![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the endocrine system?
|
-A collection of small organs scattered throughout body that release hormones.
-A chemical messaging system. |
|
|
What is a hormone?
|
-A regulatory biochemical produced in an organism and transported in the blood to stimulate specific cells or tissues into action.
|
|
|
What are the functions of hormones?
|
-Released into the blood and have physiological control over function of cells or organs.
|
|
|
What are the 4 main processes regulated by hormones?
|
1. Reproduction
2. Growth and development 3. Metabolism 4. Defense system |
|
|
How is hormone release controlled?
|
-Through a negative feedback system.
|
|
|
Where are hormones produced?
|
1. Hypothalamus
2. Pituitary gland 3. Thyroid gland 4. Parathyroid gland 5. Adrenal gland 6. Kidneys 7. Ovaries and testicles |
|
|
What hormone does the hypothalamus release?
|
-Thyroid-releasing hormone (TRH)
|
|
|
What is the target organ of thyroid-releasing hormone?
|
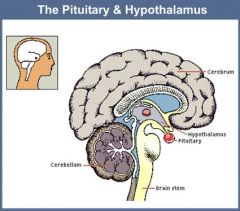
-Thyroid gland
|
|
|
What is the cascade of events in the thyroid axis?
|
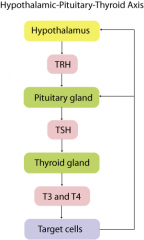
-Hypothalamus releases thyroid releasing hormone--> Pituitary
-Pituitary releases thyroid stimulating hormone --> thyroid -Thyroid releases T3 and T4 and sends negative feedback to hypothalamus to stop release of thyroid releasing hormone and stop cascade. |
|
|
What process does the thyroid regulate?
|
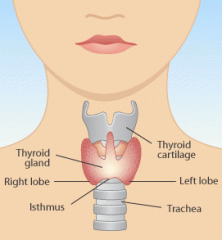
-Metabolism
|
|
|
What is the endocrine function of the pancreas?
|
-Regulate blood glucose levels.
|
|
|
What two hormones do the pancreas release?
|
1. Insulin
2. Glucagon |
|
|
What is the function of insulin?
|
-To LOWER blood glucose levels by storing glucagon as glycogen in the cells.
|
|
|
What is the function of glucagon?
|
-To RAISE blood glucose levels by stimulating liver to convert stored glycogen into glucose.
|
|
|
What is hyperthyroidism?
|
-Excessive release of thyroid hormone by autoimmune antibodies mimicking effect of TSH.
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
|
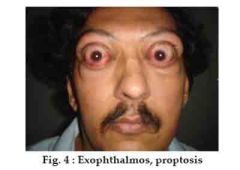
-Weight loss
-Staring gaze (bug eyes) -Feeling hot |
|
|
What is a major cause of hyperthyroidism?
|
-Graves disease
|
|
|
What are the most common treatments for hyperthyroidism?
|
-Surgery (removal of gland)
-Medicines (hormone replacement, antithyroid drugs) |
|
|
What is hypothyroidism?
|
-Too little thyroid hormone produced.
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of hypothyroidism?
|
-Weight gain
-Feeling cold -Fatigue |
|
|
What is the most common cause of hypothyroidism?
|
-Treatment of hyperthyroidism.
|
|
|
What is the most common treatment of hypothyroidism?
|
-Intake of Thyroid hormone.
|
|
|
What is Cushing's Disease?
|
-High levels of cortisone in blood due to malfunctioning adrenal gland.
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Cushing's Disease?
|
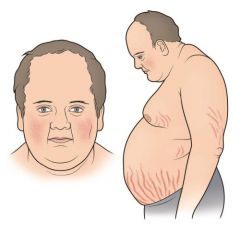
-Moon face
-Thin limbs -Abdominal fat |
|
|
What is common treatment for Cushing's Disease?
|
-Remove or destroy tumor on adrenal gland.
-Reduction in doses of cortisone treatment. |
|
|
What is Diabetes Type 1?
|
-Lack of insulin production with raised blood glucose levels.
-No insulin produced by pancreas. |
|
|
What are the symptoms of Diabetes Type 1?
|
-Weight loss
-High blood glucose levels -Thirst -Frequency in passing urine |
|
|
What are the long term effects of Diabetes Type 1?
|
-Heart and vessel damage.
-Eye problems. |
|
|
What is the treatment for Diabetes Type 1?
|
-Insulin injections.
|
|
|
What is Diabetes Type 2?
|
-Reduction in insulin production, or not enough produced to satisfy needs of body.
|
|
|
Who is most likely to be affected by Type 2 Diabetes?
|
-People over 40.
|
|
|
How is Type 2 Diabetes managed?
|
-Weight reduction
-Increased exercise -Medication to lower insulin resistance |
|
|
What are complications from Diabetes?
|
-Amputations
-Heart attack -Blindness -Kidney disease -Neuropathy -Vascular Disease |

