![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. What happens when 2 insulating materials are rubbed together? (1 mark)
|
Materials become electrically charged as the electrons are rubbed off from one material and onto the other.
|
|
|
2. When does a material become negatively charged? (1 mark)
|
Material that gains electrons becomes negatively charged.
|
|
|
3. When does a material become positively charged? (1 mark)
|
Material that loses electrons become positively charged.
|
|
|
4. What happens to materials which have similar charge to each other? (1 mark)
|
Repel
|
|
|
5. What happens to materials which are oppositely charged to each other? (1 mark)
|
Attract
|
|
|
6. In which material the electrical charges (electron) can move easily? (1 mark)
|
Metals
|
|
|
7. What is current? (1 mark)
|
Flow of electric charge (electrons).
|
|
|
8. What is the unit of current? (1 mark)
|
Amperes or Amps (A)
|
|
|
9. What is the unit of charge? (1 mark)
|
Coulombs (C)
|
|
|
10. What is the unit of time? (1 mark)
|
Seconds (s)
|
|
|
11. What is potential difference (voltage)?
(1 mark) |
Energy transferred per coulomb of charge that passes between 2 points.
|
|
|
12. What is the unit of voltage (potential difference)? (1 mark)
|
Volts (V)
|
|
|
13. What is the unit of work done? (1 mark)
|
Joules (J)
|
|
|
14. Identify the circuit symbols? (1 mark each)
|
? |
|
|
15. Give a use of a thermistor? (1 mark)
|
Thermostats, fire alarms, laptop fan as resistance decreases as temperature increases.
|
|
|
16. Give a use of LDRs? (1 mark)
|
Switching lights on when it gets dark as the resistance decreases as light intensity increases (e.g. Street lights).
|
|
|
17. Draw a current- voltage graph for a resistor at constant temperature? (1 mark)
|
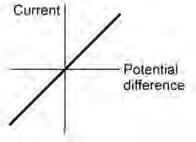
|
|
|
18. How can you measure resistance of a component? (1 mark)
|
Measure the current through, and the potential difference across the component. Then calculate resistance R=V÷I
|
|
|
19. What is the unit of resistance? (1 mark)
|
Ohms (Ω)
|
|
|
20. What can affect the amount of current in circuit? (2 marks)
|
Resistance in the circuit.The bigger the resistance, the smaller the current in circuit.
|
|
|
21. What is the total resistance in series circuit? (1 mark)
|
Total resistance is equal to sum of the resistance in the circuit. R1 + R2 = R total
|
|
|
22. What happens to current in series circuit? (1 mark)
|
Current stays the same everywhere in series circuit.
|
|
|
23. What happens to voltage in series circuit? (1 mark)
|
Voltage gets shared between the components in series circuit.
|
|
|
24. What happens to current in parallel circuit? (1 mark)
|
Current gets shared between the components in parallel circuit
|
|
|
25. What happens to voltage in series circuit? (1 mark)
|
Voltage stays the same everywhere in parallel circuit.
|
|
|
26. Draw a graph for resistance of a filament bulb? (1 mark)
|
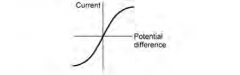
|
|
|
27. Draw a graph for a diode. (1 mark)
|
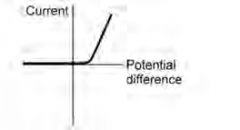
|
|
|
28. What is function of LED? (2 marks)
|
LEDs emits light when a current flows through it in forward direction. They can be used in lightning instead of filament bulbs.
|

