![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does it tell you if there are casts in the urine? |
Hematuria / pyuria is of renal origin (vs bladder if there are no casts)
|
|
|
What are the types of casts that can be present in the urine? |
- RBC casts
- WBC casts - Fatty casts ("oval fat bodies") - Granular ("muddy brown") casts - Waxy casts - Hyaline casts |
|
|
What can RBC casts in the urine indicate?
|
- Glomerulonephritis
- Ischemia - Malignant hypertension |
|
|
What can WBC casts in the urine indicate?
|
- Tubulointerstitial inflammation
- Acute pyelonephritis - Transplant rejection |
|
|
What can fatty casts ("oval fat bodies") in the urine indicate? |
Nephrotic syndrome
|
|
|
What can granular ("muddy brown") casts in the urine indicate? |
Acute Tubular Necrosis
|
|
|
What can waxy casts in the urine indicate?
|
Advanced renal disease / chronic renal failure
|
|
|
What can hyaline casts in the urine indicate?
|
Non-specific, can be a normal finding, often seen in concentrated urine samples
|
|
|
What can hematuria without casts in the urine indicate?
|
- Bladder cancer
- Kidney stones |
|
|
What can pyuria (pus) with no casts in the urine indicate? |
Acute Cystitis
|
|
|
What terms can be used to describe glomerular disorders?
|
- Focal vs Diffuse
- Proliferative - Membranous - 1° Glomerular disease - 2° Glomerular disease |
|
|
What does the term "focal" mean when naming a glomerular disorder? Example?
|
<50% of glomeruli are involved
- Eg: focal segmental glomerulosclerosis |
|
|
What does the term "diffuse" mean when naming a glomerular disorder? Example?
|
>50% of glomeruli are involved
- Eg: diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis |
|
|
What does the term "proliferative" mean when naming a glomerular disorder? Example?
|
Hypercellular glomeruli
- Eg: Mesangial Proliferative |
|
|
What does the term "membranous" mean when naming a glomerular disorder? Example?
|
Thickening of the glomerular basement membrane
- Eg: Membranous Nephropathy |
|
|
What does the term "1° Glomerular Disease" tell you about the glomerular disorder? Example?
|
Involves only glomeruli, thus a 1° disease of the kidney
- Eg: minimal change disease |
|
|
What does the term "2° Glomerular Disease" tell you about the glomerular disorder? Example?
|
Involves glomeruli and other organs, thus a disease of another organ system, or a systemic disease that has impact on the kidney
- Eg: SLE and diabetic nephropathy |
|
|
What are the types of glomerular diseases?
|
- Nephritic Syndrome
- Nephrotic Syndrome - Both |
|
|
What are the types of Nephritic Syndromes?
|
- Acute Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis
- Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis - Berger Disease (IgA Glomerulonephropathy) - Alport Syndrome *Note that the classic nephritic disorders can exhibit some nephrotic features |
|
|
What are the types of Nephrotic Syndromes?
|
- Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
- Membranous Nephropathy - Minimal Change Disease - Amyloidosis - Diabetic Glomerulonephropathy |
|
|
What are the types of glomerular diseases that are characterized as both Nephritic and Nephrotic Syndromes?
|
- Diffuse Proliferative Glomerulonephritis |
|
|
What makes a renal disease a "Nephrotic syndrome"?
|
- Massive Pr"O"teinuria (>3.5 g/day, frothy urine)
- Hyperlipidemia - Fatty casts - Edema |
|
|
What are Nephrotic Syndromes associated with? Why?
|
- Thromboembolism (hypercoagulable state d/t AT III loss in urine)
- Increased risk of infection (due to loss of immunoglobulins) |
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with the following LM findings: segmental sclerosis and hyalinosis?
|
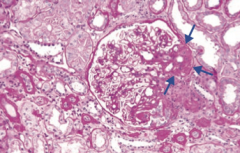
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
|
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with the following LM findings: diffuse capillary and GBM thickening?
|
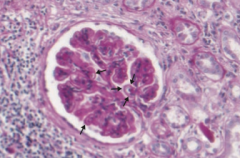
Membranous Nephropathy
|
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with the following LM findings: normal glomeruli (lipid may be seen in PCT cells)?
|
Minimal Change Disease (Lipoid Nephrosis)
|
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with the following LM findings: congo red stain shows apple-green birefringence under polarized light?
|
Amyloidosis
|
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with the following LM findings: mesangial expansion, GBM thickening, and eosinophilic nodular glomerulosclerosis (Kimmelstiel-Wilson lesion)?
|
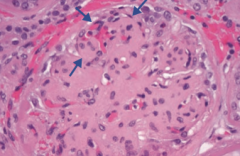
Diabetic Glomerulonephropathy
|
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with the following LM findings: thickened "tram tracks"?
|
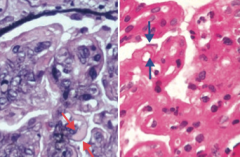
Membrano-Proliferative Glomerulonephritis (Type 1)
- Left: PAS stain - Right: H&E stain |
|
|
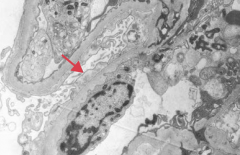
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with the following EM findings: effacement of foot processes?
|
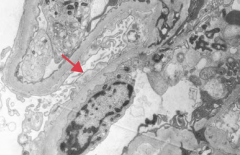
- Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
- Minimal Change Disease (Lipoid Nephrosis) = picture |
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with the following EM findings: "spike-and-dome" appearance with subepithelial deposits?
|
Membranous Nephropathy
|
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with the following immunofluorescence findings: granular as a result of immune complex deposition?
|
Membranous Nephropathy
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in African Americans and Hispanics?
|
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in Caucasian adults?
|
Membranous Nephropathy
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of nephrotic syndrome in children?
|
Minimal Change Disease (Lipoid Nephrosis)
|
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with HIV infection?
|
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
|
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with sickle cell disease?
|
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
|
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with heroin abuse?
|
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
|
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with massive obesity?
|
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
|
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with interferon treatment?
|
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
|
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with chronic kidney disease due to congenital absence or surgical removal?
|
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis
|
|
|
How do you treat Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis? Efficacy? Prognosis?
|
- Inconsistent response to steroid therapy
- May progress to chronic renal disease |
|
|
What type of disease is Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis? What changes occur in this disease?
|
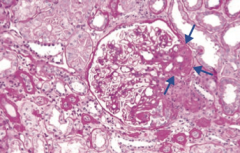
Nephrotic Syndrome:
- Segmental sclerosis and hyalinosis - Effacement of foot processes similar to in minimal change disease |
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with antibody to phospholipase A2 receptor?
|
Membranous Nephropathy
|
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with drugs like NSAIDs and penicillamine? |
Membranous Nephropathy
|
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with infections like HBV and HCV?
|
Membranous Nephropathy
|
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus?
|
Membranous Nephropathy
|
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with solid tumors? |
Membranous Nephropathy
|
|
|
How do you treat Membranous Nephropathy? Efficacy? Prognosis?
|
- Poor response to steroid therapy
- May progress to chronic renal disease |
|
|
What type of disease is Membranous Nephropathy? What changes occur in this disease?
|
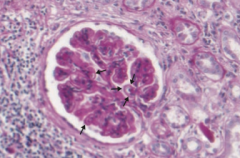
Nephrotic Syndrome
- Diffuse capillary and GBM thickening - Granular immunofluorescence as a result of immune complex deposition - "Spike and dome" appearance on EM with subepithelial deposits |
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome may be triggered by a recent infection, immunization, or other immune stimulus?
|
Minimal Change Disease (Lipoid Nephrosis)
|
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with Hodgkin Lymphoma (eg, cytokine-mediated damage)?
|
Minimal Change Disease (Lipoid Nephrosis)
|
|
|
How do you treat Minimal Change Disease (Lipoid Nephrosis)? Efficacy? Prognosis?
|
Excellent response to corticosteroids
|
|
|
What type of disease is Minimal Change Disease (Lipoid Nephrosis)? What changes occur in this disease? |
Nephrotic Syndrome:
- Normal glomeruli (lipid may be seen in PCT cells) - Effacement of foot processes |
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with chronic conditions like multiple myeloma, TB, or Rheumatoid arthritis?
|
Amyloidosis
|
|
|
Amyloidosis most commonly affects what organ?
|
Kidney is the most common organ involved in systemic amyloidosis
|
|
|
What type of disease is Amyloidosis that affects the kidney? How do you make diagnosis?
|
Nephrotic Syndrome
- Congo red stain shows apple-green birefringence under polarized light |
|
|
What are the types of membrano-proliferative glomerulonephritis?
|
- Type I: subendothelial immune complex (IC) deposits with granular immunofluorescence - "tram-track" appearance
- Type II: intramembranous IC deposits - "dense deposits" |
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with HBV and HCV? What type of deposits? Appearance?
|
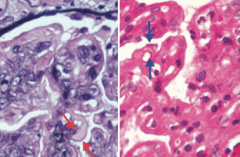
Type I Membrano-Proliferative Glomerulonephritis
- Subendothelial immune complex (IC) deposits - Granular IF - "Tram-track" appearance due to GBM splitting caused by mesangial ingrowth |
|
|
Which type of nephrotic syndrome is associated with C3 nephritic factor? Function? What type of deposits are seen in this type of nephrotic syndrome?
|
Type II Membrano-Proliferative Glomerulonephritis
- C3 nephritic factor stabilizes C3 convertase → ↓ serum C3 levels - Intramembranous immune complex (IC) deposits - "Dense deposits" |
|
|
What type of renal disease is Membrano-Proliferative Glomerulonephritis?
|
Nephritic syndrome that can also present with nephrotic syndrome
|
|
|
What causes the renal damage in Diabetic Glomerulonephropathy?
|
- Non-enzmatic glycosylation of GBM → ↑ permeability, thickening
- Non-enzymatic glycosylation of efferent arterioles → ↑ GFR → mesangial expansion |
|
|
What type of disease is Diabetic Nephropathy? What changes occur in this disease? |
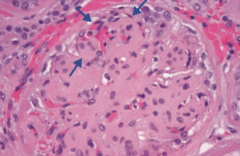
Nephrotic Syndrome
- Mesangial expansion - GBM thickening - Eosinophilic nodular glomerulosclerosis (Kimmelstiel-Wilson lesion) |
|
|
What makes a renal disease a "Nephritic syndrome"?
|
"I"nflammatory process
- When it involves glomeruli, it leads to hematuria and RBC casts in the urine - Associated with azotemia (abnormally high levels of nitrogen-containing compounds in blood), oliguria, hypertension (d/t salt retention), and proteinuria (<3.5 g/day) |
|
|
How do Nephrotic Syndromes and Nephritic Syndromes compare in terms of the proteinuria?
|
- Nephrotic Syndrome: >3.5 g/day
- Nephritic Syndrome: <3.5 g/day |
|
|
How do Nephrotic Syndromes and Nephritic Syndromes compare in terms of the urine casts?
|
- Nephrotic Syndrome: fatty casts
- Nephritic Syndrome: RBC casts |
|
|
Which type of nephritic syndrome is associated with the following LM findings: glomeruli enlarged and hypercellular?
|
Acute Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis
|
|
|
Which type of nephritic syndrome is associated with the following LM findings: crescent-moon-shape consisting of fibrin and plasma proteins (eg, C3b) with glomerular parietal cells, monocytes, and macrophages?
|
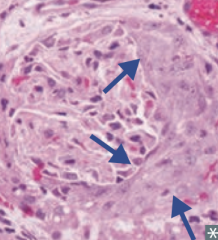
Rapidly Progressive (Crescentic) Glomerulonephritis (RPGN)
|
|
|
Which type of nephritic syndrome is associated with the following LM findings: wire looping of capillaries?
|
Diffuse Proliferative Glomerulonephritis (DPGN)
|
|
|
Which type of nephritic syndrome is associated with the following LM findings: mesangial proliferation?
|
IgA Nephropathy (Berger Disease)
|
|
|
Which type of nephritic syndrome is associated with the following EM findings: subepithelial immune complex (IC) humps?
|
Acute Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis
|
|
|
Which type of nephritic syndrome is associated with the following EM findings: subendothelial and sometimes intramembranous IgG based immune complexes often with C3 deposition?
|
Diffuse Proliferative Glomerulonephritis (DPGN)
|
|
|
Which type of nephritic syndrome is associated with the following EM findings: mesangial immune complex deposits?
|
IgA Nephropathy (Berger Disease)
|
|
|
Which type of nephritic syndrome is associated with the following immunofluorescence findings: "starry sky" granular appearance ("lumpy-bumpy) due to IgG, IgM, and C3 deposition along GBM and mesangium?
|
Acute Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis
|
|
|
Which type of nephritic syndrome is associated with the following immunofluorescence findings: crescent-moon-shape consisting of fibrin and plasma proteins (eg, C3b) with glomerular parietal cells, monocytes, and macrophages?
|
Rapidly Progressive (Crescentic) Glomerulonephritis (RPGN)
|
|
|
Which type of nephritic syndrome is associated with the following immunofluorescence findings: granular?
|
Diffuse Proliferative Glomerulonephritis (DPGN)
|
|
|
Which type of nephritic syndrome is associated with the following immunofluorescence findings: IgA based immune complex deposits in mesangium?
|
IgA Nephropathy (Berger Disease)
|
|
|
What type of renal pathology is Acute Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis? Who is more likely to have this kind of damage? Cause?
|
Nephritic Syndrome
- Most frequently in children - Occurs ~2 weeks after group A streptococcal infection of pharynx or skin; type III hypersensitivity reaction - Resolves spontaneously |
|
|
What type of reaction mediates Acute Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis?
|
Type III Hypersensitivity reaction (antigen-antibody complexes) to group A streptococcal infection of pharynx or skin
|
|
|
What renal pathology presents with peripheral and periorbital edema, dark urine (cola-colored), and hypertension? What lab values would you check?
|
Acute Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis:
- ↑ Anti-DNase B titers - ↓ Complement levels |
|
|
What type of renal pathology is Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis (RPGN)? What disease processes may result in this pattern?
|
Nephritic Syndrome: |
|
|
What type of renal pathology is caused by Goodpasture Syndrome? What findings are associated with this syndrome?
|
Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis (RPGN)
- Type II hypersensitivity (antibodies produced by the immune response bind to antigens on the patient's own cells) - Abs to GBM and alveolar basement membrane → linear immunofluorescence - Presents with hematuria and hemoptysis |
|
|
What type of renal pathology is caused by Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener)? What findings are associated with this syndrome?
|
Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis (RPGN)
- PR3-ANCA / c-ANCA |
|
|
What type of renal pathology is caused by Microscopic Polyangiitis? What findings are associated with this syndrome?
|
Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis (RPGN)
- MPO-ANCA / p-ANCA |
|
|
What is the prognosis for Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis (RPGN)?
|
- Poor prognosis |
|
|
What is the most common cause of death in patient with SLE? What type of pathology is this?
|
Diffuse Proliferative Glomerulonephritis (DPGN)
- Can present as nephrotic syndrome and nephritic syndrome concurrently |
|
|
Which type of renal pathology often presents or flares with a URI or acute gastroenteritis? Signs?
|
IgA Nephropathy (Berger Disease) = Nephritic Syndrome
- Episodic hematuria with RBC casts |
|
|
Which type of renal pathology is caused by a mutation in type IV collagen? Implications?
|
Alport Syndrome = Nephritic Syndrome |
|
|
What is the cause of Alport Syndrome?
|
- Mutation in type IV collagen → thinning and splitting of glomerular BM
- Most commonly X-linked |
|
|
Which type of renal pathology presents with glomerulonephritis, deafness, and less commonly eye problems?
|
Alport Syndrome |
|
|
What type of disease is Acute Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis? What changes occur in this disease?
|
Nephritic Syndrome |
|
|
What type of disease is Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis? What changes occur in this disease?
|
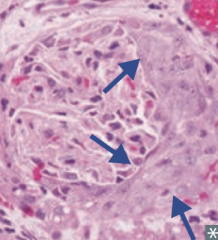
Nephritic Syndrome
- Crescent-moon shape consists of fibrin and plasma proteins (eg, C3b) with glomerular parietal cells, monocytes, and macrophages |
|
|
What type of disease is Diffuse Proliferative Glomerulonephritis (DPGN)? What changes occur in this disease?
|
Nephritic Syndrome
- "Wire looping" of capillaries - Subendothelial and sometimes intramembranous IgG-based immune complexes, often with C3 deposition - Granular appearance on immunofluorescence |
|
|
What type of disease is IgA Nephropathy? What changes occur in this disease?
|
Nephritic Syndrome
- Mesangial proliferation - Mesangial immune complex deposits - IgA based immune complex deposits in mesangium - Seen with Henoch-Schönlein purpura |
|
|
What type of disease is Alport syndrome? What changes occur in this disease?
|
Nephritic Syndrome
- Glomerulonephritis - thinning and splitting of glomerular BM - Deafness - Eye problems (less commonly) |

