![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Adrenaline dose for NEWBORN |
20mcg/kg 0.2ml/kg |
|
|
|
Adrenaline dose for children (not newborn) |
0.1ml/kg 10mcg/kg |
|
|
|
What determines tachycardia treatment? |
QRS size |
|
|
|
Amiodarone dose for refractory VF/pVT |
5mg/kg after third shock Can be given again after fifth |
|
|
|
What type of ETT can be used for intubation? |
Age/4+4 Uncuffed. Cuffed also can be used (except neonates) |
|
|
|
CHILD Asystole immediate management? |
Ventilations, CPR, access, adrenaline 10mcg/kg, 2 min CPR, reassess, if Asystole still, adrenaline 3-5 mins |
|
|
|
PEA Causes? |
All of the Hs and Ts |
|
|
|
How will SVT present? |
P waves not present. Regular rhythm with narrow QRS. >220 INFANT >189 CHILD |
|
|
|
Bronchiolitis tends to affect most severely |
Children with congenital heart disease and preterm infants. |
|
|
|
Where is the xiphisternum? |
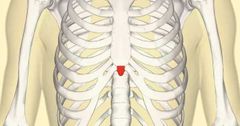
|
|
|
|
What is immediate treatment for 8 month old FBAO, conscious but coughing ineffectively. |
5 back blows, 5 chest thrusts, reassess consciousness level |
|
|
|
Treatment for circulatory decompensated child in SVT |
Synchronized cardioversion in time with R waves. |
|
|
|
What should adrenaline not be mixed with? |
Sodium Bicarbonate. Not a resus drug. |
|
|
|
What accounts for 70% of pediatric deaths in trauma within 48h post injury |
Brain injuries |
|
|
|
What are rarely required in NEWBORN resuscitation |
Chest compressions. Normally a ventilatory cause which solves issue. |
|
|
|
Irregular respirations and bradycardia in an infant should have what anticipated? |
Eventual CPR |
|
|
|
Newborn is born blue and floppy with <60 and gasping resps. Initial management is? |
Airway opening and positive pressure ventilation |
|
|
|
What factors determine post birth management? |
Colour Tone Breathing HR |
Close the bloody hatch! |
|
|
Pediatric resp rates |
<1 year: 30-40min 1-2: 26-34min 2-5: 24-30min 5-12: 20-24min >12: 12-20min |
From the start 40 + 4 / - 6 |
|
|
Child HR ranges |
Newborn - 3 month: 85-205 3 month - 2 years: 100-180 2 - 10 years: 60-140 >10 years 60-100 |
From the start 125 80 80 40 |
|
|
BP Ranges |
1 month systolic: 75 1 year systolic: 95 5 year systolic: 100 10 year systolic: 110 15 year systolic: 120 |
|
|
|
Weight estimate formula off of age |
(age+4) × 2 = kg |
|
|
|
Fluid output targets |
Infant >2ml/kg/hr 1 year+ >1ml/kg/hr |
|
|
|
Red flag HR: Infant |
<100 |
|
|
|
Red flag HR: 0-1years |
<80 >180 |
|
|
|
Red flag HR: 1+ |
>160 |
|
|
|
Delivery of rescue breaths for INFANT |
Neutral head Cover mouth+nose with own Blow 1 sec -> observe chest rise Repeat another 4 times (5 total) |
|
|
|
Delivery of rescue breaths for >1 YEAR |
Pinch nose HTCL Blow one sec Repeat 4 times (5 total) |
|
|
|
Dex dose + % |
2ml/kg 10% |
|

