![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Forces |
• A push or pull • Whenever two objects interact, they exert forces on each other • These forces are equal in size & opposite in direction |
|
|
|
Resultant Force |
When a number of forces act at a point they add up to a resultant force
|
|
|
|
What if the force is the same? |
The greater the mass of The object, the lower its acceleration ~ Lower mass = Higher acceleration ~ Force = N ~ Mass = Kg |
|
|
|
Velocity |
•Velocity~ The direction an object is travelling as well as its speed |
|
|
|
Speed |
• Distance= speed x time • Speed= distance / time • Time= distance / speed |
|
|
|
Distance Time Graphs |
• time = x axis • distance = y axis • gradient = diff. in distance/ diff. in time {speed} • faster = steep line • straight= constant • slower= less steep • stationary= horizontal |
|
|
|
Acceleration |
= change in speed = the rate at which velocity changes • has a direction • if a car has negative acceleration it is slowing or moving backwards •when the velocity of an object changes, it is accelerating and/or changing direction • if the speed stays the same but the direction changes, the object is accelerating
Acceleration= change in velocity/time taken for change |
|
|
|
Hooke's Law |
= the forces applied to an object is directly proportional to its extension • Forces can also change the shape of an object • Hooke investigated relationship between the force applied to an object and the change in its length {extension} • When the force increases, so does the extension • this relationship is continues until the limit of proportionality. Above this point, the spring starts to deform |
|
|
|
Hooke's Law |
= the forces applied to an object is directly proportional to its extension • Forces can also change the shape of an object • Hooke investigated relationship between the force applied to an object and the change in its length {extension} • When the force increases, so does the extension • this relationship is continues until the limit of proportionality. Above this point, the spring starts to deform |
|
|
|
Work done and Energy Transfer |
• Work done= Energy transferred • No work= no energy • Work done when a force is used to move something through a distance against an opposing force • The distance against an opposing force |
|
|
|
Hooke's Law |
= the forces applied to an object is directly proportional to its extension • Forces can also change the shape of an object • Hooke investigated relationship between the force applied to an object and the change in its length {extension} • When the force increases, so does the extension • this relationship is continues until the limit of proportionality. Above this point, the spring starts to deform |
|
|
|
Work done and Energy Transfer |
• Work done= Energy transferred • No work= no energy • Work done when a force is used to move something through a distance against an opposing force • The distance against an opposing force |
|
|
|
Power |
= work done in a given time or rate • A more powerful object will do more work in a certain time. It will transfer more electrical energy every second • 1 watt = 1 Joule of work done every second • |
|
|
|
Hooke's Law |
= the forces applied to an object is directly proportional to its extension • Forces can also change the shape of an object • Hooke investigated relationship between the force applied to an object and the change in its length {extension} • When the force increases, so does the extension • this relationship is continues until the limit of proportionality. Above this point, the spring starts to deform |
|
|
|
Work done and Energy Transfer |
• Work done= Energy transferred • No work= no energy • Work done when a force is used to move something through a distance against an opposing force • The distance against an opposing force |
|
|
|
Power |
= work done in a given time or rate • A more powerful object will do more work in a certain time. It will transfer more electrical energy every second • 1 watt = 1 Joule of work done every second • |
|
|
|
Gravitational Potential Energy |
• The GPE of an object is the energy it has transferred because of its position in a gravitational field • Energy depends on; ~Mass of object ~Height above ground ~Strength of gravitational field * Law of conservation- energy can't be created or destroyed, only transferred |
|
|
|
Momentum |
• Momentum of a moving object depends on mass and velocity • The total amount of momentum is a system of objects that interact only with each other always stay the same • if two moving objects collide, the total momentum of the two objects does not change • if any external forces act on the objects (i.e. Friction) then momentum is not conserved. Total momentum before= total after • in car crashes, the sudden stop means that a very large change in momentum happens very quickly |
|
|
|
Momentum |
• Momentum of a moving object depends on mass and velocity • The total amount of momentum is a system of objects that interact only with each other always stay the same • if two moving objects collide, the total momentum of the two objects does not change • if any external forces act on the objects (i.e. Friction) then momentum is not conserved. Total momentum before= total after • in car crashes, the sudden stop means that a very large change in momentum happens very quickly |
|
|
|
Current Potential Difference |
• Graphs that pass through 0 have a constant positive gradient show that... ~ The current through the resistor is directly proportional to the potential difference, the current will double ~ Double the potential difference= double the current ~ Change in potential difference= change in same proportion • If it's more difficult for electrons to pass through a component, the component has a higher resistance Resistance goes up, current goes down |
|
|
|
Electrostatics |
• When you rub certain types of insulating materials together, they become charged. •Charge is caused by electrons being transferred from one material to another •If 2 bodies are charged the same they will repel each other • Opposite charges attract each other |
|
|
|
Electrostatics |
• When you rub certain types of insulating materials together, they become charged. •Charge is caused by electrons being transferred from one material to another •If 2 bodies are charged the same they will repel each other • Opposite charges attract each other |
|
|
|
Circuit diagrams |
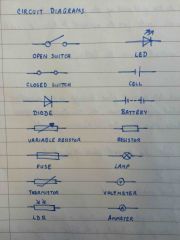
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Electrostatics |
• When you rub certain types of insulating materials together, they become charged. •Charge is caused by electrons being transferred from one material to another •If 2 bodies are charged the same they will repel each other • Opposite charges attract each other |
|
|
|
Circuit diagrams |
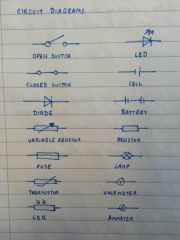
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Series |
•If you add more components, the resistance of the circuit will increase •Its harder for current to flow through a circuit w/ several components because electrons have to flow through each one in town • The current in a series circuit is the same everywhere in the circuit because the electrons have to flow at the same rate through all the components |
•If you add more components, the resistance of the circuit will increase •Its harder for current to flow through a circuit w/ several components because electrons have to flow through each one in town • The current in a series circuit is the same everywhere in the circuit because the electrons have to flow at the same rate through all the components |

