![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Ex.s of mutations that are beneficial
|
CCR5 protein mutation
CCR5 acts as a co-receptor with CD4 for HIV on lymphocytes. so lacking CCR5 makes one resistant to HIV infection |
|
|
|
What mutation is found in chromosome 22q11 syndrome?
What are other names for this syndrome? What are the symptoms of this syndrome? |
Large scale/chromosomal deletion. About 3 million base pair deletion.
Heart defect, cleft palate, autism. 1/4000 births |
|
|
|
Why do most large scale inversions function normally?
|
Because the whole gene may be contained in the inversion and will be transcribed together
|
|
|
|
What mutation causes Hunter syndrome? In what protein?
What symptoms of the Hunter syndrome? Any popn most affected? |
Large scale inversion mutation that occurs between the functional gene and its inactive pseudogene. Leads to the loss of an enzyme, Iduronate-2-sulfatase, I2S, which is used to degrade mucopolysaccharides.
Heart disease, restricted airways, enlargement of liver and spleen X-linked so most common in males |
|
|
|
What mutation causes hemophilia?
|
Insertions of LINES into factor VII and IX genes which are important in the intrinsic line of the clotting cascade
|
|
|
|
What mutations cause Burkitt's lymphoma?
What is Burkitt's lymphoma? |
Translocation of the c-myc proto-oncogene on chromosome 8 onto adjacent Ig heavy chain region on chromosome 14.
It is a cancer of the lymphocytes. the oncogene translocated on an Ig which is active in lymphocytes contributes to the lymphoma |
.
|
|
|
What are mis-sense mutatations
What are conservative and non-conservative missense mutations? |
A single base change in a gene
Conservative: base change does not result in changes in chemical nature of bases. ex. acid aa switched for another acidic aa Non-conservative: chemical nature not conserved during switch ex. of chemical natures affected during switch: Hydrophobic --> hydrophilic acidic --> basic |
|
|
|
What are nonsense mutations?
|
When the base switch leads to the formation of a stop codon
|
|
|
|
What are frameshift mutations?
|
Addition or deletion of bases not in multiples of 3. Switches the coding info downstream
|
|
|
|
What is Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome?
What are some the symptoms? What kind of inheritance mostly? |
Mutations in Collagen
Vascular problems, fragile vessels (type IV) Hypermobility (type III) Hyperextensibility/skin loose (type I/II, classical) Sprains and dislocations etc. Autosomal dominant inheritance |
|
|
|
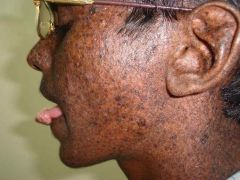
Xeroderma pigmentosum?
Caused by a failure to repair thymidine dimers. |
|
|
|
Name some causes of point mutations
|
1.Unavoidable errors in DNA replication, avg error rate 10^(-)
2. Spontaneous chemical changes 3. Chemical mutagens |
|
|
|
Give examples and describe some spontaneous chemical changes
|
Describe:
1. Depurination: Cleavage of purine base from deoxyribose sugar. DNA polymerase inserts an A in the mRNA strand 2. Deamination: Cytosine --> Uracil. Deamination cos removes an amine grp from cytosine to form uracil |
|
|
|
Difference btw DNA and RNA
|
Respectively:
1. Deoxyribose sugar vs. ribose sugar 2. Double-stranded long chains vs. single stranded short chains 3. DNA has Thymine vs. RNA has Uracil 4. Storage of genetic info vs. messenger of genetic info |
|
|
|
Examples of chemical mutagens...
|
1. Chemical deaminating agents
2. Alkylating agents 3. Intercalating agents 4. UV radiation Give an example of the following... Describe... 1. Nitrous acid 2. Chloromethane 3. Ethidium bromide and Aflatoxin-B 4. UV radiation |
|
|
|
Describe the mechanism and/or effects of the following:
Examples are: Describe... 1. Nitrous acid 2. Chloromethane 3. a. Ethidium bromide and b. Aflatoxin-B 4. UV radiation |
1. An oxidative deaminating agent that converts C --> U so changes base pairing on mRNA from G --> A
2. Adding of methyl grp to G which changes its base pairing C --> T. Good news: repair enzyme O6-methyl guanine-DNA methyltransferase reomoves methyl grp and restores guanine 3. Height of molecule inserted = height of base pair. This leads to addition of single base a. Used in lab to detect DNA by UV flourescence b. Fungal product found on stored grains and peanuts 4. Causes mutant thimidine dimers. Dimerized thymidines are unable to base pair correctly |
|
|
|
An example of a genes involved in DNA repair systems
What does a mutation in this gene usually result in? |
BRCA 1 and 2 genes encode proteins involved in DNA repair especially breaks
Defect in genes mostly associated with breast cancer, and inc risk of ovarian cancer |
|
|
|
Rank the ff in dec radiation dose:
Chest x-ray, dental x-ray, yearly mammogram, Chest CT scan, Head CT |
Dental x-ray --> chest x-ray --> yearly mammogram --> head CT --> chest CT
|
|

