![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define metabolism and describe the differences between anabolism and catabolism |
metabolism is th chemical rxns that occur within an organism.
catabolism is the chemical rxns that breakdown compounds and release energy aka exergonic rxns
anabolism are chemical rxns that synthesize combounds by putting energy into the system aka endogonic |
|
|
Describe enzymatic action |
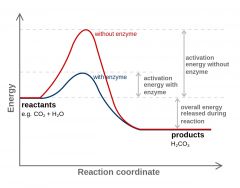
lowers the activaton energy for a specific chemical rxn. It does not get used up and it does not get changed. Enzymes are organic catalysts |
|
|
Discuss ATP |
ATP is the energy currency of te cell. It is regenerated from ADP + phosphate
It is made through cellular respiration which most is made through oxidative phosphorylation |
|
|
Compare and contrast aerobic and anaerobic respiration with emphasis on the substrates, products, terminal electron acceptors, and quantity of ATP produced. This will include discussing glycolysis, Kreb's cycle and electron transport system |
Glycolysis -anaerobic -Substrate- organic molecule (glucose) -Terminal electron acceptors- NADH -ATP -2
Transition- aerobic -Substrate- Pyruvate -products- AcetylCoA and CO2 -Terminal electron acceptors- NADH -ATP- 0
Kreb cycle -substrate- acetylCoA -products- -electron carriers- NADH and FADH -ATP
Electron Transport substrate- oxygen + electrons products- H2O ATP- 32-36
|
|
|
Describe fermentation |
It is partial oxidation of your chemical source
There are two types: 1) Alcohol fermentation 2) Lactic Acid fermentation
Alcohol fermentation- uses this process when your TEA is not readily available or when you dont have an ECT. It makes two by products: alcohol and CO2
Lactic Acid Fermentation- uses substrate level phosphorylation. IT does not go to the ECT. Glucose is partially oxidize into pyruvate and then into lactic acid . The by products of lactic acid: ATP and lactic acid. Lactic acid lowers your blood pH. |
|
|
Define gene, chromosome, genetic code, genotype, and phenotype |
gene- A site on a chromosome that provides information for a certain cell function. A specific segment of DNA tht contains the necessary code to make a protein or RNA molecule
chromosome- The tightly coiled bodies in cells that are the primary sites of genes
genetic code- the set of rules by which information encoded within genetic material (DNA or mRNA) is translated into proteins
genotype- the genetic makeup of an organism
phenotype- The observable characteristics of an organism produced by the interaction between its genetic potential (genotype) and the environment |
|
|
Characterize the structure of the bacterial chromosome and describe replication |
composed of DNA Haploid- single chromosomes and single set of genes
replication 1) Unwad and Unzip the DNA by breaking hydrogen bonds 2) Bring in backbone (deoxyribose and phosphate along with appropriate bases) 3) Rezip- rebond hydrogen bond and rewad Left with two complete copies of DNA Master enzyme: DNA polymerase |
|
|
describe protein synthesis |
You go through a process called transcription where you synthenize a mRNA from a specific segment of DNA (gene) so that instructions for a specific protein can leave the nucleoid and be translated. This requires a master enzyme RNA Polymerase. Once transcripted it leaves the nucleoid and goes to the cytoplasm to find a ribosome. The mRNA is then decoded and appropriate amino acids are placed in order to construct a primary sequence. A series of codons makes amino acids. Amino acids are chained with peptide bonds. Depending on how many amino acids it takes to build a specific protein, a protein is made. |
|
|
Describe the genetic code |
the genetic code encompasses the means of giving "start" and "stop" messages to amino acid synthesis
the genetic code may be expressed as RNA codons or DNA codons. DNA codons make up genes. RNA codons carry messages necessary to carry out teh synthesis of proteins in mRNA |
|
|
Describe regulation of gene expression according to the operon model |
It consists of a promoter which tells the RNA Polymerase that the gene starts here. Which strand it is. And which direction it goes.
The Terminator tells teh RNA Polymerase its the end. |
|
|
Classify mutations by type |
Spontaneous Mutation- It just happens. Its caused by mistakes. This is natural 2types: Point mutation-changes a single base within a gene. It changes the amino acid that is place and the results Nonsense-changes a base in DNA and turns th triplet into a terminator strand. This stops codons and mRNA. This would end transcription
Frameshift mutation- Addition: you add a base and it shifts the triplet codes deletion: you delete a base and it shifts the triplet
Induced mutation- Genetically modified. Its how we genetically alter it benefit us. |
|
|
Compare mechanisms of genetic transfer among bacteria |
Vertical transfer- from one bacterium to all daughter cells (binary fission)
Horizontal Transfer- from one bacterium to another bacterium. You exchange it, and it doesnt' have to be a shared exchange. There are three ways to get Horizontal Transfer 1) congjugation- generally have to transfer by a plasmid so it must have a pillus.(may not be mutual) 2)Transduction- must have bacteria phage (virus that infects bacteria). During maturation have packing of bacterial DNA into phage capsid (protein coat) 3)Transformation- picking up naked DNA from the environment and engulfing it to use it. |
|
|
Discuss genetic engineering |
it is the deliberate modification of an organism's genome. |

