![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
bones, stones, abdominal groans, psychic moans, and fatigue overtones
|
Hyperparathyroidism
|
|
|
dz states that must be r/o in the presence of hypercalcemia
|
malignant tumors
multiple myeloma sarcoidosis |
|
|
medical tx for hyperparathyroidism
|
large fluid intake
biphosphonates |
|
|
complications of hyperparathyroidism (3)
|
pathologic fractures
urinary tract infections renal failure |
|
|
renal resistance to parathyroid hormone
|
pseudo-hypoparathyroidism
|
|
|
circumoral tingling, tetany, muscle cramps, irritability, and seizures
|
hypoparathyroidism
|
|
|
Lethargy, personality changes, blurry vision, and mental retardation
|
chronic hypoparathyroidism
|
|
|
most common cause of hyperthyroidism
|
graves dz
|
|
|
contraindication for the use of radioactive iodine
|
pregnancy
|
|
|
why should asa be avoided in thyrotoxicosis?
|
asa will raise free t4 levels
|
|
|
most common cause of hypothyroidism
|
hashimoto's thyroiditis
|
|
|
drugs that can induce hypothyroidism (3)
|
1. amiodarone
2. sulfonamides 3. lithium |
|
|
worst complication of hypothyroidism
|
myxedema coma
|
|
|
altered mental status, hypothermia, hypothyroidism
|
myxedema coma
|
|
|
fatigue, dry mouth and eyes, and a diffusely enlarged, firm nodular thyroid
|
Chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis (hashimoto's)
|
|
|
stony, hard thyroid gland and signs of dysphagia, dyspnea, pain, and hoarseness
|
Riedel's thyroiditis
|
|
|
tx for subacute thyroiditis
|
asa
|
|
|
tx for riedel's thyroiditis
|
steroids and tamoxifen for long term tx
|
|
|
most common thyroid neoplasm
|
papillary ca
|
|
|
test to separate ACTH-dependent from ACTH-independent hypercortisolism
|
Corticotropin-releasing hormone
|
|
|
test to screen for adrenal hyperfunction
|
dexamethasone test
|
|
|
adrenal inhibitors for the tx of cushing's syndrome
|
metyrapone and ketoconazole
|
|
|
diagnostic test for adrenal insufficiency
|
simplified cosyntropin stimulation test
cortisol level below 20mg/dL is a positive test |
|
|
X-linked disorder w/ accumulation of long chain fatty acids in the adrenal cortex, testes, and brain. Pts usually present in the 3rd decade w/ peripheral neuropathy and progressive spastic paraplegia. MLDx?
|
Adrenoleukodystrophy
|
|
|
hormone controlling cortisol release
|
Ceramide trihexoside
|
|
|
most common cause of death in acromegaly pt
|
heart failure
|
|
|
history of birth asphyxia, neonatal hypoglycemia, microphallus, or midline defects growing at a diminished velocity
|
growth hormone deficiency
|
|
|
autosomal genetic disorder that causes dwarfism
|
achondroplasia
|
|
|
Prolactin inhibitory factor
|
dopamine
|
|
|
ddx for hyperprolactinemia (5)
|
cirrhosis
pregnancy hypothyroidism renal failure pituitary tumor |
|
|
3 common dopamine agonists for tx of hyperprolactinemia
|
Cabergoline (Dostinex)
Bromocriptine (Parlodel) Pergolide (Permax) |
|
|
criteria for dx of dm
|
Symptoms of diabetes + random plasma glucose > 200mg/dL.
Fasting plasma glucose > 125 x 2 Two-hour tolerance test plasma glucose > 200 |
|
|
AE of sulfonylurea
|
hypoglycemia and weight gain
|
|
|
mention 3 common sulfonylureas
|
Glimepiride (Amaryl)
Glipizide (Glucotrol) glyburide (Diabeta) |
|
|
Mention 2 meglitinides and their use in preventing hyperglycemia
|
repaglinide (prandin)
Nateglinide (Starlix) THEIR MOA IS SIMILAR TO SULFONYLUREAS BUT LACKS THE SULFA COMPONENT THEREFORE INDICATED IN SULFA ALLERGIC PATIENTS W/ TYPE 2 DM |
|
|
mention 2 common TZDs
|
Pioglitazone (Actos)
Rosiglitazone (Avandia) |
|
|
this anti-diabetic drug can cause fluid retention and CHF
|
TZDs
|
|
|
MOA of TZDs
|
Decrease peripheral insulin resistance
|
|
|
mention 2 common alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
|
Acarbose (Precose)
Miglitol |
|
|
MOA of alpha-glucosidase inhibitors
|
Decrease post-prandial sugar absorption from the small intestines
|
|
|
pts should take this drug 1 hr before or 4-6 hr after taking other medications due to interference w/ absorption
|
bile acid sequestrants
cholestyramine (questran) colesevelam (welchol) |
|
|
AE of fibric acid derivatives (2)
|
cholelithiasis
drug-induced hepatitis |
|
|
mention 2 common fibric acid derivatives
|
fenofibrate (tricor or lipofen)
gemfibrozil (Lopid) |
|
|
bloody nipple discharge suggests...?
|
INTRADUCTAL PAPILLOMA OF THE BREAST IS MORE COMMON BUT ALWAYS R/O INTRADUCTAL CA
|
|
|
Most common breast ca
|
INVASIVE DUCTAL CA
|
|
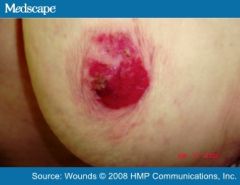
Macular rash over the nipple
|
PAGET'S BREAST DISEASE
|
|
|
Pts w/ choriocarcinoma will present w/ which thyroid disorder?
|
HYPERTHYROIDISM (MOLAR TISSUE PRODUCES TSH OR THYROTROPIN)
|
|
|
Hyperthyroidism during pregnancy can result in which two complications?
|
1. PREMATURE DELIVERY
2. NEONATAL THYROTOXICOSIS |
|
|
Post-partum galactorrhea and amenorrhea plus hyperprolactinemia which can lead to uterine and ovary atrophy
|
CHIARI-FROMMEL SYNDROME
|
|
|
pt in ICU w/ low T3 an nml T4 and TSH..DX?
|
SICK EUTHYROID SYNDROME
|
|
|
Pt presents c/o anxiety and shaky hands as well as heat intolerance. There's a h/o radio-contrast iodine and amiodarone therapy for a-fib. No exophthalmos or lymphedema are noted. Palpation of the thyroid reveals multiple nodules. MLDx?
|
TOXIC MULTINODULAR GOITER (JODBASEDOW'S DISEASE)
|
|
|
Pt presents c/o anxiety and shaky hands as well as heat intolerance. There's a h/o radio-contrast iodine and amiodarone therapy for a-fib. No exophthalmos or lymphedema are noted. Palpation of the thyroid reveals multiple nodules. MLDx?
|
TOXIC MULTINODULAR GOITER (JODBASEDOW'S DISEASE)
|
|
|
Mention 2 advantages of TZDs over Metformin
|
MORE GLYCEMIC CONTROL DURATION
REDUCED PROGRESSION FROM PRE-DIABETES TO DM 2 |

