![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the three sutures of the cranium |
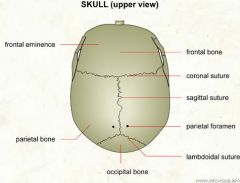
1. Coronal 2. Lambdoid 3. Sagittal |
|
|
What is the opening to the nasal cavity in a bony skull and why is this different to a prosection? |
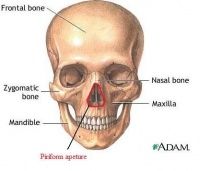
The piriform opening looks like a single opening but in a prosection this is two openings divided by the cartilaginous septum. |
|
|
What does the floor of the nasal cavities form? |
The hard palate |
|
|
Where is the zygomaticotemporal foramen located? |
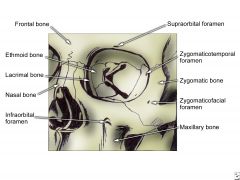
In the inner surface of the orbit, lower lateral corners |
|
|
What does the infra temporal fossa open into? |
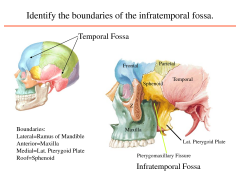
It opens into the pteryogopalatine fossa beneath the orbit |
|
|
What is found in the pterygopalatine fossa? |
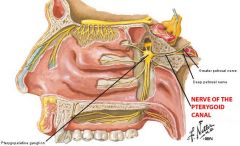
Parasympathetic ganglion is found here. |
|
|
Name the three layers of the meninges |
1. Pia mater 2. Arachnoid mater 3. Dura mater
|
|
|
Characteristics of the dura mater, and what are the two layers present? Are these two layers always fused? |
1. External, dense and inelastic. 2. Two layers are periosteal which strongly adheres to bone, and the meningeal layer.
The two layers are always fused except when forming dural sinuses. |
|
|
What is a dural sinus and what does it do? |
Venous channels between the layer of the dura mater, drain blood from the brain and cranial bone. Where the meningeal layer forms extensions and folds |
|
|
What tissue forms dural sinuses, are valves present?
|
Endothelium lines dural sinuses, there are no valves present. |
|
|
Where do the dural sinuses drain? |
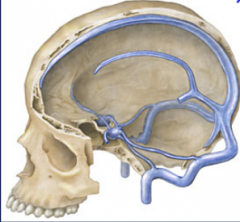
Into the internal jugular.
|
|
|
What is the falx cerebri |
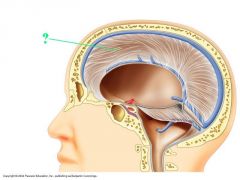
A longitudinal fold in the meningeal layer that divides the two hemispheres |
|
|
What is the tentorium cerebelli? |
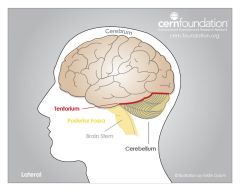
A fold in the meningeal layer between the cerebellum and the occipital lobes of the cerebral hemispheres |
|
|
What is the falx cerebelli? |
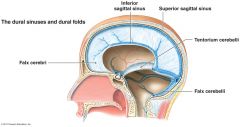
Meningeal folds into the posterior cerebellar notch to partially separate the cerebellar hemispheres. Attaches to the inferior surface of the tentorium cerebelli.
|
|
|
Features of the arachnoid mater |
Thin, covers the brain but does not penetrate the sulci, except for the longitudinal fissure |
|
|
What does the arachnoid mater consist of? |
Arachnoid and arachnoid trabeculae (delicate connective tissue strands that connect the pia and arachnoid mater). |
|
|
What flows beneath the arachnoid mater? |
Cerebrospinal fluid
|
|
|
What is the sella diaphragm made of what does it contain? |
It is a flat piece of dura mater that covers the sella turcica and the pituitary gland with a space for the infundibulum of the hypothalamus. |
|
|
Where is the pia mater found and what does it attach to? |
Innermost thin membrane found on the surface of the brain and attaches to the sulci |

