![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Adrenal gland
|
- Cortex is derived from intermediate mesoderm
- Medulla derived from neural crest cells (from adjacent sympathetic ganglion) - At 4 months after birth, the fetal cortex disappears and the permanent cortex is visible with zonations |
|
|
Cortex layers
|
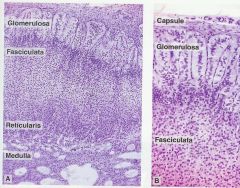
- Zona glomerulosa: beneath capsule, is composed of columnar or pyramidal cells and arranged as rounded or arched cords
- Zona fasiculata: (middle), cells arranged in straight cords, 1 or 2 cells thick and perpendicular to surface - Zona reticularis: cells in anastomosing network; Lipofuscin granules and pyknotic nuclei present |
|
|
Hormones of cortex
|
- Glomerulosa cells: secrete the mineralocorticoid - Aldosterone (controlled by angiotensin II and ACTH to a lesser degree)
- Fasciculata cells: secrete glucocorticoids - Cortisol under control of ACTH - Reticularis cells: secrete steroid sex hormones (dehydroepiandosterone) under control of ACTH |
|
|
SER & Mitochondria hormones
|
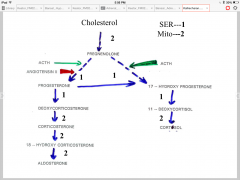
- cortex hormones are not stored in granules, they diffuse freely since they are steroids
|
|
|
Adrenal medulla
|
- neural crest
- composed of Chromaffin cells (secrete epinephrine and norepinephrine from stored vesicles) - these are modified sympathetic postganglionic neurons without processes - Catecholamines from cytosol are transported via Mg-activated ATPase into vesicles |
|
|
Pheochromocytoma
|
- a rare tumor derived from chromaffin cells that produces excessive catecholamines
|
|
|
Medulla blood supply
|
- Directly from cortical capillaries and medullary arterioles
- Glucocorticoids transported from cortex to medulla stimulate PNMT to convert norepinephrine to epinephrine |
|
|
Stimulation of adrenal medulla
|
- Sympathetic (ACTH) stimulation: Dopamine ---> Norepinephrine
- Cortisol stimulation: Norepinephrine ---> Epinephrine |
|
|
G-protein couples receptors
|
- Alpha receptors preferentially bind norepinephrine:
α1 ~ α2 > β1 >>> β2 (very weak) - Beta receptors bind epinephrine: β1 ~ β2 >> α1 ~ α2 - All receptors will bind either catecholamine in a stress or crisis state |
|
|
Mineralocorticoids
|
- Aldosterone
- 18-OH Corticosterone (from 18-methylation process) |
|
|
Glucocorticoids
|
- Cortisol
- Corticosterone (can function as primary glucocorticoid if cortisol is blocked, primary glucocorticoid in some animals) - Limited 18-dehydroxylation |
|
|
Primary adrenal androgens
|
- Androstenedione, Dehydroepiandosterone (DHEA) (these are weak androgens, weakly bind (if at all) with sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG) and albumin
- Testosterone (very small amount, <1.0%) - Released during puberty (functional before gonads) |
|
|
CYP11A1 and StAR
|
- Regulate steroidogenesis
- P450 side-chain cleavage - 20-22 Desmolase - Inner mitochondrial membrane - Converts cholesterol to pregnenolone - StAR = steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (regulates rate of intracellular transport of cholesterol across the outer mitochondrial membrane) |
|
|
CYP11B1
|
- often called 11-hydroxylase (converts 11-deoxycortisol to cortisol and also converts 11-deoxycorticosterone to corticosterone)
- cortisol is synthesized and secreted from the mitochondria |
|
|
Bound steroids
|
- Adrenal hormones transported in the blood bound to CBG (corticosteroid binding globulin - binds cortisol and corticosterone) and albumin
- steroids bound to albumin are the most bioavailable - steroids bound to CBG may be utilized but are predominantly metabolized in the liver |
|
|
Corticoid metabolism
|
- major degradation site is liver; secondary is kidney
- conjugated with sulfate or glucuronic acid - excreted in urine - Cortisol metabolism and production are increased in both hyperthyroid and obese patients, resulting in no net change in baseline plasma levels - Aldosterone degradation shifted to kidney in patients with impaired liver function |
|
|
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
|
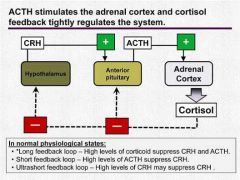
- CRH stimulates secretion of both hypothalamic and pituitary POMC gene-derived peptides, the latter resulting in glucocorticoid secretion.
- Serum level of Cortisol is the main factor regulating the system |
|
|
ACTH
|
- stimulates production of ACTH receptor
- stimulates StAR protein (indirect) - stimulates CYP11A - factors regulating ACTH receptor: ACTH, Glucocorticoids, Angiotensin II - cortex makes ~15-25 mg cortisol a day |
|
|
steroid receptors
|
- Glucocorticoid receptor (GR) and mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) exhibit a high degree of homology
- Corticoid receptors PR and AR share a relatively high degree of homology in the DBD (DNA binding domain) and LBD (Ligand binding domain), so ligands may bind with promiscuity to any of these receptors |
|
|
Cortisol
|
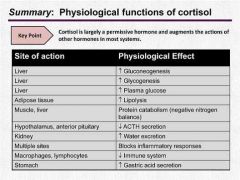
- anti-anabolic or permissive functions
- converts protein to glycogen and then to glucose for fuel - Inhibits protein synthesis - Inhibits glucose uptake and decreases glucose utilization in hypoglycemia - enhances glucagon release - Permissive effects: 1) does not directly stimulate muscle glycogenolysis - rather amplifies effects of glucagon 2) regulates level of GLUT4 protein, regulating the effects of insulin |
|
|
RAAS
|

- Angiotensiogen (preprohormone from liver) ---> cleaved in circulation by Renin ---> Angiotensin I (prohormone) ---> ACE in lungs ---> Angiotensin II (active)
|
|
|
Fight or Flight response
|
- Acute physiological effects:
1) (Nor)epinethrine from medulla pumped into circulation 2) Norepinephrine binds α1 receptors in hepatocytes (stimulates gluconeogenesis - mobilize glucose) 3) Epinephrine binds β2 receptors on pancreatic β-cells (small spurts of insulin) - Extended physiological effects (extended run/fight): 4) CRH starts positive ultrashort feedback loop to produce more CRH 5) increased ACTH stimulates steroidogenesis and increases cortisol production |
|
|
Addisons disease
|
- Primary adrenal insufficiency
- elevated ACTH with low adrenal output - chronic disorder, symptoms develop slowly - symptoms: Salt craving, darkening of skin, nausa & vomiting, low BP/dizziness on standing, muscle/joint pain, women get decreases libido and hair production - Secondary Adrenal insufficiency (not addisons): Low ACTH, Low adrenal output |
|
|
Addisonian crisis
|
- Acute failure of adrenal function (needs immediate attention)
- most often occurs after infection, trauma, severe stress - Severe symptoms with rapid onset: Shock, severe dehydration, very low BP, loss of consciousness, sodium / potassium imbalance |
|
|
Cushings syndrome
|
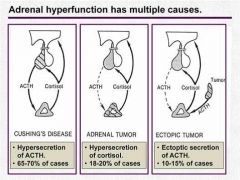
- from prolonged exposure to elevated glucocorticoids
(usually from overuse of exogenous glucocorticoid) - endogenous cases are rare |
|
|
Progesterone from cholesterol
|
- Desmolase is needed to catalyze reaction of Cholesterol to Pregnenolone, which then converts to Progesterone
- ACTH promotes desmolase reaction - StAR (steroidogenic acute regulator) protein, which feeds cholesterol to desmolase, is the Regulated step |
|
|
Synthesis of corticosteroids/sex steroids
|
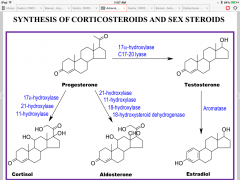
|
|
|
Steroid hydroxylations
|
Steroid-H + O2 + NADPH + H -- P450 ----> Steroid-OH + NADP +H20
- Monooxydase reaction b/c O2 is a substrate (only use one atom) - P450 is heme-containing (activates O2) |
|
|
Testosterone
|
- Dihydrotestosterone is a more potent androgen than testosterone (and gets made at target tissues)
- Testosterone: 6-8% ends up as Dihydrotestosterone, 0.3% as Estradiol, and the rest as inactive products |
|
|
Steroid hormones
|
- made from cholesterol
- oxidative side chain cleavage - hydroxylations (P450 dependent) - No vesicular storage - Bound to transport proteins in blood: transcortin (glucocorticoids) and SHBG (estrogen, androgens) - Action on nuclear receptors - most effects are slow-onset, long-lasting - inactivation in liver |
|
|
Licorice-induced hypertension
|
- A component of licorice root prevents oxidation of cortisol to cortisone
- inhibition of 11-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase |
|
|
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
|
- adrenogenital syndrome
- Deficiency of 21-hydroxylase or 11-hydroxylase - Reduced corticosteroids (makes for lack of negative feedback inhibition to pituitary) - Elevated ACTH - Overproduction of adrenal androgens - Treatment: Cortisol to induce feedback |
|
|
5α-reductase deficiency
|
- Ambiguous external genitalia
- Virilization at puberty |
|
|
21-Hydroxylase deficiency
|

|
|
|
11-hydroxylase deficiency
|

|
|
|
Hydrocortisone (cortisol)
|
- Oral, IV (in addisonian crisis)
- increase dose with stress, infections, surgery - Low anti-inflammatory & salt-retaining activity - Short-acting (8-12 hours) - Typical adverse effects of glucocorticoids - Treatment: Addison's disease |
|
|
Prednisone
|
- Moderate anti-inflammatory activity
- low salt-retaining activity - intermediate-acting (12-36 hours) - Typical adverse effects of glucocorticoids |
|
|
Dexamethasone
|
- High anti-inflammatory activity
- Long-acting (24-72 hours) - Typical adverse effects of glucocorticoids |
|
|
Ketoconazole
|
- Inhibits p450 enzymes
- inhibits corticosteroid synthesis - inhibits androgen synthesis - Adverse effect: gynecomastia in males - Treatment: Cushings disease |
|
|
Mifepristone (RU 486)
|
- Glucocorticoid receptor antagonist
- Progesterone antagonist - Treatment: Cushings disease |
|
|
Fludrocortisone
|
- Oral
- increase dose with exercise, sweat, diarrhea - High salt-retaining activity - moderate anti-inflammatory activity - lasts 8-12 hours - Treatment: Addisons disease |
|
|
Spirinolactone
|
- Aldosterone receptor antagonist
- Anti-androgen - K+ sparing diuretic - decrease Na+ reabsorption; decrease K+ secretion - slow onset (several days) - must wait for breakdown of proteins made before aldosterone was blocked |
|
|
Epinephrine
|
- β1-receptor: increase HR & contractile force
- β2-receptor: bronchial dilation - increase BP, respiration - Treatment: Anaphylactic shock (hypotension) |

