![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
62 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
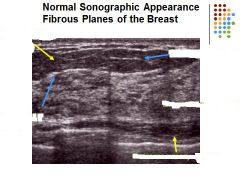
What are the missing labels?
|
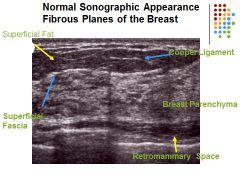
Left: Superficial Fat
Superficial Fascia Right: Cooper ligament Breast Paranchyma retromammary space Skin line – hyperechoic Superficial fascia plane - hyperechoic Subcutaneous tissue- a. Cooper’s ligaments - hyperechoic Mammary zone – a. Glandular breast parenchyma appears moderately hyperechoic b. Fat breast lobules should demonstrate a medium gray echo pattern Retromammary zone – hypoechoic a. Deep fascia plane - hyperechoic Pectoralis muscles – moderately hyperechoic Fat = medium level gray Breast parenchyma = moderately hyperechoic Retromammary space = hypoechoic to breast parenchyma Cooper ligaments and fascia planes = hyperechoic |
|
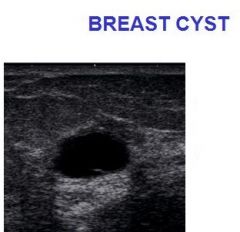
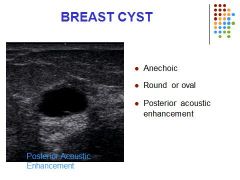
Describe the sonographic appearance of the breast cyst.
|
Obstructed lactiferous duct
Most common pathological finding in women presenting with a palpable breast lump Clinically firm, smooth and relatively mobile mass Cysts may demonstrate low level internal echoes from cellular debris Cysts can be multilocular or septated Thick walls or irregular borders can be associated with malignancy |
|
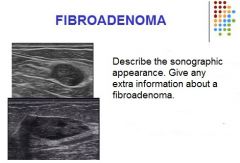
|
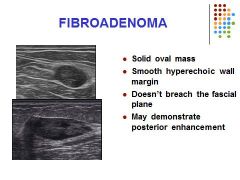
Influenced by estrogen levels
Most common benign solid tumor of the breast Frequently multiple 20 – 35 years age Hyperplastic or proliferative process in a single terminal ductal unit Can spontaneous resolve Rubbery, mobile oval mass |
|
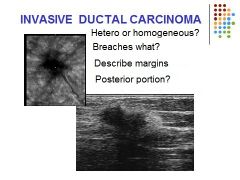
|
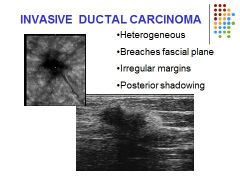
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma= 70% of cases present with a palpable mass. Demonstrates as a solid heterogeneous irregular shaped lesion. Ill defined margins; spiculated appearance. Shadowing
|
|
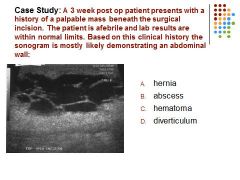
|
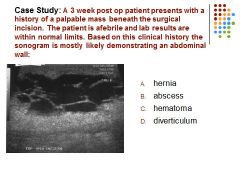
C – hematoma….. Afebrile patient with a complex mainly cystic mass is most suspicious for a hematoma
|
|
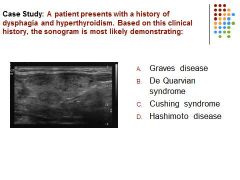
|
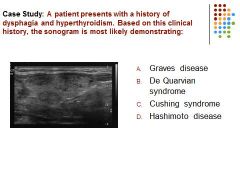
A) Graves disease is characterized by pronounced hyperthyroidism and associated with multilocular nodules (image demonstrates a multinodular goiter) Cushing disease is associated with the adrenal glands (excessive production of cortisol)
|
|
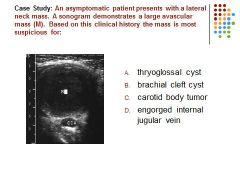
|
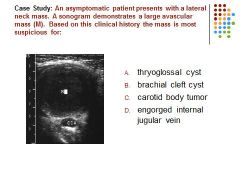
C) Brachial
|
|
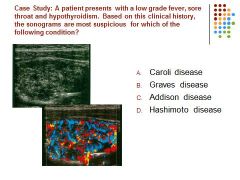
|
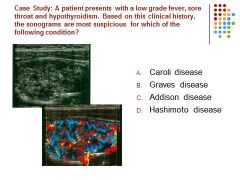
D) Hashimoto disease demonstrates as an enlarged hypoechoic hypervascular thyroid parenchyma. Pts may demonstrate leukocytosis also or even asymptomatic.
Graves disease is not as likely to demonstrate such an overall vascular thyroid gland. Caroli disease is associated with the intrahepatic biliary ducts Addison disease is associated with the adrenal gland |
|
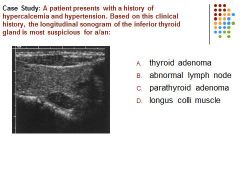
|
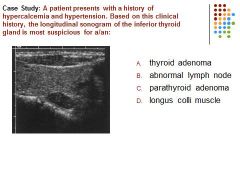
C. A patient with a history of hypercalcemia and a hypoechoic mass posterior to the thyroid gland is most suspicious for a parathyroid adenoma.
Thyroid adenoma is generally asymptomatic. |
|
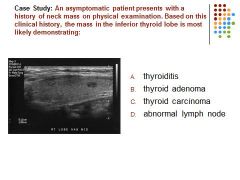
|
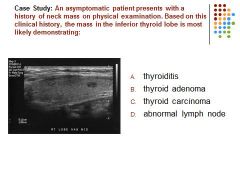
B. Thyroid adenomas are generally asymptomatic and demonstrate on ultrasound as a well define echogenic mass. A prominent peripheral halo may also be demonstrated.
The gland overall does not appear enlarged or hypoechoic as seen in cases of thyroiditis. |
|
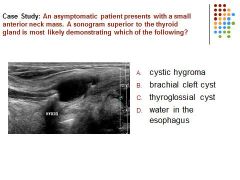
|
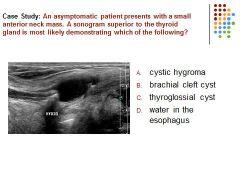
C. A thyroglossal cyst is located between the tongue and thyroid isthmus. Brachial cleft cyst is located in the lateral neck
|
|
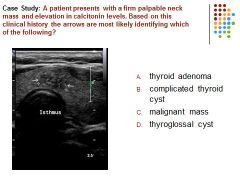
|
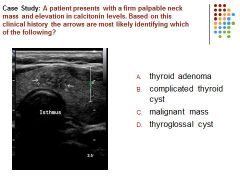
C – an irregular complex mass is identified in a patient with an elevation of calcitonin (associated with medullary thyroid carcinoma) is most suspicious for a malignant mass
|
|
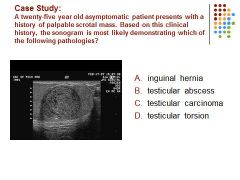
|
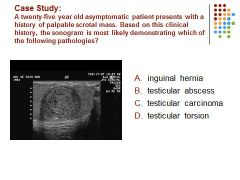
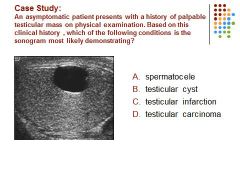
C. A hypoechoic intra-testicular mass is identified in a young adult male, most suspicious for malignancy.
|
|
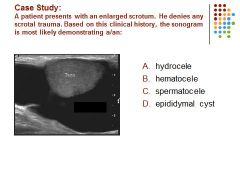
|
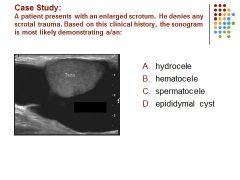
A. Fluid in the scrotal sac in a patient without a history of trauma is most likely a hydrocele.
|
|
|
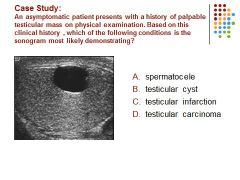
B. A smooth anechoic intra-testicular mass demonstrating posterior enhancement is identified in an asymptomatic patient most suspicious for a cyst.
|
|
|
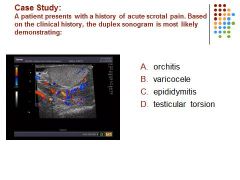
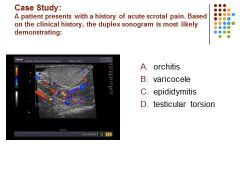
C. Hypervascular blood flow is identified in a swollen hypoechoic epididymus most suspicious for epididymitis
|
|
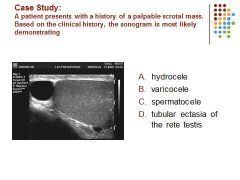
|
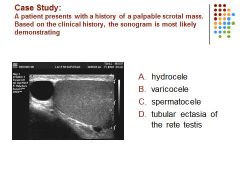
C. a spermatocele is a retention cyst of the rete testis.and located superior to the testis.
|
|

|

D. All of the conditions may cause scrotal pain but epididymitis is the most common cause of acute scrotal pain.
|
|
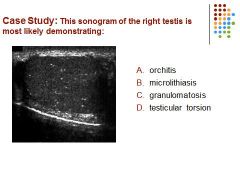
|
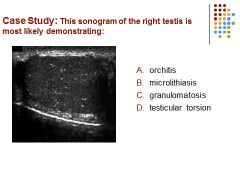
B) Microlithiasis
|
|

|

C. a lower urinary tract infection is the most common cause of epididymitis
|
|

|

C. An adolescent patient is most likely to develop testicular torsion than epididymitis.
|
|
|
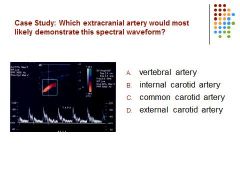
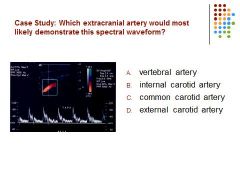
D) The wave form is demonstrating high resistance and also temporal taps used to distinguish the ECA from the ICA.
Vertebral and ICA demonstrate a low resistance CCA demonstrates a combination of both low and high resistance.. |
|
|
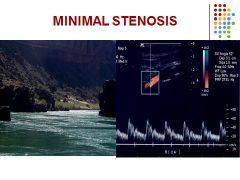
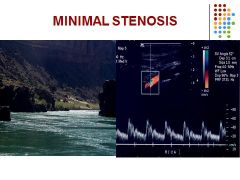
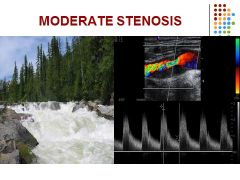
Mild or no increase in flow velocities
PSV < 125 cm/sec and EDV < 40 cm/sc ICA/CCA = < 2.0 |
|
|
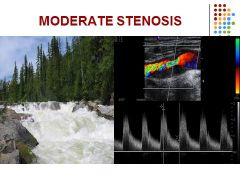
Stenosis 50 – 69 %
Mild increases in peak systolic and end diastolic velocities PSV 125 – 230 cm/sec and EDV 40 – 100 cm/sec ICA/CCA = 2.0 – 4.0 |
|
|
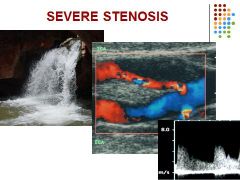
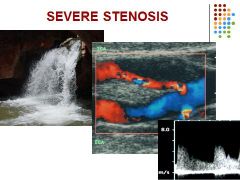
Stenosis 70% and greater
PSV > 230 cm/sec and EDV > 100 cm/sec ICA/CCA ratio > 4.0 Severe stenosis increases velocities in contralateral carotid arteries |
|

|

Disruption of the normal laminar flow in which eddies occur
Spectral broadening = Wide range of frequencies Spectral bruit = flow reversal Turbulence = Reynolds number above 2000 |
|
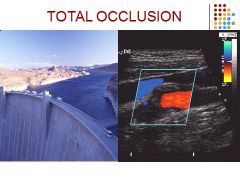
|
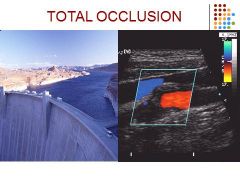
No detectable intraluminal blood flow (audible thump)
Monophasic ipsilateral CCA Increase velocities in contralateral carotid arteries or vertebral arteries |
|
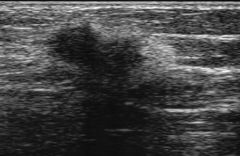
This image represents:
A) A benign mass of the testicle B) A benign mass of the breast C) A malignant mass of the testicle D) A malignant mass of the breast |
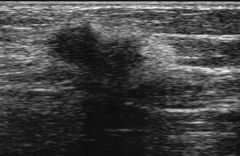
D) A malignant mass of the breast
|
|
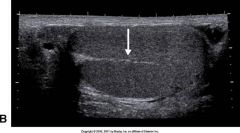
The arrow seen in this image is:
A) tunica vaginalis B) head of the epidymis C) spermatocele D) mediastinum testis |
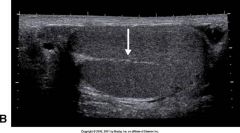
D) mediastinum testis
|
|
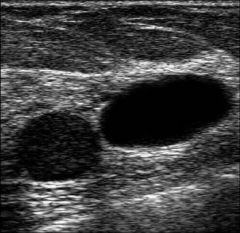
This image represents:
A) a cystic mass in the breast B) a complex mass in the breast C) two cyst in the thyroid D) two cyst in the breast |
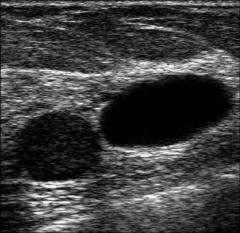
D) two cyst in the breast
|
|
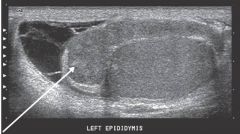
Which pathology?
A) hydrocele B) microliths C) epididymitis D) choriocarcinoma |
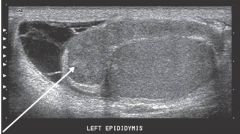
C) epididymitis
|
|
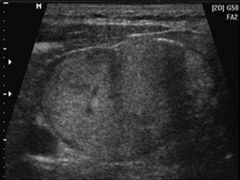
This image represents a mass in the:
A) thyroid gland B) scrotum C) breast D) testicle |
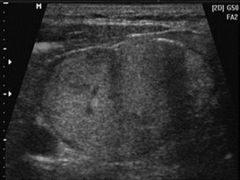
A) thyroid gland
|
|
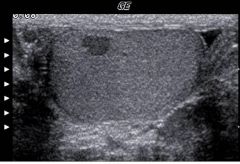
This image represents:
A) A cyst in the testicle B) a benign testicular mass C) testicular torsion D) seminoma |
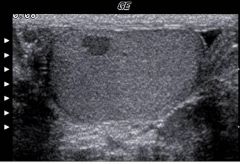
D) seminoma
|
|
|
The most common type of thyroiditis is:
A) deQuervain’s B) Courvoisier’s C) Hashimoto’s D) Stein-Leventhal |
C) Hashimoto’s
|
|
|
The landmark for the posteriolateral border of the thyroid is:
A)trachea B) esophagus C) strap muscle D) common carotid artery E) superior thyoid artery |
D) common carotid artery
|
|
|
Hyperthyroidism associated with a diffuse goiter is associated with:
A) papillary carcinoma B) Grave's disease C) Hashimoto's thyroiditis D) adenoma |
B) Grave's disease
|
|
|
The muscle that lies posterior to the breast is the
A) Cooper's muscle B) pectoralis muscle C) levator ani muscle D) rectus muscle E) transverse muscle |
B) pectoralis muscle
|
|
|
What is the most common benign breast mass in women during their reproductive years?
A) cyst B) abscess C) fibroadenoma D) enlarged lymph nodes E) hyperplasia |
C) fibroadenoma
|
|
|
The sonographic appearance of a benign breast mass includes all of the following EXCEPT:
A) well-circumscribed borders B) round or oval in shape C) smooth borders D) taller in size than wider E) homogeneous with moderate low level echoes |
D) taller in size than wider
|
|
|
The most important signs to look for in determining a cystic lesion of the breast include all except which of the following?
A) well-defined borders B) good through transmission C) anechoic D) disruption of architecture |
D) disruption of architecture
|
|
|
Clinical findings of lumpy, painful, tender breasts that vary with monthly cycles usually represent:
A) carcinoma B) fibrocystic disease C) cyst D) adenoma |
B) fibrocystic disease
|
|
|
The most common solid benign tumor of the breast is:
A) fibrocystic disease B) fibroadenoma C) papilloma D) lipoma |
B) fibroadenoma
|
|
|
Characteristic findings of breast carcinoma include all except which of the following?
A) attenuation of sound B) irregular margins C) strong posterior margin D) inhomogeneous low-level internal echo pattern with calcifications |
C) strong posterior margin
|
|
|
In documenting a sonographic breast mass, which of the following statement(s) apply?
1. The sonographic image recording the mass should be labeled appropriately according to either breast quadrant or breast clock face position. 2. The sonographic image recording the mass should be labeled appropriately according to which breast contains the mass. 3. The sonographic image recording the mass should be labeled appropriately according to transducer orientation (i.e., sagittal, transverse, radial, or antiradial). 4. The sonographic image should ideally record the size of the mass in all three dimensions. A) 1, 2, and 3 B) 1 and 3 C) all D) 4 only |
C) all
|
|
|
Ultrasound is often of benefit in guiding breast procedures, except for which of the following?
A) cyst aspiration B) fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC), which is used in many centers for diagnosis of a solid mass C) large core needle biopsy of a solid mass D) large core needle biopsy of microcalcifications not visible on ultrasound |
D) large core needle biopsy of microcalcifications not visible on ultrasound
|
|
|
Advantages of breast ultrasound over mammography in evaluating the breast include all except which of the following?
A) limited radiation exposure to the patient B) differentiation of cystic versus solid smooth masses C) more comfortable examination for the patient D) better visualization of juxtathoracic deep tissues |
A) limited radiation exposure to the patient
|
|
|
twisting of the spermatic cord, which cuts off the blood supply to the testicle
|
testicular torsion
|
|
|
Inflammation or infection of the long coiled tube attached to the upper part of each testicle
|
epididymitis
|
|
|
Inflammation of the testis
|
Orchitis
|
|
|
A collection of fluid between two layers of tissue surrounding the testicle
|
hydrocele
|
|
|
cystic dilation of a duct in the head of the epididymis or in the rete testis
|
spermatocele
|
|
|
Elongation and enlargement of the veins of the pampiniform plexus
|
varicocele
|
|
|
a rip or tear in the tunica albuginea resulting in extrusion of the testicular contents
|
testicular rupture
|
|
|
Failure of descent of one or both of the testes into the scrotum
|
cryptorchidism
|
|
|
Acute hydroceles may be caused by all of the following EXCEPT:
A) Infarction B) tumor C) testicular torsion D) trauma E) infection of the testis or epididymis |
C) testicular torsion
|
|
|
The most common location for a spermatocele is:
A) head of the epididymis B) body of the epididymis C) tail of the epididymis D) tunica vaginalis E) mediastinum testis |
A) head of the epididymis
|
|
|
A 15-year-old boy presents with sudden intense right scrotal pain, nausea and vomiting. A sonogram is performed, and an enlarged hypoechoic right scrotum with decreased arterial flow is documented. The left scrotum is normal. This is most consistent with...
A) testicular rupture B) varicocele C) spermatocele D) torsion E) hydrocele |
D) torsion
|
|
|
On a longitudinal scan of the scrotum, the most superior portion is the:
A) ductus deferens B) rete testis C) head of the epididymis D) tunical albuginea E) spermatic cord |
C) head of the epididymis
|
|
|
On a sonographic examination, a seminoma of the testicle may appear as:
A) solid, homogeneous mass B) large, multilocular cystic mass C) small, simple cyst D) diffuse enlargement of the testicle E) small, complex mass |
A) solid, homogeneous mass
|
|
|
The left testicular vein drains into the
A) IVC B) left internal iliac vein C) common internal iliac vein D) left renal vein E) prostatic vein |
D) left renal vein
|
|
|
The mediastinum testis appears sonographically as:
A) a homogenous mass like structure within the pampiniform plexis B) a heterogenous mass like structure in the mid testis C) an anechoic linear echo through the mid testis D) an echogenic linear echo through the mid testis |
D) an echogenic linear echo through the mid testis
|
|
|
What ultrasound technique and patient technique could be performed to assist in the diagnosis of a varicocele?
A) patient performs a valsalva maneuver while the sonographer scans the area using Doppler B) patient lies perfectly flat while sonographer squeezes the testicle while imaging with Doppler C) sonographer scans in gray scale and measures the size increase of the vein diameters D) patient performs the rapid, shallow breathing technique while sonographer scans with Doppler |
A) patient performs a valsalva maneuver while the sonographer scans the area using Doppler
|

