![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
most common cause of cataracts
|
aging
|
|
|
amiodarone
steroids phenothiazines are drugs associated with what eye disorder |
cataracts
|
|
|
most common type of glaucoma
|
open-angle g.
|
|
|
sudden onset eye pain, blurred vision, fixed dilated pupil
|
primary angle-closure g.
|
|
|
diagnostic tests for glaucoma
|
goldmann's applanation
schiotz's tonometry |
|
|
normal intraocular pressure
|
10-24 mmHg
|
|
|
test to determine anterior chamber angle
|
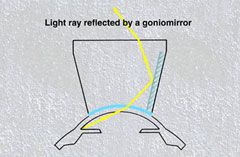
gonioscopy
|
|
|
sudden monocular painless vision loss, cherry red spot on funduscopy
|
central retinal artery occlusion
|
|
|
tx for neovascularization in central retinal vein occlusion
|
laser photocoagulation
|
|
|
silver and copper wiring, flame-shaped hemorrhages, av nicking
|
hypertensive retinopathy
|
|
|
most common type of strabismus
|
esotropia
|
|
|
age of stable ocular alignment
|
2 months
|
|
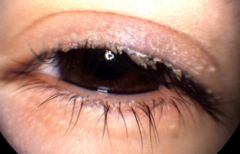
red eye-lids with dry scales
|
staph blepharitis
|
|
|
bug in contact lens conjunctivitis
|
pseudomonas
|
|
|
triangular fleshy lesion on the nasal side of the eye
|
pterygium
|
|
|
most common orbital fx
|
blowout fx
|
|
|
infra-orbital anesthesia, diplopia, step-off deformity of the intra-orbital ridge
|
blowout fx
|
|
hanging teardrop sign and open bomb-bay door sign
|
blowout fx
|
|
|
monocular double vision, leukocoria, glare
|
cataracts
|
|
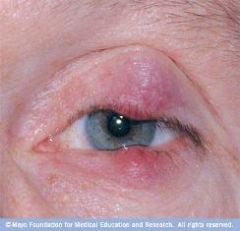
painless inflammation of the mebomian's glands
|
chalazion
|
|
|
tx for chalazion
|
steroid injections for small lesions
surgery |
|
|
profuse eye discharge, minimal itching, generalized redness and no peri-auricular nodes
|
bacterial conjunctivitis
|
|
|
profuse eye tearing, peri-auricular lymphadenopathy
|
viral conjunctivitis
|
|
|
severe eye itching, milky hyperemia, no nodes or discharge
|
allergic conjunctivitis
|
|
|
foreign body sensation, with pain, tearing, and photophobia
|
corneal abrasion
|
|
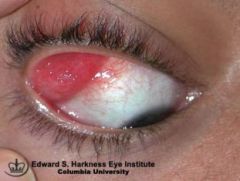
diseases in children and adults associated with dacryoadenitis
|
children: Mumps and HSV-1 most commonly, measles or influenza
adults: gonorrhea, sarcoidosis,Sjogren's |
|
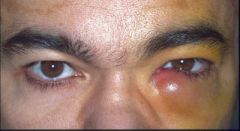
bugs associated with dacryocystitis
|
h. flu
staph aureus beta hemolytic strep |
|
|
pain, swelling and redness over the temporal area of the upper eyelid
|
dacryoadenitis
|
|
|
use cotton-tip aplicator
long term topical anesthetic steroids mri are contraindicated tecniques in what case? |
removal of foreign body from the eye
|
|
|
most common bug in hordoleum
|
staph aureus
|
|
|
leading cause of permanent blindness in the elderly
|
macular degeneration
|
|
|
macular degeneration non-exudative vs exudative
|
non-exudative: drunsen (yellow-white deposits scattered throughout the macula
exudative: neovascularization |
|
|
most common bugs in orbital cellulitis
|
h. flu
pneumococcus |
|
|
medical term for swelling of the conjunctiva
|
chemosis
|
|
|
pain, hyperemia, proptosis in a child
|
orbital cellulitis
|
|
|
patient complains of a curtain falling over the eye, flashes and floaters
|
retinal detachment or amarousis fugax if transient
|
|
|
hallmark clinical finding of retinitis pigmentosa
|
night blindness (nyctalopia)
|
|
|
fundoscopy reveals "bone spicules"
|
retinitis pigmentosa
|
|
|
Hearing loss and retinitis pigmentosa
|
USHER SYNDROME
|
|
|
Most common congenital anomaly of the nose
|
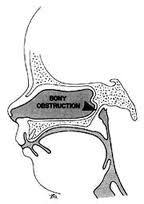
CHOANAL ATRESIA
|
|
|
Pt can't see but denies blindness. Bilateral oclussion of the posterior cerebral arteries is noted. Dx?
|
VISUAL ANOSOGNOSIA OR ANTON SYNDROME
|
|
|
Optic ataxia, loss of panoramic vision and supranuclear gaze palsy.
|
BALINT SYNDROME
|
|
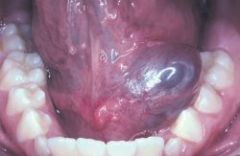
Cyst of the sublingual salivary gland to one side of the lingual frenulum that resembles a frog's belly due to its thin wall
|
RANULA
|
|
|
Most common cause of persistent stridor in childs
|
LARYNGOMALACIA
|

