![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
86 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the shape of the earth?
|
Oblate spheroid
|
|
|
How is position measured on the earth?
|
Latitude/Longitude
|
|
|
How is direction measured on the earth
|
As an angular position of one point to another.
|
|
|
What unit is used to measure angular position?
|
Degrees
|
|
|
What unit is used to measure distance?
|
Nautical miles
|
|
|
What unit is used to measure speed?
|
Knots
|
|
|
Define a rhumb line
|
A track which crosses all meridians of longitude at the same angle.
|
|
|
Define a great circle
|
A circle on the surface of the earth, the centre of which lies at the centre on the earth.
|
|
|
Define curve of equal bearing
|
Curve connecting all points where the great circle bearing of a given point is the same.
|
|
|
Define convergence
|
The angle between meridians.
|
|
|
Define convergence angle
|
The angular difference between the rhumb line and the great circle track.
|
|
|
State the significance of lunar activity on aviation operations
|
Useful when navigating visually... Because you can see stuff...
|
|
|
Define the term 'daylight' in aviation operations
|
The start of morning twilight until the end of evening twilight.
|
|
|
When is twilight?
|
Morning twilight: The time when the centre of the sun is 6 degrees below the celestial horizon until the centre of the sun is at the celestial horizon.
Evening twilight: The time when the centre of the sun is at the celestial horizon until the centre of the sun is 6 degrees below the celestial horizon. |
|
|
When does a pilot need to calculate 'Beginning of Daylight' or 'End of Daylight'?
|
Pilots without the correct ratings need to know when they can fly.
|
|
|
What is the international date line?
|
The 180 degree meridian with minor excursions to keep groups of islands together.
(This is the line in the Pacific Ocean where you can travel back a day or skip a day.) |
|
|
What is the Gregorian calendar?
|
The internationally accepted calendar.
|
|
|
What is a leap year?
|
A year where an extra day is added.
|
|
|
What is the relationship between longitude (arc) and time?
|
15 degrees around the Earth = 1 hour
|
|
|
What is Local Mean Time
|
Time based on the mean sun with reference to the observers meridian.
|
|
|
Define UTC
|
The local mean time at the meridian of longitude that runs through the observatory at Greenwich London.
|
|
|
Convert 300825 UTC to LMT at the 120°'W meridian
|
120°W = 8 hr behind (Meridians to the west are behind) so subtract 8 hours from UTC
30 08 25 UTC – 8 30 00 25 LMT at 120°W Answer: 300025 LMT. |
|
|
If it is 231531 LMT on the 150°E
meridian of longitude, what time is it in UTC? |
150°E = 10 hr ahead (Meridians to the east are ahead)
so subtract 10 hours from LMT (opposite). 23 15 31 LMT at 150°E – 10 00 23 05 31 UTC Answer: 230531 UTC. |
|
|
If it is 282340 on the 138°15′W meridian of longitude, express this LMT in coordinated universal time (UTC).
|
138°15′W = 9 hr 13 min behind (Meridians to the west are behind) so add this to LMT.
28 23 40 LMT at 138°15′W + 9 13 28 32 53 and of course 32 hr = 1 day 8 hr 29 08 53 UTC Answer: 290853 UTC. |
|
|
Convert 300825 UTC to LMT at the
138°15′W meridian. |
138°15′W = 9 hr 13 min behind (Meridians to the west are behind) so subtract this from UTC (opposite).
30 08 25 UTC – 9 13 29 23 12 LMT at 138°15′W Answer: 292312 LMT. |
|
|
Convert 131440 UTC to LMT at the 65°E meridian
|
65°E = 4 hr 20 min ahead (Meridians to the east are ahead) so add this to UTC
13 14 40 UTC + 4 20 13 19 00 LMT at 65°E Answer: 131900 LMT. |
|
|
Define Standard Time
|
Local time adapted for a given area.
|
|
|
CST
|
Central Standard Time
|
|
|
CDT
|
Central Daylight-saving Time
|
|
|
EST
|
Eastern Standard Time
|
|
|
EDT
|
Eastern Daylight-saving Time
|
|
|
WST
|
Western Standard Time
|
|
|
WDT
|
Western Daylight-saving Time
|
|

|
Civil Aerodrome on land
|
|

|
Military aerodrome on land
|
|

|
VOR only
|
|

|
Compulsory reporting point
|
|

|
On request reporting point
|
|

|
Control zone boundary
|
|

|
Primary road
|
|
|
Charts should be folded in a concertina pattern, True/False?
|
True. (Fun fact: This is also called an accordion fold.)
|
|
|
List the desirable properties of maps to be used for navigation
|
- Good shapes (Surface features portrayed with their true shape)
- Good angles (Correct angular relationship between all surfaces preserved) - Good distances (Distance correctly represents distances on earth) - Rhumb lines and great circles represented as straight lines |
|
|
Define WAC
|
- World Aeronautical Chart
- 1:1,000,000 - Primary reference for pre-flight planning and visual en-route navigation outside main terminal area - Lambert conformal conic projection |
|
|
Define VNC
|
- Visual Navigation Chart
- 1:500,000 - Provide pilots operating under VFR and navigating by visual reference with controlled airspace overlay on a topographical base - Lambert conformal conic projection |
|
|
Define VTC
|
- Visual Terminal Chart
- 1:250,000 - Based on a cylindrical projection, present complete topographic, cultural and aeronautical information within and around major terminal areas in Australia. - Transverse Mercator projection (cylindrical) |
|
|
Define ERC
|
- En Route Chart
- Scale depends on area - Present en route aeronautical information of concern to visual pilots (e.g. restricted areas, aerodrome radio nav aids). - Lambert conformal conic projection |
|
|
Define PCA
|
- Planning Chart Australia
- Contains: ■ ARFOR boundaries; ■ WAC coverage and chart titles; ■ location names and abbreviations; ■ estimated FIS VHF coverage at 5,000 ft; ■ estimated FIS VHF coverage at 10,000 ft; ■ HF network boundaries; ■ AERIS outlets; and ■ FLIGHTWATCH frequencies and agencies. |
|
|
What kind of projection do Lambert charts and Mercator charts use respectively?
|
Lambert: Conformal Conic
Mercator: Conformal Cylindric |
|
|
Give an example of a Lambert and Mercator chart.
|
Lambert: WAC, VNC, ERC
Mercator: VTC |
|
|
What is the shape of a great circle track on a Lambert, Polar Stereographic and Mercator chart?
|
Lambert: Straight
Polar Stereographic: Straight Mercator: Curved |
|
|
What is the shape of a rhumb line on a Lambert and Mercator chart?
|
Lambert: Curved
Mercator: Straight |
|
|
What type of projection is a Polar Stereographic chart and where is it used?
|
An azimuthal projection used for navigation purposes around polar regions.
|
|
|
How do you know if a WAC is current?
|
It contains the date of publication and an indication of when a newer edition is due.
|
|
|
How are WAC's numbered?
|
ID number at the top of the chart alongside the unique name given to it.
|
|
|
DAP
|
Departure and Approach Procedures
|
|
|
What charts are used to enable navigation along air routes by reference to radio navigation aids?
|
ERCs and TACs
|
|
|
Define TAS
|
Actual speed through the air
|
|
|
Define magnetic dip
|
The angle of the Earth's magnetic field to the surface
|
|
|
On what aircraft headings are compass acceleration errors maximum?
|
Easterly/Westerly
|
|
|
On what aircraft headings are compass turning errors maximum?
|
Northerly/Southerly
|
|
|
What is magnetic variation?
|
The angular difference between the magnetic north pole and the true north pole.
|
|
|
What is magnetic deviation?
|
The angular difference between the compass heading and the magnetic heading.
|
|
|
Given:
Variation = 10°E Track = 100°T What is the magnetic track? |
90°
|
|
|
Given:
Variation = 20°E Track = 90°T What is the magnetic track? |
70°
|
|
|
Given:
Variation = 20°E Magnetic track = 80° What is the track? |
100°T
|
|
|
Given:
Variation = 20°W Track = 140°T What is the magnetic track? |
160°
|
|
|
Given:
Variation = 50°W Track = 220°T What is the magnetic track? |
270°
|
|
|
What is airspeed compressibility error?
|
At high speed air becomes compressed, increasing its density and giving a higher IAS
|
|
|
What is wind drift?
|
The angle between the heading and the track as a result of wind
|
|
|
What is a DR position?
|
A position for an aircraft that has been calculated working from a known position and accounting for direction and speed over time. (Dead Reckoning)
|
|
|
Define the 1 in 60 rule
|
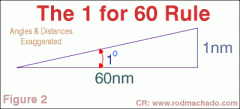
1nm subtends 1° at a distance of 60nm
|
|
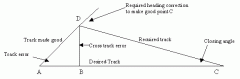
At position D a pilot determined that they were 2nm left of track.
Use the 1 in 60 rule to determine: 1. The alteration of heading at 'D' to parallel track and 2. The alteration of heading at 'D' to track direct to 'C' AB = 20nm BC = 40nm |
1.
- 2nm cross track error over 20nm. - 60/20 * 2 = 6nm cross track error over 60nm - DAB = 6° - 6° clockwise alteration to parallel track 2. - 2nm cross track error over 40nm - 60/40 * 2 = 3nm cross track error over 60nm - DCB = 3° - 9° clockwise alteration to track direct to C (6+3) |
|
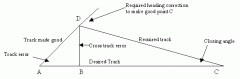
At position D a pilot determined that they were 2nm left of track.
Use the 1 in 60 rule to determine: 1. The alteration of heading at 'D' to parallel track and 2. The alteration of heading at 'D' to track direct to 'C' AB = 30nm BC = 80nm |
1.
- 2nm cross track error over 30nm. - 60/30 * 2 = 4nm cross track error over 60nm - DAB = 4° - 4° clockwise alteration to parallel track 2. - 2nm cross track error over 80nm - 60/80 * 2 = 1.5nm cross track error over 60nm - DCB = 1.5° - 5.5° clockwise alteration to track direct to C (4+1.5) |
|
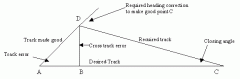
At position D a pilot determined that they were 4nm left of track.
Use the 1 in 60 rule to determine: 1. The alteration of heading at 'D' to parallel track and 2. The alteration of heading at 'D' to track direct to 'C' AB = 15nm BC = 20nm |
1.
- 4nm cross track error over 10nm. - 60/15 * 4 = 16nm cross track error over 60nm - DAB = 16° - 16° clockwise alteration to parallel track 2. - 4nm cross track error over 20nm - 60/20 * 4 = 12nm cross track error over 60nm - DCB = 12° - 28° clockwise alteration to track direct to C (16+12) |
|
|
Heading/TAS + Wind vector =
|
Track/Groundspeed
|
|
|
A pilot maintains a flight planned heading (HDG) and the track made good (TMG) is 5° to the left of track. Once the pilot re-intercepts his flight planned track (TR) how should the pilot adjust the aircraft's HDG to maintain this TR?
|
Adjust 5° right because of Wind Correction Angle
|
|
|
A pilot departs 'a' at 1645 for a 180nm flight to 'd', ETA 'd' 1745. The aircraft is overhead 'b' (on track 60nm from 'a' at 1703). If the planned GS was 180 kts, what is the revised ETA 'd'
|
- Trip should have taken 60 minutes (1645-1745)
- 1/3 of the trip has been completed (60nm/180nm) - 20 minutes should have elapsed (1/3 * 60 mins) - Only 18 minutes have elapsed (1645-1703) - The aircraft is 2 minutes early 1/3 in, so it will be 6 minutes early by the end - Revised ETA = 1739 |
|
|
A pilot departs 'a' at 1225 for a 120nm flight to 'd', ETA 'd' 1345. The aircraft is overhead 'b' (on track 30nm from 'a' at 1249). What is the revised ETA 'd'
|
- Trip should have taken 80 minutes (1225-1345)
- 1/4 of the trip has been completed (30nm/120nm) - 20 minutes should have elapsed (1/4 * 80 mins) - 24 minutes have elapsed (1225-1249) - The aircraft is 4 minutes late 1/4 in, so it will be 16 minutes late by the end - Revised ETA = 1401 |
|
|
A pilot departs 'a' at 0700 for a 200nm flight to 'd', ETA 'd' 0740. The aircraft is overhead 'b' (on track 80nm from 'a' at 0712). What is the revised ETA 'd'
|
- Trip should have taken 40 minutes (0700-0740)
- 2/5 of the trip has been completed (80nm/200nm) - 16 minutes should have elapsed (2/5 * 40 mins) - 12 minutes have elapsed (0700-0712) - The aircraft is 4 minutes early 2/5 in, so it will be 8 minutes early 4/5 in and 10 minutes early by the end - Revised ETA = 0730 |
|
|
Define transit bearing
|
A form of position line which has been established by the visual observation of two features on the ground when they have been brought into alignment.
|
|
|
Define compass bearing
|
The angle between north and the line passing through the compass and the point of interest.
|
|
|
Define radio bearning
|
A bearing from a radio navigation aid (e.g. NDB, VOR)
|
|
|
Define GS
|
- Groundspeed
- The speed of an aircraft in flight relative to the ground over which it is travelling |
|
|
Define TAS
|
- True Airspeed
- The actual speed of an aircraft relative to the air through which it is flying |
|
|
Define velocity
|
A vector which represents the combination of direction and speed
|
|
|
Define Line of Constant Bearing
|
Any line drawn on the Earth's surface which crosses all meridians at the same angle, also called a rhumb line
|

