![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How many RNAP do eukaryotes have? What do they do? |
Three RNAPI - synthesises RNA precursors (18s, 28s and 5.8s rRNA) RNAPII - makes mRNA RNAPIII - synthesises small non coding RNA (tRNA anf 5s RNA) |
|
|
How are yeast and human RNAP similar? |
Yeast RNAPI, II and III have 14, 12 and 16 subunits respectively. Human RNAPII also has 12 subunits. Yeast and human subunits interchangeable. |
|
|
Similarities between bacteria (E. coli) and human RNAP? |
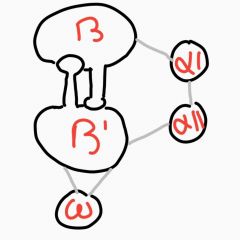
Homology exists. Largest human subunit, RPB1 is similar to beta' RPB2 similar to second largest beta subunit. RPB3 and 11 similar to alpha subunits. RPB6 similar to omega subunit |
|
|
What is the CTD? |
Carboxy terminal domain found on biggest subunit of RNAPII. Tandem repeats of consensus sequence: Tyr-ser-pro-thr-ser-pro-ser Yeast has 26 repeats, drosophila 42 and humans 52. It is relatively unstructured. |
|
|
CTD modifications? |
Can be post transationally modified e.g. phosphorylation (usually of serine) and proline isomerisation. These affect transcription stages. CTD is landing site for many nuclear factors. |
|
|
CTD role in initiation? |
Umodified CTD is vital for PIC formation. High affinity for mediator. Cdk7 of TFIIH enables promoter release/elongation start by phosphorylating ser 5 and 7. |
|
|
CTD role in elongation? |
Proximal promoter pausing is a refulatory event. Caused by RNAPII binding to NELF and DSIF. P-TEFb (cdk9 and cyclin T) phosphorylates NELF to disassociate it. Also phosphorylates ser 2 AND DSIF to recruit chromatin modifying and transcription factors. |
|
|
CTD role in RNA processing? |
mRNA capping - high levels of ser5P found in early transcription, recruits mRNA capping complex. Splicing - phosphorylation of CTD (ser2 thought to recruit spliceosome. Chromatin modification - ser5P recruits proteins associated to set1 to 5'end to methylate H3K4. |
|
|
CTD role in termination? |
Phosphorylation of residues important. Ser7P does 3' processing of small non coding RNA. Thr4 does 3' processing of histones in vertebrates. |
|
|
What are sequence elements? Examples? |
Control transcriptional activity. Core - RNAPII and GTFs bind Enhancer and PPE - activator and repressor proteins bind (PPE must be close to core enhancer can be anywhere in seq e.g. in genes/introns) Insulator - binds to nuclead factors in order to compartmentalise DNA into transcriptional domains so enhancers can't act on wrong genes |
|
|
What is a focused core promoter? |
- 1 transcriptional start site. - regulated (on/off switch) - high levels if trans |
|
|
What is a dispersed promoter? |
- most are dispersed - multiple TSS within 100 bases - constitutive (on all the time) - houskeeping genes - low levels of trans |
|
|
Sequence elements in focused promoter? |
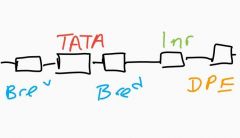
TATA box - AT rich (many promoters don't have this) BRE - B recognition elements Inr - initiator seq (most common even dispersed have these) DPE - downstream promoter element |
|
|
CpG population? |
Under represented but evolutionary pressure to prevent loss of CpG in important places leads to CpG islands. CpG islands coincide with promoters of known genes. Oxidative deamination: c to u and cm to t. |
|
|
What sequences do CpG islands contain? |
- lack TATA and DPE - have several weak Inr - binding sites for TFs e.g. E2F and Sp1 |
|
|
Type of promoter at CpG islands? |
- multiple start sites - constitutive BUT - can be regulated by:
1. Methylation of C: long term repression as methyl binding domain proteins recruit HDAC
2. Polycomb group proteins: dynamic repression (switched on and off) and leads to repressive epigenetic marks. |
|
|
What does RNAPII need for in vivo trans? |
- GTFs (DABFEH - all multiprotein except B) - correct core - unwound DNA - RNAP in correct orientation |
|
|
TFIID structure? |
Has TBP and 13-15 TBP associated factors.
TAFs make sequence specific contacts with DNA. TBP-SAGA complex can replace TFIID at some promoters. |
|
|
Role of TAFS? |
- contact with DNA - recognised modified histones - target for activators |
|
|
What are TATA less promoters? |
Prevelant in housekeeping genes. Sequence is that of TATA box but differs by 2 or more bases. |
|
|
Role of TAFs in TATAless promoters? |
Interact with DNA downstream TATA box to compensate for weak TBP binding via additional contacts. Also is upstream 1st nucleosome so prevents this from interrupting promoter thus gene is expressed. |
|
|
Issue with TATA promoters? |
TSS and initiation complex overkap with 1st nucleosome. Nucleosome represses gene transcription. Rely on SAGA protein to help unravel DNA and unblock promoter. |
|
|
TFIIA |
3 subunits. Stabilises TBP-TATA complex by - preventing TBP dimer formation - preventing non productive TAF1 and TBP interaction Is a coactivator. |
|
|
TFIIB |
Contact made with DNA via BRE
Recruits RNAP/TFIIF complex. Acts as bridge between them and TFIID.
Interacts with activators
Stabilises TFIID/promoter complex
Transcription start site selection influenced by this and RNAPII |
|
|
TFIIF |
Heterotetramer Recruited with RNAPII and stays bound to RNAPII during elongation. Stimulates elongation via suppressing pausing. Other roles: - helps RNAPII recruitment - recruits TFIIE and TFIIH - TSS selection and promoter escape |
|
|
TFIIF |
Heterotetramer Recruited with RNAPII and stays bound to RNAPII during elongation. Stimulates elongation via suppressing pausing. Other roles: - helps RNAPII recruitment - recruits TFIIE and TFIIH - TSS selection and promoter escape |
|
|
TFIIE |
Heterotetramer Direct interaction with RNAPII, TFIIF, TFIIB and promoter. Recruits TFIIH - Stimulates CDK kinase, ATPase and helicase activity of TFIIH. |
|
|
TFIIH |
Most complex and largest GTF (almost as large as RNAPII) Has around 10 subunits, some with enzymatic activity (p52 and p8) Cdk7 phosphorylates ser5 before primoter escape ATPase stimulates transcription initiation and escape Helicase involved in promoter melting Plays role in transcription couples nucleotide excision repair |
|
|
What is PIC? |
For transcription to initiate the GTFs and RNAPII must assemble as pre initiation complex at core promoter. |
|
|
What is basal transcription? |
In vitro when GTFs and RNAPII bind to core causing low levels of transcription. |
|
|
Holoenzyme model? |
Different to stepwise. TFIID interacts first. Followed by recruitment of of preassembled complex (holoenzyme) Contains mediator and coactivators Stepwise and holoenzyme used at diff promoters? Or same promoters at diff times? |
|
|
What is a mediator? |
A super coactivator needed for transcription. Bridge between transcription machinery and activators. Scaffold site for PIC assembly. Conserved structure. Yeast and human subunits also conserved. |
|
|
Transcription elongation? |
After PIC assembly there is conformational change wherein DNA melts and 2 template strand passes through RNAP active site. Initially get short abortive transcription with 3-10 bp products as elongation complex not stable. Promoter contacts released when 30 bp nascent transcript made. |
|
|
GTFs in transcription elongation? |
EF compete with GTFs to cause promoter release.
TFIID, A, E, H and mediator stay bound to promoter (reinitiation complex)
RNAPII, TFIIF and B released. |
|
|
Experiment proving TFIID is bound to promoter? |
TFIID/TBP preincubated with DNA template that makes 68 bp transcript. RNAPII and GTFs (except D) preincubated with 112 template. Reactions mixed, nucleotides added and several rounds of transcription occurs. Only products made are 68bp long. |
|
|
Experiment proving TFIIB leaves promoter? |
TBP, TFIIA and B preincubated with 68bp template. TBP and TFIIA preincubated with 112 bp template. Mixed. RNAPII, GTFs and nucleotides added. 5 mins: only 68bp products 15 mins: both 68 and 112 |
|
|
Alternative GTFs? |
Tissues or genes have specific alternative GTFs. TBP related factors replace TBP. E.g. TRF2 binds to altered TATA box. Some cells have TAFs that aid TRFs. Allows complex pattern of gene expression for multicellular organisms. |
|
|
Alternative GTFs in histone transcription? |
Around 100 copies of histone genes. H1 is has different expression levels to H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 . H1 uses TRF2 instead of TBP. |
|
|
Alternative GTFs in myogenesis? |
Differentiation from myoblasts to myotubes. TFIID downregulated and replaced with TRF3-TAF3 complex. |
|
|
TRF1 |
- insects - binds to TATA - mediates RNAPIII trans of tRNA using BRF1 |
|
|
TRF2 |
- cell dev, differentiation and cycle progression in fish and frogs - doesn't bind to TATA as it lacks 3 conserved phenylalanines - often used to regulate promoters containing DPE |
|
|
TRF3 |
- vertebrates - homologous to TBP - mediates embryonic gene exp |
|
|
XR: TFIID |
1. TBP saddle shaped mol binds to minor groove of DNA causing 90° bend 2. N terminal of TAF1 can bind to TBP inhibiting TBP-TATA interaction 3. Core of histone folds enable TAF-TAF interactions |
|
|
XR: TFIIA |
1. Binds to underside of TBP |
|
|
XR: TFIIB |
1. Thought binding to BRE enables assembly of PIC in correct orientation 2. Helix-turn-helix motif at c terminus of TFIIB binds to BRE |
|
|
XR: TFIIF |
1. 2 subunits: alpha and beta 2. Prevents non specific interaction of RNAPII to DNA 3. Helps minor opening of RNAPII clamp |
|
|
XR: TFIIE |
1. 2 subunits. Alpha has acidic c terminal that binds strongly to TFIIH and beta c terminak binds to single stranded DNA - stabilises open promoter complex. |
|
|
XR: Inr |
Initiator seq recognised by TAF1 and 2. Higher TATA occurrence in absence of Inr or Inr-like sequences. |
|
|
XR: TCT motif. |
Rare motif. Encodes proteins involved in translation. Single T to A conversion turns it into Inr. |
|
|
XR: DPE |
Found in drosophila but rare in humans.
Dependant upon Inr. Position to Inr important, one nucleotide diff means it might not work. |
|
|
XR: chromatin modification |
TAF3 binds to H3K4me3 to facilitate PIC by recruiting TFIID. H3K4me3 found downstream TSS and in active promoters. |

