![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hypothalamus |
Releasing hormones |
|
|
Anterior Pituitary |
ACTH TSH GH PRL FSH LH |
|
|
Posterior Pituitary |
ADH Oxytocin |
|
|
Thyroid Gland |
T4 T3 Calcitonin |
|
|
Parathyroid Glands |
PTH |
|
|
Thymus |
Thymosin |
|
|
Pancreas |
Insulin Glucagon |
|
|
Adrenal Glands |
Epinephrine Norepinephrine Glucocorticoids (cortisol) Aldosterone Androgens |
|
|
Pineal Gland |
Melatonin |
|
|
Kidney |
Erythropoietin Calcitriol |
|
|
Heart |
Atrial Naturetic Peptide |
|
|
Digestive Tract |
Digestive regulatory Hormones |
|
|
Ovaries |
Estrogen Progesterone Inhibin |
|
|
Testes |
Testosterone Inhibin |
|
|
ACTH |
adrenocorticotropin hormone -regulates the activity of the cortex of the adrenal gland |
|
|
TSH |
thyroid stimulating hormone -stimulates production and release of thyroid hormone |
|
|
GH |
growth hormone -stimulates growth of bone, cartilage and muscle |
|
|
PRL |
Prolactin -breast development and maintains lactation after childbirth |
|
|
FSH |
Follicle Stimulating Hormone -causes formation of ovarian follicles and stimulates estrogen production |
|
|
LH |
Luteinizing Hormone -initiates ovulation and maintains corpus luteim |
|
|
ADH |
Anti diuretic Hormone -reduce urine and sweat output -increases water re-absorption in the kidneys |
|
|
Oxytocin |
-Uterine contractions |
|
|
Thyroid Hormones |
T3
T4 |
|
|
Calcitonin |
Promotes Ca2 deposition and bone formation.
|
|
|
PTH |
Parathyroid Hormone
-Raises blood calcium levels |
|
|
Insulin |
Stimulates glucose and amino acid uptake.
Lowers blood glucose. |
|
|
Glucagon |
Stimulates glycogenolysis.
Raises blood glucose. |
|
|
Epinephrine and Norepinephrine (Adrenal Medulla) |
Fight or flight response
Increase heart rate, increase skeletal muscle blood flow, decrease skin blood flow |
|
|
Cortisol (adrenal cortex: zona fasciculata) |
release in response to stress
increase formation of glucose from protein and fat decrease inflammation |
|
|
Aldosterone (adrenal cortex: zona glomerulosa) |
increase blood volume by causing kidneys to retain sodium in exchange for potassium
increased blood volume= increased blood pressure |
|
|
Androgens (adrenal cortex: zona reticularis) |
male sex hormones produced in small quantities
converted to estrogens upon entering the blood |
|
|
Melatonin |
produces sleepiness during darkness
|
|
|
Erythropoietin |
EPO
stimulates bone marrow to produce more red blood cells, increasing the oxygen carrying capacity of blood |
|
|
Calcitriol |
promotes absorption of Ca2 and phosphate
stimulates calcium release from bone |
|
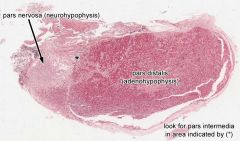
|
anterior lobe -pars distalis -pars intermedia posterior lobe |
|
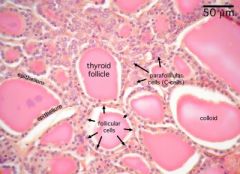
|
follicle cells colloid in follicle (thyroglobulin) c cells (calcitonin) |
|
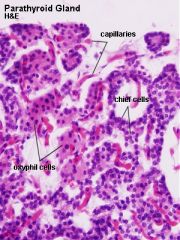
|
principle cheif cells oxyphil cells |
|
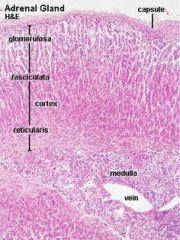
|
medulla cortex -zona golmerulosa -zona fasciculata -zona reticularis |
|
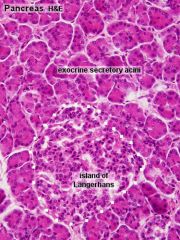
|
pancreatic islet acini |
|
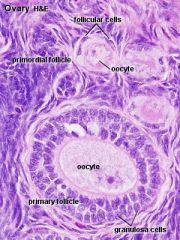
|
estrogen progesterone |
|
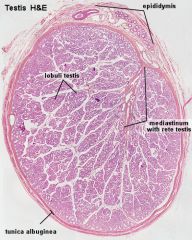
|
testosterone |
|
|
Mechanism of Type 1 Diabetes |
autoimmune disorder
immune system destroys insulin producing beta cells in kidney insulin dependent bc body does not produce insulin |
|
|
Mechanism of Type 2 Diabetes |
cause by loss of sensitivity to insulin
body still produces insulin |
|
|
Normal Blood Glucose Concentration |
70-100 mg/dl
|
|
|
How is Diabetes diagnosed? |
A fasting value over : 140 on 2 separate times. A BG value over: 200 in 2 hour glucose test |

