![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
You are asked to scan the SMA. At which time would you normally find a low resistance wave form in the SMA?
A) before a meal (pre-prandial B) after a meal (post-prandial |
B) after a meal (post-prandial
|
|
|
Which of the following vessels is NOT included in the "seagull sign"?
A) hepatic artery B) left gastric artery C) splenic artery D) celiac trunk |
B) left gastric artery
|
|
|
Which of the following is the primary cause of kidney disease?
A) smoking B) untreated hypertension C) sedentary lifestyle D) salty foods |
B) untreated hypertension
|
|
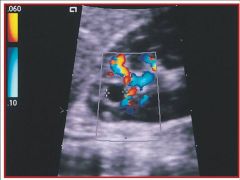
Referencing the sonographic image, predict why the sonographer is using color flow Doppler.
A) to differentiate fat content from blood flow B) to differentiate a muscle from a vessel C) to determine if the anechoic area is a vessel, a simple cyst or a tumor with flow |
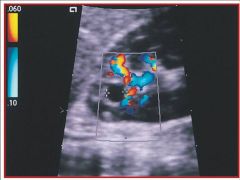
C) to determine if the anechoic area is a vessel, a simple cyst or a tumor with flow
|
|
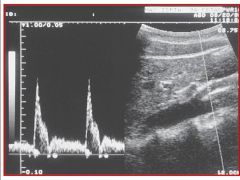
Referencing the sonographic image of the SMA, do you think the waveform was obtained while the patient was fasting or after they had eaten?
A) fasting B) after having eaten |
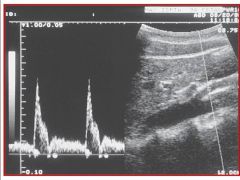
A) fasting
|
|
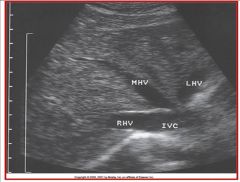
Referencing the sonographic image, the sonographer is scanning transverse orientation to the patient and is obtaining an image of the IVC and hepatic veins. In which direction would the sonographer angle the transducer to obtain this image?
A) superiorly B) inferiorly C) anteriorly D) posteriorly |
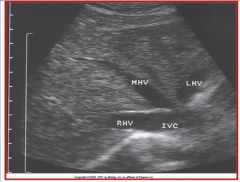
A) superiorly
|
|
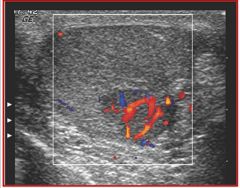
Referencing the sonographic image of the scrotum, the color Doppler has identified a pathology. Which statement best describes the pathology?
A) cystic tumor, most likely benign B) cystic tumor, most likely malignant C) solid tumor, most likely benign D) solid tumor, most likely malignant |
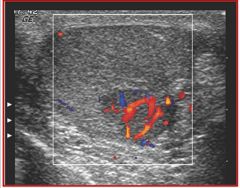
D) solid tumor, most likely malignant
|
|
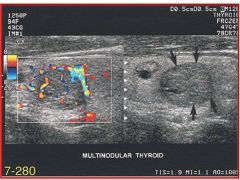
Referencing the sonographic image of the thyroid gland, the color flow Doppler has identified a tumor. Which of the following statements most accurately describes the blood flow findings?
A) increased vascularity both peripherally and to some degree centrally B) decreased vascularity with little evidence of flow C) increased peripheral vascularity but no central vascularity D) increased central vascularity with no peripheral vascularity |
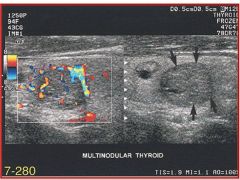
A) increased vascularity both peripherally and to some degree centrally
|
|
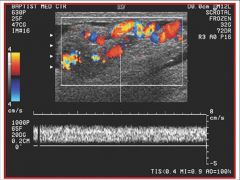
Referencing the sonographic image of the testicle, the sonographer uses color flow Doppler to rule out a particular pathology. What is the name of the pathology that the sonographer is trying to rule out and what are the findings?
A) the pathology is a solid testicular tumor and it is present B) the pathology is a solid testicular tumor and it is absent C) the pathology is a varicocele and it is present D) the pathology is a varicocele and it is absent |
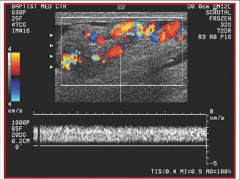
C) the pathology is a varicocele and it is present
|
|
|
This structure arises from the posterolateral wall of the aorta directly into the hilus of the kidney.
A) right renal artery B) inferior mesenteric artery C) left renal artery D) superior mesenteric artery |
C) left renal artery
|
|
|
This structure arises from the celiac trunk to supply blood flow to the spleen
A) gastroduodenal artery B) splenic artery C) celiac axis D) superior mesenteric artery |
B) splenic artery
|
|
|
This structure leaves the posterolateral wall of the aorta; travels posterior to the inferior vena cava to enter the hilum of the kidney.
A) right renal artery B) left renal artery C) celiac axis D) left gastric artery |
A) right renal artery
|
|
|
Smallest lobe of the liver; lies posterior to the left lobe and anterior to the inferior vena cava; superior border is the ligamentum venosum.
A) left lobe B) right lobe C) falciform ligament D) caudate lobe |
D) caudate lobe
|
|
|
This structure arises from the posterolateral wall of the aorta directly into the hilus of the kidney.
A) right renal artery B) inferior mesenteric artery C) left renal artery D) superior mesenteric artery |
C) left renal artery
|
|
|
This structure arises from the celiac trunk to supply blood flow to the spleen
A) gastroduodenal artery B) splenic artery C) celiac axis D) superior mesenteric artery |
B) splenic artery
|
|
|
This structure leaves the posterolateral wall of the aorta; travels posterior to the inferior vena cava to enter the hilum of the kidney.
A) right renal artery B) left renal artery C) celiac axis D) left gastric artery |
A) right renal artery
|
|
|
Smallest lobe of the liver; lies posterior to the left lobe and anterior to the inferior vena cava; superior border is the ligamentum venosum.
A) left lobe B) right lobe C) falciform ligament D) caudate lobe |
D) caudate lobe
|
|
|
This structure arises from the posterolateral wall of the aorta directly into the hilus of the kidney.
A) right renal artery B) inferior mesenteric artery C) left renal artery D) superior mesenteric artery |
C) left renal artery
|
|
|
This structure arises from the celiac trunk to supply blood flow to the spleen
A) gastroduodenal artery B) splenic artery C) celiac axis D) superior mesenteric artery |
B) splenic artery
|
|
|
This structure leaves the posterolateral wall of the aorta; travels posterior to the inferior vena cava to enter the hilum of the kidney.
A) right renal artery B) left renal artery C) celiac axis D) left gastric artery |
A) right renal artery
|
|
|
Smallest lobe of the liver; lies posterior to the left lobe and anterior to the inferior vena cava; superior border is the ligamentum venosum.
A) left lobe B) right lobe C) falciform ligament D) caudate lobe |
D) caudate lobe
|
|
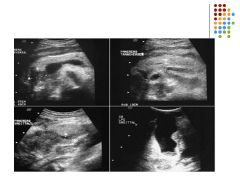
A 56 year old male with a 1 week history of jaundice and pain has reported a 3 month history of nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and diarrhea. Based on the sonographic images, what is the most likely differential diagnosis?
A) acute pancreatitis B) chronic pancreatitis C) pancreatic adenocarcinoma D) pancreatic pseudocyst |
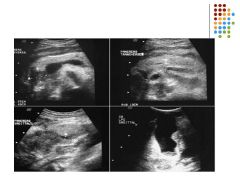
C) pancreatic adenocarcinoma
|
|
|
Marked elevation of which of the following choices is typically associated with biliary obstruction?
A) BUN B) amylase C) bilirubin D) alkaline phosphatase |
D) alkaline phosphatase
|
|
|
This part of the pancreas lies in the left hypochondrium near the hilus of the spleen and upper pole of the left kidney.
A) body of the pancreas B) tail of the pancreas C) uncinate process D) head of the pancreas |
B) tail of the pancreas
|
|
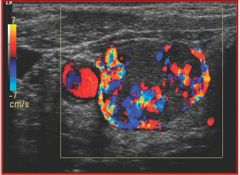
Referencing the sonographic image of a thyroid nodule, what vessel is demonstrated in the image?
A) right jugular vein B) right carotid artery C) left jugular vein D) left carotid artery |
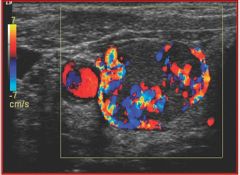
B) right carotid artery
|
|
|
The small, curved tip of the pancreatic head that lies posterior to the superior mesenteric vein is called the:
A) C-loop of the duodenum B) uncinate process C) portal-splenic confluence D) bowel |
B) uncinate process
|
|
|
The right kidney normally lies slightly ______________than the left kidney
A) crooked B) higher, superior C) lower, inferior D) posterior |
C) lower, inferior
|
|
|
The normal wall thickness of the gallbladder is less than _____ mm.
A) 3 B) 1 C) 4 D) 7 |
A) 3
|
|
|
All of the following are liver function tests established to analyze how the liver is performing under normal and diseased conditions EXCEPT:
A) AST (SGOT) B) ALT (SGPT) C) alkaline phosphatase D) prothrombin time E) creatinine |
E) creatinine
|
|
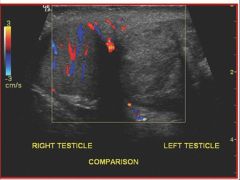
Referencing the sonographic image of a testicular exam, the sonographer has used color flow Doppler to determine if a particular pathology is present. What did the sonographer find.
A) normal study of both testicles B) normal right testicle and most likely torsion of the left testicle C) normal left testicle and most likely torsion of the right testicle D) both testicles demonstrate torsion |
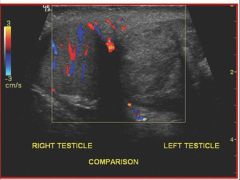
B) normal right testicle and most likely torsion of the left testicle
|
|
|
Renal cell carcinoma commonly invades the IVC via the:
A) renal vein B) renal artery C) portal vein D) splenic vein |
A) renal vein
|
|
|
A triangular-shaped lesion on the peripheral border of the kidney most likely represents a(n):
A) renal tumor B) artifact from rib C) IVC compression D) junctional parenchymal defect |
D) junctional parenchymal defect
|
|
|
On ultrasound, the sonographic appearance of acute pancreatitis compared to chronic pancreatitis would be:
A) homogeneous B) echogenic C) calcified D) hypoechoic |
D) hypoechoic
|
|
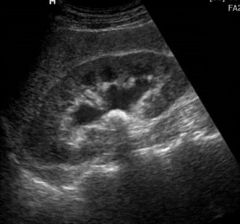
View the image and select the correct pathology.
A) renal stone B) renal abscess C) renal stone with hydronephrosis D) severe hydronephrosis |
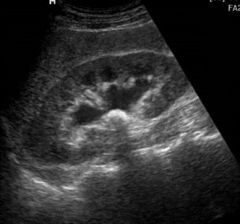
C) renal stone with hydronephrosis
|
|
|
Non-shadowing, low-amplitude echoes in a dependent gallbladder is most characteristic of:
A) stones B) porcelain gallbladder C) cholecystitis D) sludge |
D) sludge
|
|
|
A potential space located between the liver edge and right kidney is:
A) Douglas’ pouch B) Morison’s pouch C) cul-de-sac D) Winhauer’s space |
B) Morison’s pouch
|
|
|
Dilatation of the renal pelvis with thinning of the renal cortex is characteristic of:
A) duplex collection system B) column of Bertin C) hydronephrosis D) extrarenal pelvis |
C) hydronephrosis
|
|
|
A cortical bulge in the lateral border of the kidney is called a/an:
A) junctional parenchymal defect B) dromedary hump C) column of Bertin D) extrarenal pelvis |
B) dromedary hump
|
|
|
The most common type of thyroiditis is:
A) deQuervain’s B) Courvoisier’s C) Hashimoto’s D) Stein-Leventhal |
C) Hashimoto’s
|
|
|
The landmark for the posteriolateral border of the thyroid is:
A) trachea B) esophagus C) strap muscle D) common carotid artery E) superior thyoid artery |
D) common carotid artery
|
|
|
A 15-year-old boy presents with sudden intense right scrotal pain, nausea and vomiting. A sonogram is performed, and an enlarged hypoechoic right scrotum with decreased arterial flow is documented. The left scrotum is normal.This is most consistent with...
A) testicular rupture B) varicocele C) spermatocele D) torsion E) hydrocele |
D) torsion
|
|
|
On a sonographic examination, a seminoma of the testicle may appear as:
A) solid, homogeneous mass B) large, multilocular cystic mass C) small, simple cyst D) diffuse enlargement of the testicle E) small, complex mass |
A) solid, homogeneous mass
|
|
|
The left testicular vein drains into the
A) IVC B) left internal iliac vein C) common internal iliac vein D) left renal vein E) prostatic vein |
D) left renal vein
|
|
|
The muscle that lies posterior to the breast is the
A) Cooper's muscle B) pectoralis muscle C) levator ani muscle D) rectus muscle E) transverse muscle |
B) pectoralis muscle
|
|
|
The sonographic appearance of a benign breast mass includes all of the following EXCEPT:
A) well-circumscribed borders B) round or oval in shape C) smooth borders D) taller in size than wider E) homogeneous with moderate low level echoes |
D) taller in size than wider
|
|
|
The mediastinum testis appears sonographically as:
A) a homogenous mass like structure within the pampiniform plexis B) a heterogenous mass like structure in the mid testis C) an anechoic linear echo through the mid testis D) an echogenic linear echo through the mid testis |
D) an echogenic linear echo through the mid testis
|
|
|
What ultrasound technique and patient technique could be performed to assist in the diagnosis of a varicocele?
A) patient performs a valsalva maneuver while the sonographer scans the area using Doppler B) patient lies perfectly flat while sonographer squeezes the testicle while imaging with Doppler C) sonographer scans in gray scale and measures the size increase of the vein diameters D) patient performs the rapid, shallow breathing technique while sonographer scans with Doppler |
A) patient performs a valsalva maneuver while the sonographer scans the area using Doppler
|
|
|
Diminished vascular structures within the liver parenchyma most likely represent:
A) obstructive portal disease B) cirrhosis C) Budd-Chiari syndrome D) acute viral hepatitis |
B) cirrhosis
|
|
What abnormality is seen in this image?
A) hydronephrosis B) urolithiasis C) horseshoe kidney D) tadpole sign |
A) hydronephrosis
|
|
|
Typical symptoms a patient may have with an abscess formation include all of the following EXCEPT:
A) fever. B) decreased white blood count C) pain D) increased white blood count |
B) decreased white blood count
|
|
|
The amoebic abscess may reach the liver through the:
A) hepatic artery B) gastroduodenal artery C) hepatorectal artery D) portal vein |
D) portal vein
|
|
|
The maximum outer diameter of the normal appendix can measure up to:
A) 3 mm B) 4 mm C) 5 mm D) 6 mm |
D) 6 mm
|
|
|
Pyonephrosis refers to the presence of:
A) blood in a dilated collecting system B) pus in a dilated collected system C) urine in a dilated collecting system D) a perinephric abscess |
B) pus in a dilated collected system
|
|
|
A thickened muscle in the pylorus that prevents food from entering the duodenum is:
A) intussusception B) appendicolith C) hypertrophic pyloric stenosis D) appendicitis |
C) hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
|
|
|
When bowel prolapses into distal bowel and is propelled in an antegrade fashion is known as:
A) hypertrophic pyloric stenosis B) intussusception C) projectile vomiting D) appendicitis |
B) intussusception
|
|
|
The target and pseudokidney sign are found in what abnormality?
|
Intussusception
|
|
|
This is considered the infantile form of hepatocellular carcinoma.
A) neuroblastoma B) Wilms' tumor C) hepatoblastoma D) both a and b |
C) hepatoblastoma
|
|
|
The etiology of extrahepatic obstruction includes all EXCEPT which of the following?
A) bile duct perforation B) choledochal cyst C) biliary atresia D) hepatitis |
D) hepatitis
|
|
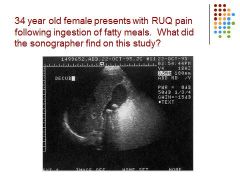
What is it? What is the criteria for this?
|
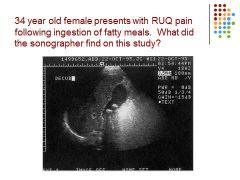
Gallstones in GB – US criteria: posterior shadowing, mobile echogenic focci / symptoms: positive murphy sign, pain in RUQ especially after fatty meals
|
|
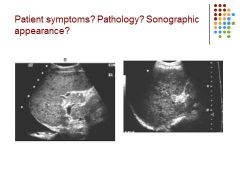
|
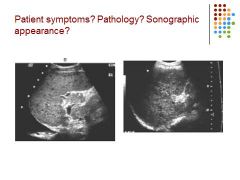
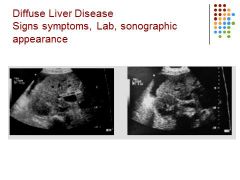
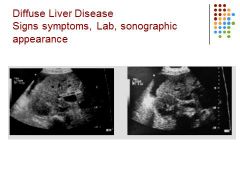
Symptoms: Itching (pruritus), jaundice, edema, bruising, weight loss
Pathology: cirrhosis Sonographic appearance: heterogeneous liver – hypoechoic spots in the liver, pleural effusion, liver small |
|
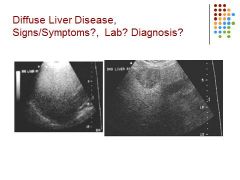
|
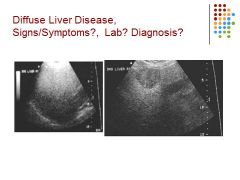
Heterogenous, echogenic liver – fatty liver – focal sparing seen in right picture
|
|
|
Kidney stone – hematuria
|
|
|
Ascites seen, liver is heterogeneous, small – cirrhosis / lab work that will be off is ALT, increase pro time, bilirubin, AST, alk phos / pt will be jaundiced / alk phos also means obstruction
|
|
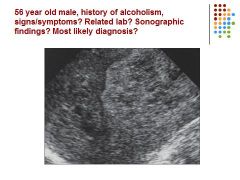
|
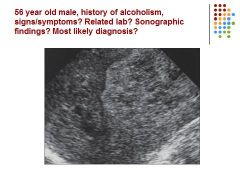
Fatty – cirrhosis though because of history – or hepatocellular carcinoma, depending on labs and pt history
|
|
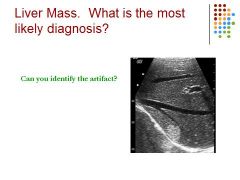
|
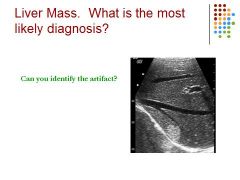
Most likely hemangioma: vascular tumor, round, echogenic - Artifact is Mirror image – high reflection
|
|
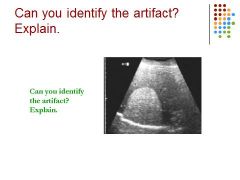
|
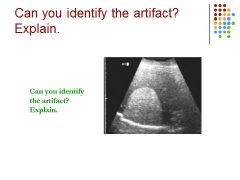
Speed of sound error – looks like diaphragm is broken
|
|
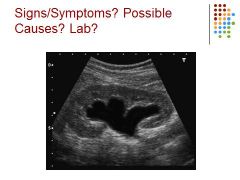
|
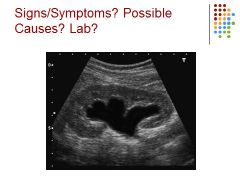
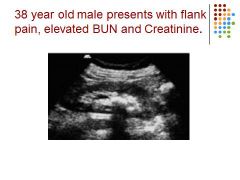
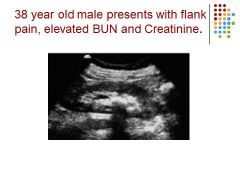
Hydronephrosis – possibly caused by a blockage, elevated BUN creatinine – mild hydro because of rounded calyces
|
|
|
Blockage in CBD causes mass effect in liver – normal limit for CBD is 6mm, but if GB is removed it can be larger and is used to hold bile
|
|
|
Pt has gallstones and caliectasis (Dilation of the calices, usually due to obstruction or infection), when women are pregnant, they can get mild hydro, uti, and gallstones
|
|
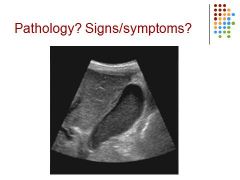
|
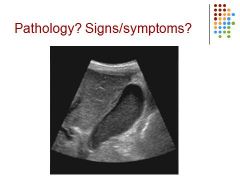
Sludge in GB – could be from fasting, if symptoms – pain nausea, vomiting, murphy sign – pain over GB when pressed
|
|
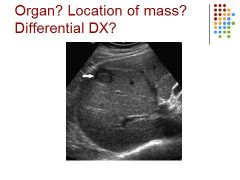
|
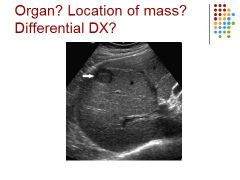
Hepatocellular carcinoma – mets is usually more than one
|
|
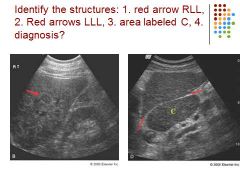
|
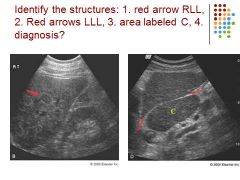
1. Red Arrow: nodular liver
2. Red arrows: ligamentum venosum 3. Prominent Caudate lobe 4. Diagnosis: cirrhosis |
|
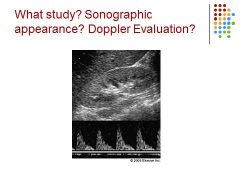
|
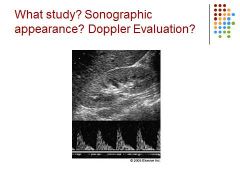
Diminished diastolic flow – decub patient
|
|
|
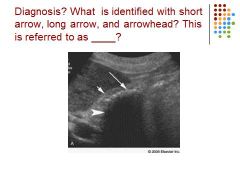
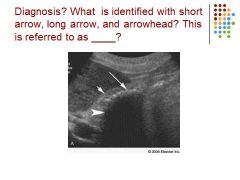
WES – top arrow: echo / middle arrow: wall / last arrow: shadow
Diagnosis - gallstones |
|
|
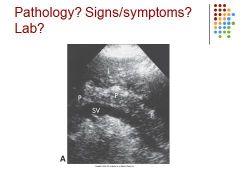
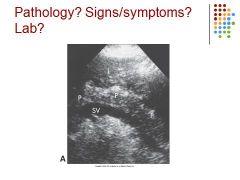
Chronic pancreatitis
|
|
|
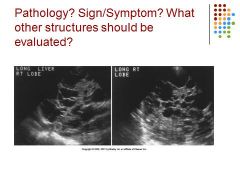
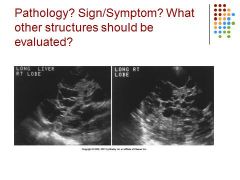
Multicystic liver – scan the kidney to check as well
|
|
|
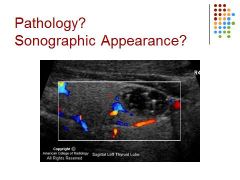
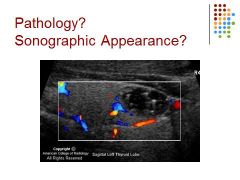
Thyroid – complex nodule / comet tail artifact is common with benign nodules / vascularity is increased around the nodule
|
|
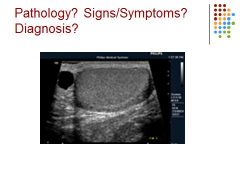
|
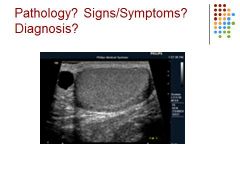
Spermatocele -
|
|
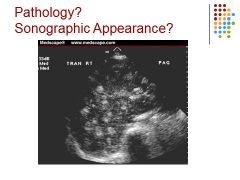
|
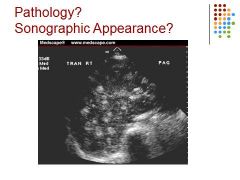
Mets to liver with breast cancer – bulls eye appearance
|
|
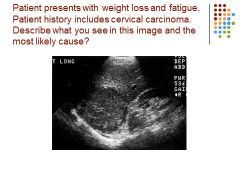
|
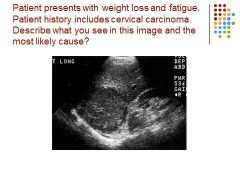
Hepatocellular Cancer to liver - mets
|
|
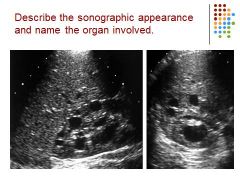
|
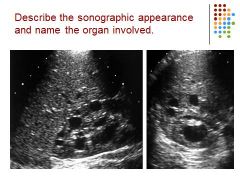
Polycystic kidney
|
|
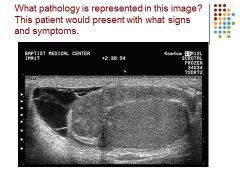
|
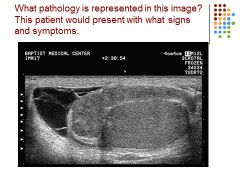
Epididymitis – hetero, enlarged epi – caused complex hydrocele – pain, swelling
|
|
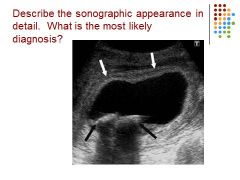
|
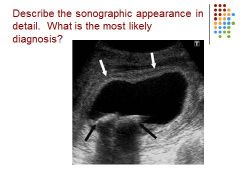
GB – thickened wall – stones – acute cholecystitis (inflammation of GB caused by gallstones in the GB)
|
|
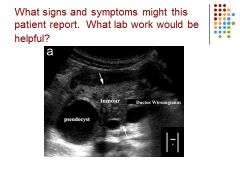
|
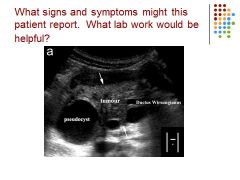
Pancreas – pseudocyst – tumor adenocarcinoma – dilated duct of wirsung
|
|
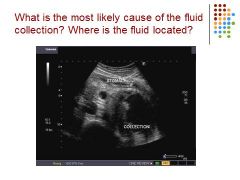
|
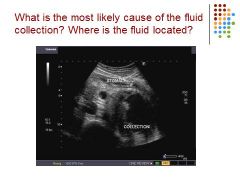
Inferior to stomach so it’s a pseudocyst on the panc
|
|
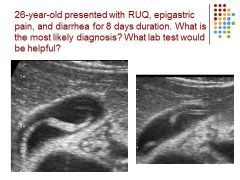
|
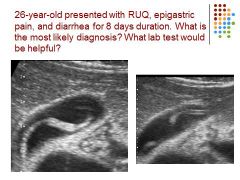
Ascariasis – worm – non-shadowing, mobile, 5 cm long, tubular echogenic structure
|
|
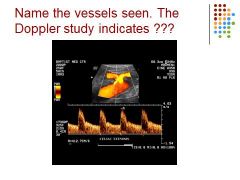
|
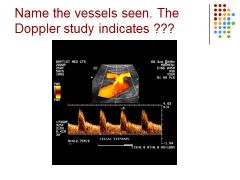
Celiac trunk – HA and Splenic Art – celiac stenosis
|
|
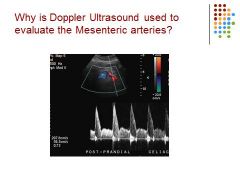
|
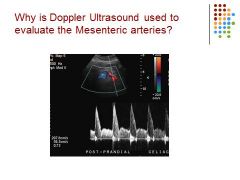
They are trying to rule out Crohn’s (a form of inflammatory bowel disease) or make sure there isn’t an occlusion
|

