![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Families of:
Ascaris lumbricoides Toxocara canis Enterobius vermicularis |
Ascaridae [superfamily Ascaridoidea]
Toxocaridae [superfamily Ascaridoidea] Oxyuridae (human pinworm) |
|

Description Ascaris lumbricoides
|
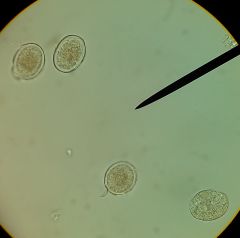
Huge nematodes. females up to 35cm, males 17cm
three lips, each w/2 basal papillae each lip has two small rows of denticles at margin eggs have thick, lumpy shell |
|
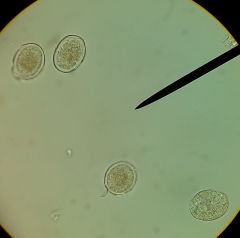
Ascaris lumbridoides
telling males from females? (pictured, unfertilized eggs. they're somewhat longer than fertilized eggs) |

males have ventrally curved tail and two copulatory spicules but no gubernaculum
females have straight tail. vulva near end of first third of body |
|
|
Life cycle of Ascaris lumbricoides
|
unhatched juveniles swallowed in contaminated food or water -> hatch in duodenum ---- penetrate mucosa and submucosa into blood or lymph --> lungs (but many get lost during migration and appear in many tissues causing acute problems) -> juveniles molt twice in lungs, grow to 1.4-1.8mm -> migrate up to pharynx where they are swallowed. Juveniles that have not molted 3rd time into stage 4 can't survive gastic stomache environment -> small intesting where they mature into adults
|
|
|
Ascaris lumbricoides pathogenesis
|
1. in lungs, when worms break in they cause small pools of blood to accumulate, causes edema, clogging of airways known as Ascaris pneumonitis; can result in other infections of lungs
2. wandering worms die in random tissues, cause inflammation 3. worms eat stuff in intestines, not tissue; can cause malnutrition, stunted growth, cognitive impairments in children 4. can cause fatal intestinal blockage 5. Wandering females. w/o males, females wander out anus, to bile ducts, appendix, ears, mouth, nose, trachae etc can result in death/pain/horror |
|
|
Ascaris lumbricoides geography
|
pretty much world-wide; americas, europe, africa, asia.
eggs resistant to cold, desiccation, harsh chemicals but vulnerable to high temps and sunlight |
|
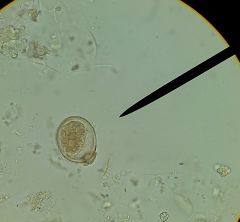
Toxocara canis description
what does it infect? where (type of ecological setting) distinctive features? |
large roundworm of carnivores
infects small intestine of dogs, foxes, coyotes etc cosmopolitan females 18cm, males 10cm posterior end curved ventrally |
|
|
Toxocara canis
Telling male from female? |
Tail of mail is abruptly reduced in diameter, 5 pairs of lateral papillae, 20 pairs of pre-anal papillae.
females: vulva in 1st quarter of body |
|
|
Toxocara canis life cycle
|
may be direct or indirect via rodents.
direct: infective eggs swallowed by host, hatch in small intestine. Some 2nd stage juveniles enter hepatic portal system -> lungs via liver or heart -> next depends on age and species of host |
|
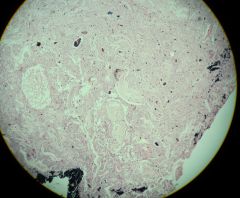
Enterobius vermicularis description
Pictured: adults in appendix |
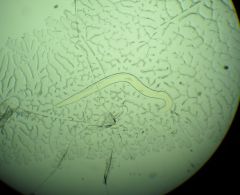
Human pinworm
3 lips like ascaris, no buccal capsule inflated cuticle at anterior end excretory pore basal end of esophagus has distinct bulb males haploid, females diploid pictured: male adult |
|

Geography of Enterobius vermicularis (Oxyuridae)?
pictured: female adult |
Cosmopolitan, but rare in tropics.
Found in 50% of US children |
|
|
How do you tell sex in Enterobius vermicularis?
|
males have curved tail at end. females are straight.
Also, females 2x large, 13mm vs 5mm. |
|
|
Enterobius vermicularis female morphology
|

Vulva slightly anterior to middle of body
two ovaries in amphidelphic arrangement w/single uterus may be spindle-shaped if gravid |
|
|
Enterobius vermicularis male morphology
spicule present? how many testes? |
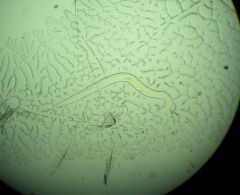
curved tail
single testis tail is broadly rounded, has single spicule lateral caudal alae |
|
|
Life cycle Enterobius vermicularis
Unusual among helminths! |
Direct.
At night gravid females exit anus, lay eggs, then crawl back in. Upon ingestion of the eggs, juveniles hatch and reach maturity in cecal region Eggs can be inhaled, very light. or person scratches irritated perianal area, spreading eggs and getting them on hands |
|
|
Enterobius vermicularis: what do the eggs look like?
|
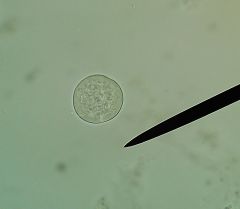
Round, no shell, not operculated. Boring, really.
light eggs are deposited by females at night around anus. Gross as hell. |
|
|
pathogenesis of Enterobius vermicularis
|

disease called enterobiassis
human pinworm eats epithelial cells and bacteria in intestinal tract. Low cost to host. Not symptomatic in small numbers. pictured: juvenile form |

