![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Xerophytic
|
Plants with many coping mechanisms to deal with aridity.
|
|
|
Trichomes
|
Hairs on the shoot with a variety of functions.
|
|
|
1) Pith
2) Primary Xylem 3) Vascular Cambium 4) Primary Phloem 5) Cortex 6) Epidermis |
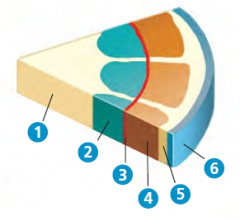
Name the structures
|
|
|
1) Secondary xylem
2) Vascular cambium 3) Secondary phloem 4) Cork cambium 5) Cork 6) Bark 7) Layers of periderm |
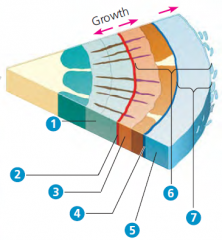
|
|
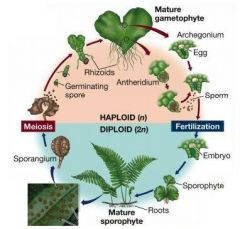
|
Identify the difference between sporophyte and gametophyte life cycle phases.
|
|
|
Gametophyte
|
What phase can gametangia be found in?
|
|
|
Only secondary xylem.
|
What is wood?
|
|
|
Everything peripherial of vascular cambium.
|
What is bark?
|
|
|
Diameter of cells. The diameter of the cells are larger in spring and summer because it is a period of more growth, thus the cells would need to transport more water... in winter it is in a period of slower growth, the the cells are smaller. The tropic don't have as drastic of seasons.
|
Why is it so easy to distinguish layers of secondary xylem and why would they be less apparent in the tropics?
|
|
|
Aridity
Heat Light Soil Water High CO2 |
What helps transpiration?
|
|
|
Humidity
Soil Water Low |
What inhibits transpiration?
|
|
|
They need to present as many chloroplast as possible to the outer surface of the leaf for maximum light absorption.
|
Why is palisade layer arranged the way it is?
|
|
|
Production of photosynthates
Interchange of gases Food Storage Water evaporation |
Functions of leaves.
|

