carboxylated compounds - convert form non-polar (lipid-soluble toxins) to more polar intermediates - free radicals are produced by this process - antioxidants, particularly glutathione are needed to neutralise the free radicals - when high levels of toxin exposure produce so many free radicals that glutathione levels are depleted the phase 2 processes dependent on glutathione stop, producing oxidative stress and liver damage - some substances, including caffeine, alcohol, digoxin and barbiturates can cause hyperactivity of cytochrome P450 enzymes - producing high levels of damaging free radicals - some substances can slow down P450 activity, e.g. grapefruit Phase 2 reactions - subsequent conjugation pathways with glucuronic acid, acetyl or methyl radicals or glycine, taurine or sulphate - liver adds another substance to make it less harmful - convert the intermediates to polar (water-soluble) excretory derivatives - the intermediates formed by phase 1 are more reactive than the phase 1 toxins, so phase 2 pathways must be carried out at the same rate to avoid a build up of these intermediates |
|
|
describe the acinus
|
Acinus - microcirculatory unit, 3 zones
Zone 1 - close to afferent arteriole - oxidative energy metabolism - fatty acid oxidation - citric acid cycle - respiratory chain Zone 2 - intermediate area Zone 3 - close to terminal hepatic veins - can occur at lower levels of oxygen - xenobiotic metabolism - glycolysis - lipogenesis - ketogenesis |
|
|
list the liver function tests
|
bilirubin
albumin alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and/or aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
alkaline phosphatase gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT) total protein |
|
|
LFTs in different forms of jaundice
|

|
|
|
define cirrhosis
|
A chronic disease of the liver marked by degeneration of cells, inflammation and fibrous thickening of tissue
End stage liver disease Diffuse process with fibrosis and nodule formation |
|
|
complications of cirrhosis
|
portal hypertension
- portal-systemic shunts and varices - ascites - splenomegaly liver failure hepatocellular cancer |
|
|
effects of liver failure
|
impaired production of
- albumin - transport proteins - coagulation and fibrinolysis proteins - complement - protease inhibitors jaundice coagulation disorders altered intermediary metabolism, e.g. impaired synthesis of urea and glycogen altered xenobiotic metabolism, e.g. drugs immune, circulatory and endocrine disturbances |

