![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What does BJT stand for? |
Bipolar Junction Transistors |
|
|
|
What type of power supply is NPN used in? |
Positive power supplies |
|
|
|
What type of power supply is PNP used in? |
Negative power supplies |
|
|
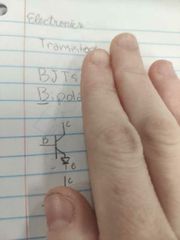
NPN or PNP? |
NPN |
|
|

NPN or PNP? |

PNP |
|
|
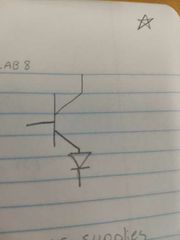
Label these |
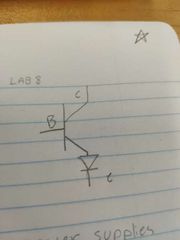
|
|
|
|
What do b, e, and c stand for respectively? |
Base, emitter, collector. |
|
|
|
What is a transistor? |
An amplifier. |
|
|
|
What do transistors do? |
Amplify current or voltage. |
|
|
|
What can transistors be used as? |
Either as amplifiers, or as switches. |
|
|
|
Do transistors have contact bounce? |
No, they are solid state. |
|
|
|
Do transistors have moving parts? |
No, they are solid state. |
|
|
|
Do transistors move slow or fast? |
Very very fast. |
|
|
|
Will arc spikes be bigger or smaller when using a transistor? |
Much much bigger, using a diode is a must. |
|
|
|
Measuring between B and C on an NPN will get you how many volts? |
7/10 |
|
|
|
Measuring between B and E on a transistor will get you what? |
7/10ths of a volt. |
|
|
|
Measuring between C and E on a transistor will get you what? |
An open. |
|
|
|
When using a smaller resistor between B and E, what happens to base current? |
It goes up. |
|
|
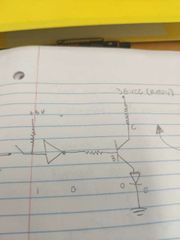
What happens here? |
No B current, no C current. |
|
|
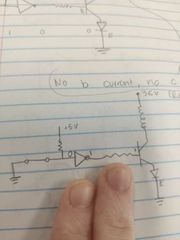
What happens here? |
Current flows. |
|
|
|
Cut off is how much resistance? |
Infinite |
|
|
|
Fully saturated is how much resistance? |
Zero. |
|
|
|
Turned off is how much resistance? |
Infinite |
|
|
|
Turned on is how much resistance? |
None. |
|
|
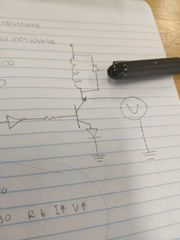
If the relay is off, what will you measure? |
Source. |
|
|
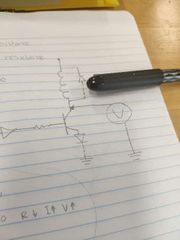
If the relay is on, what will you measure? |
Zero. |
|
|
|
What is forward biased? |
Turned on |
|
|
|
What is reverse biased? |
Turned off |
|
|
|
When do diodes flow? |
When forward biased |
|
|
|
How much will a diode drop? |
. 7 volts |
|
|
|
What are diodes made from? |
Silicon |
|
|
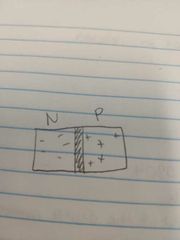
What is this? |
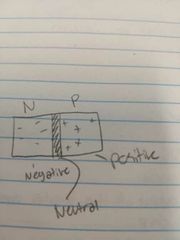
A PN junction diode. |
|
|
|
What is the middle called? |
The depletion region |
|
|
|
What is the depletion region? |
A region that is depleted of carriers. |
|
|
|
What would cause the electrons to leap through the depletion region? |
If they get .7 volts of motivation. |
|
|
|
What is the barrier voltage of a diode? |
. 7 volts. |
|
|

Is this diode wired forward or reverse biased? |
Forward biased. |
|
|
|
What happens when a diode is wired in reverse bias? |
Current flows for a second, but then stops, because both sides have just become neutral, which renders the entire diode an insulator. |
|
|
|
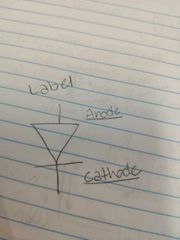
|
|
|
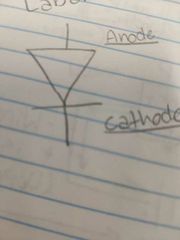
What is this? |
A diode. |
|
|
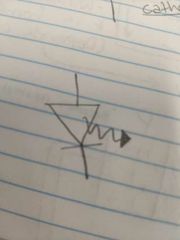
What is this? |
An LED |
|
|
|
Which is more positive, the cathode or the anode? |
The anode is more positive. |
|
|
|
Which is more negative, the cathode or the anode? |
The cathode is more negative. |
|
|
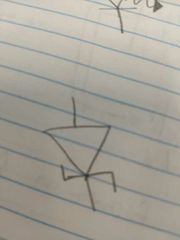
What is this? |
A zener diode. |
|
|
|
How does a zener diode work? |
Like a regulator. |
|
|
|
What are the types of materials semiconductors are made of? |
Silicon, and germanium. |
|
|
|
What voltage does a silicon semiconductor drop? |
. 7 volts |
|
|
|
What voltage does a germanium semiconductor drop? |
. 2 volts. |
|
|
|
What is a diode? |
A semiconductor device. |
|
|
|
How many terminals does a diode have? |
Two. |
|
|
|
Diode allows flow in how many directions? |
One direction only. |
|
|
|
Does a diode act like an insulator or a conductor? |
Both. |
|
|
|
What are diodes typically made from? |
Silicon |
|
|
|
What are the three main purposes of a diode? |
Isolation, arc suppression, and rectification. |
|
|
|
What two types of material are diodes made from? |
N type and P type. |
|
|
|
What voltage does a diode drop when reverse biased? |
All voltage. |
|
|
|
What is PIK inverse voltage? |
The maximum voltage a reverse wired diode will resist. |
|
|
|
What is rectification? |
Converting AC into DC. |
|
|
|
Do electrons flow through caps? |
No. |
|
|
|
What do caps resist? |
Changes in voltage. |
|
|
|
What do caps not care about? |
Current. |
|
|
|
What does electrolytic equal? |
Cap. |
|
|
|
What is RMS? |
AC wave to DC equivalent. |
|
|
|
What is a device that is a semiconductor? |
A transistor. |
|
|
|
When acting as a switch, what does a transistor act like? |
A relay. |
|
|
|
How many pins does a transistor have? |
Three. |
|
|
|
What are the three pins of a transistor? |
Collector, emitter, and base. |
|
|
|
How many types of transistors are there? |
NPN and PNP |
2. What are they? |
|
|
Where is the emitter found? |
On the E leg. |
|
|
|
What is a transistor made of? |
P and N material, like a diode, but stacked. NPN. PNP. |
|
|
|
N type has more what? |
Free electrons and negatively charged particles. |
|
|
|
P type has more what? |
Holes or positively charged particles. |
|
|
|
What is the smallest region of a transistor? |
The base. |
|
|
|
What is the largest region of a transistor? |
The collector. |
|
|
|
When do electrons flow from the emitter into the base on transistors? |
When the emitter and the base are forward biased. |
|
|
|
How many pins does a phototransistor have? |
2. |
|
|
|
What is an example of an opto-isolator? |
A phototransistor. |
|
|
|
What do optoisolators do? |
Prevent high voltages from affecting the system receiving the light. |
|
|
|
What is this symbol? |

Phototransistor. |
|
|
|
What does SCR stand for? |
Silicon controlled rectifier. |
|
|
|
What categories do SCRs belong to? |
Thyristor. |
|
|
|
What are SCRs made up of? |
N and P regions like transistors. Four this time. |
|
|
|
What is the SCR? |
Only conducts 180 degrees, doesn't pass AC. |
A rectifier. What does that do? |
|
|
What do SCRs act like? |
Very fast on switches. |
|
|
|
Are SCRs for low or high currents? |
High currents. |
|
|
|
When turned on, what is an SCRs resistance? |
Very low. |
|
|
|
What is the stable state of an SCR? |
It's a bi-stable device, it is on or off. |
|
|
|
When troubleshooting an SCR, what can the problem be? |
The SCR or the Load. |
|
|
|
What are internal resistors across the gate and the cathode used for in SCRs? |
To prevent false triggering, an event in which the SCR turns on accidentally. |
|
|
|
Are SCRs more for AC or DC current? |
AC. |
|
|
|
What do SCRs do in an AC circuit? |
Turn themselves on and off. |
|
|
|
How much of an AC waveform do SCRs conduct? |
180° |
|
|
|
How is a a triac made? |
When 2 SCRs are joined in reverse parallel. |
|
|
|
What does triac stand for? |
Triode AC switch. |
|
|
|
Is the triac good for high power control circuits? |
No. |
|
|
|
What are triacs used in? |
Simple, low level operations. Dimmer switches. Control of fans and small Motors. |
|
|

What voltage is connected to the relay? What's being switched be the transistor? |
24 volts and 5 volts respectively. |
|

