![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Regulation of the release of hormones from the anterior lobe of hypophisis (3 types) |
1)Hypothalamic sescretion- polypeptide releasing hormones (+dopamine) 2)paracrine and autocrine secretions of the pituitary cells (growth factors + cytokines 3) feedback effect of circulating hormones (negative feedback TRH,TSH) |
|
|
|
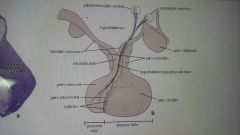
Gross structure and development of the pituitary gland |
Weight- 0.6-1.5 (multiparous women) Sella turcica, diaphragma turcica (sphenoid bone ) Origin: -adenohypophysis-ectoderm of the orthopharynx ( rathke pouch) -neurohypophysis- neuroectoderm of the 3rd ventricle (diencephalon) Compounds: -adenohypophysis- pars tubelaris, pars intermedia, pars distalis -neurohypophysis - pars nevrosa, infundibulum (continuous of eminentia mediana) |
|
|
|
Where are the hypothalamohypophyseal tracts ? |
Infundibulum of the hypophysis
|
|
|
|
Blood supply of the pituitary gland? |
Unusual, - aa. Hypophyseales superiores- supply the median eminence, infundibulum, pars tuberalis -aa Hypophyseales inferiores- pars nevrosa ---hypothalamohypophyseal portal system |
|
|
|
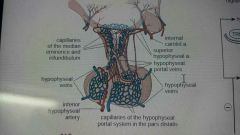
Hypothalamohypophyseal portal system |
The superior hypophyseal arteries, supply the median eminence, infundibulum and pars tuberalis. The blood from there drains into the hypophyseal portal veins which gives a rise to a secondary capillary plexus, which carries the neuroendocrine secretions from the hypothalamus to the pars distalis (anterior lobe) , then to the sinus cavernosus. |
|
|
|
Nerve supply (pituitary gland) |
Infundibulum and pars nevrosa- posterior lobe Anterior lobe- postsynaptic fibers ANS |
|
|
|
GH Somatotropin |
Stimulates liver to synthese and secrete insuline like growth factor (igf 1), which stimulates chondrocytes in skeletal bones, and progenitor cells in skeletal muscles |
|
|
|
Prolactin PRL |
Promotes mammary gland development, milk formation initiation, secretion of casein, lactalbumin, lipids and carbohydrates in milk |
|
|
|
ACTH Adrenocorticotrophic hormone |
Maintains structure, stimul secretion of glucocorticoids and gonadocorticoids by zona fasciculata and zona reticularis of the adrenal cortex |
|
|
|
FSH foliclestimulating hormone |
Ovogenesis and spermatogenesis stimulation |
|
|
|
LH- luteinising hormone |
Final matruration of the ovarian folicle regulation, ovulation regulation, corpus luteum formation regulation, stimulates steroid secretion by graafov folikul i corpus luteum Maintenance of and androgen secretion of the Leydig cells |
|
|
|
Thyrotropic hormone TSH |
Growth thyroid epithelial cells, stimulation production and release of thyroglobulin and thyroid hormones |
|

