![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the 2 layers of the peritoneum and where are they located? |
Parietal- lines abdominal wall |
|
|
What structures are found in the retroperitoneum? |
Suprarenal glands |
|
|
Originates from the LVOT. |
Aorta |
|
|
Responsible for supplying small and large bowel with blood. |
SMA |
|
|
What are the branches that make up the celiac axis? |
1. hepatic artery |
|
|
What are the types of aneurysms? |
Fusiform and saccular |
|
|
What is cholangitis? |
Inflammation of the bile ducts |
|
|
A TIPS shunt connects what 2 vessels. |
Portal vein to the hepatic vein |
|
|
What does the hormone CCK do? |
Hormone that is sent by the small intestines into the blood stream that stimulates the GB to contract |
|
|
Pain over the GB when the transducer is used to compress the RUQ |
Murphy's sign |
|
|
What is BPH? |
Benign prostatic hyperplasia |
|
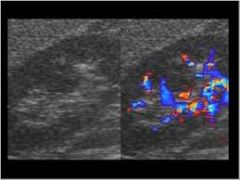
|
Hypertrophied column of bertin |
|
|
___________ areas of the breast primarily function to produce and transport milk . |
Glandular tissue |
|
|
Fibrocystic Change |
Multiple cysts of varying sizes in both breasts |
|
|
Focal or diffuse thyroid gland enlargement due to iodine deficiency. |
Goiter |

