![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What constitutes a healthy, active lifestyle? |
A lifestyle that contributes positively to physical, mental and social wellbeing, and includes regular exercise and physical activity. |
|
|
Name three social, physical and mental benefits of a healthy, active lifestyle. |
SOCIAL Mix with others Make new friends Meet current friends Develop teamwork/cooperation Work with others MENTAL Relieve/Prevent stress and tension Mental challenge (Can I do it?) Increase self-esteem and confidence Help the individual feel good Contribute to the enjoyment of life Aesthetic appreciation PHYSICAL Contribute to good physical health Physical Challenge (Can I do it?) Increase fitness Improve performance Improve any of the HREs |
|
|
Describe how physical activity can: Increase individual wellbeing |
Sport can be a mental and physical challenge. Exercise can increase fitness levels through properly planned training, and can also cause weight-loss alongside a controlled diet. Sport can also provide a mental challenge, giving feelings of success when obstacles have been overcome. |
|
|
Describe how physical activity can: Help the individual feel good (serotonin levels) |
Exercise produces serotonin- the 'feel-good' hormone - so is beneficial to the mind. Weight loss and/or muscle gain can also help the individual look and therefore feel good. |
|
|
Describe how physical activity can: Help relieve stress and prevent stress-related illness |
Sport can provide a distraction from everyday life and relieve tension caused by school, work and family pressures. Cannot solve problems, but can make them easier to face by providing a complete distraction. |
|
|
Describe how physical activity can: Increase self-esteem and confidence |
Most physical activity is a physical challenge, which a participant might be proud to overcome, increasing self-esteem and confidence. Sport can also come with body confidence, as weight is lost, for example. |
|
|
Describe how physical activity can: Contribute to good health |
Sport improves the immune system, so participants are better at coping with illnesses such as the common cold and flu, but also more serious illness. Also improves the heart and lungs in various ways. |
|
|
Describe how physical activity can: Contribute to enjoyment of life |
Most sports are enjoyable, and people take part because they want to, however this can be affected by the reason for participation - someone forced to take part will not enjoy sport. |
|
|
Explain how participation in physical activity can stimulate: Co-operation |
Working in groups in team games improves teamwork and cooperation necessary for daily life, as it's important to encourage and support your team-mates. |
|
|
Explain how participation in physical activity can stimulate: Competition |
Most sports are competitive, and competition requires psychological preparation as well as being a distraction from daily life. |
|
|
Explain how participation in physical activity can stimulate: Physical Challenge |
Coming back to sport after a long time away, for example after an injury, can provide a very satisfying physical challenge to overcome. |
|
|
Explain how participation in physical activity can stimulate: Aesthetic Appreciation |
Moments in sport are sometimes beautiful, although this is not always appreciated as much as winning. Normally associated with dance, gym or ice-skating, but can also be for a delicate chip in golf or a perfect goal. Experienced by the performer or the observer. |
|
|
Explain how participation in physical activity can stimulate: The development of friendships and social mixing |
Most clubs have a strong social side, and sport means involvement with other people. Training with others can greatly help with motivation, developing old friendships and sparking new ones. |
|
|
Identify the six key influences on achieving sustained involvement in physical activity. |
People, image, cultural, resources, health and wellbeing, socio-economic |
|
|
Name the influences in: People |
Family, peers, role models |
|
|
Name the influences in: Image |
Fashion, media coverage |
|
|
Name the influences in: Cultural |
Age, disability, gender, race |
|
|
Name the influences in: Resources |
Access, availability, location, time |
|
|
Name the influences in: Health and Wellbeing |
Illness, health problems |
|
|
Name the influences in: Socio-Economic |
Cost, perceived status of the activity |
|
|
Name the 4 roles available to participants in physical activity. |
Leadership, officiating, volunteering, performing |
|
|
What are the qualities needed to be a: Leader? |
Enthusiastic Motivational Well-organised Sound knowledge of the sport Good analysis of performance Patience Good communication |
|
|
What are the qualities needed to be a: Official? |
Sound knowledge of rules Fitness Patience Good communicator Confidence Ability to apply rules fairly |
|
|
What are the qualities needed to be a: Volunteer? |
Don't need in depth knowledge of event but often helps Good communicator Patience Well-organised Enthusiastic Willing (to take on a variety of tasks in their spare time) |
|
|
What are the qualities needed to be a: Performer? |
Natural ability Motivation Determination Sound knowledge of rules and tactics Opportunity (to play) |
|
|
Explain the sports participation pyramid with regard to foundation, participation, performance, and elite stages. |
The size of the pyramid shows the amount of people at each level- the wider the base, the more people reach excellence at the top. Foundation Young children learning/experiencing basic sporting skills, for example school PE. Provides a basis for personal and future development in sport. Participation When young people begin to participate regularly in a specific activity for enjoyment. Could mean joining a sports club (which links to the next level). Performance Young people who concentrate on sport specific skills to develop talent in a specific sports. Quality coaching is essential at this level. Elite/Excellence Where individuals reach sporting excellence. Fewer people take part at this level, and governing bodies are responsible for development of players as they pass from county to regional to national squads. |
|
|
What are the three common purposes of initiatives? |
1) Increase participation in sport to improve health, with a focus on priority groups. 2) Retain people in sport through an effective network of clubs, sports, facilities, coaches, volunteers and competition. 3) Create opportunities for talented performers to achieve success. |
|
|
Name 3 initiatives involved in the provisions of opportunities for becoming, or remaining, involved in physical activity. |
Sport England Youth Sport Trust National governing bodies |
|
|
Explain health and how it relates to a balanced, healthy lifestyle and performance in activities. |
A state of complete mental, physical and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of disease and infirmity. Health can enhance performance (how well a task is carried out). Health can be improved by regular participation in physical activity, which also helps prevent illness. |
|
|
Explain fitness and how it relates to a balanced, healthy lifestyle and performance in activities. |
Ability to meet the demands of the environment. The environment can be everyday life, or the sporting environment. Fitness can be improved by regular exercise. No fitness can increase stress, which is not positive for a healthy, active lifestyle. |
|
|
Explain exercise and how it relates to a balanced, healthy lifestyle and performance in activities. |
A form of physical activity which maintains or improves health and/or physical fitness. Lack of exercise can cause hypokinetic diseases such as heart disease, high blood pressure and back pain. Can relieve stress and tension. Can increase fitness (see fitness card) |
|
|
What are the 5 components of HRE? |
Cardiovascular fitness Muscular strength Muscular endurance Flexibility Body composition |
|
|
What is cardiovascular fitness? Give an example of when it might be needed in sport. |
The ability to exercise the whole body for prolonged periods of time. Marathon running, or any game sport. Coping through long rehearsals (dance). Relevant example. |
|
|
What is muscular strength? Give an example of when it might be needed in sport. |
The amount of force a muscle can exert against a resistance. Scrum in rugby, or weight-lifting. Relevant example. |
|
|
What is muscular endurance? Give an example of when it might be needed in sport. |
The ability to use voluntary muscles multiple times without getting tired. Any repetitive game, e.g tennis or badminton.Relevant example. |
|
|
What is flexibility? Give an example of when it might be needed in sport. |

The range of movement around a joint. Kicking a football, or performing complex tricks in gymnastics or dance. Relevant example. |
|
|
What is body composition? Give an example of when it might be needed in sport. |
The percentage of body weight which is fat, muscle or bone. Different sports need different body types (see somatotypes). Relevant example. |
|
|
What are the 6 components of SRF? (ABC PRS) |
Agility Balance Co-ordination Power Reaction Time Speed |
|
|
What is agility? Give an example of when it might be needed in sport. |
The ability to change the position of the body quickly and to control the movement of the whole body. Relevant example. |
|
|
What is balance? Give an example of when it might be needed in sport. |
The ability to retain the body's centre of mass (gravity) above the base of support with reference to static (stationary) and dynamic (changing), conditions of movement, shape and orientation. Relevant example. |
|
|
What is co-ordination? Give an example of when it might be needed in sport. |
The ability to use two or more body parts together. Relevant example. |
|
|
What is power? Give an example of when it might be needed in sport. |
The ability to do strength performances quickly (power = strength x speed). Relevant example. |
|
|
What is reaction time? Give an example of when it might be needed in sport. |
The time between the presentation of a stimulus and the onset of a movement. Relevant example. |
|
|
What is speed? Give an example of when it might be needed in sport. |
The differential rate at which an individual is able to perform a movement or cover a distance in a period of time. Relevant example. |
|
|
What is a PAR-Q? |
Physical Activity Readiness Questionnaire |
|
|
What are three questions that may be asked in a PAR-Q? |
Have you ever been advised by your doctor that you have a heart condition? Do you ever feel pain in your chest when you do physical activity? Have you ever felt pain in your chest when you were not doing physical activity? Do you ever feel faint or have spells of dizziness? Do you have a bone or joint problem that could be made worse by exercise? Do you have high blood pressure? Are you currently taking any medication. Are you pregnant or have you had a baby in the last six months? Is there any other reason why you should not participate in physical activity? What is your date of birth? Signature from legal guardian (if under 16) and participant. |
|
|
What is the test for cardiovascular fitness? |
Cooper's 12-minute run test |
|
|
What is the test for muscular strength? |
Hand grip strength test |
|
|
What is the test for flexibility? |
Sit and reach flexibility test |
|
|
What is the test for muscular and cardiovascular endurance? |
Harvard Step Test Treadmill Test |
|
|
What is the test for agility? |
Illinois agility run |
|
|
What is the test for balance? |
Standing stork test |
|
|
What is the test for power? |
Sergeant jump test |
|
|
What is the test for reaction time? |
Ruler drop test |
|
|
What is the test for speed? |
30-metre sprint |
|
|
What is the test for co-ordination |
Three ball juggle (or two ball bounce test) |
|
|
What is the second test for power? |
Standing broad jump |
|
|
What are the principles of training (SPORI), and how can you apply them to a training session? |
Specificity Matching training to the requirements of an activity. Progressive Overload Gradually increasing the amount of overload so as to gain fitness without the risk of injury. Rest and Recover The body can only recover and adapt while resting. Individual Needs/Differences Training should be focused on an individual's skills and areas of weakness to avoid injury and improve performance. Based on body build, sport (and position) and personal aims. |
|
|
What does FITT stand for? |
Frequency Intensity Time Type |
|
|
What is reversibility, why might it occur and how might it impact performance? |
Any adaptation that takes place as a consequence of training will be reversed when you stop training. Performance will decrease due to reversibility. |
|
|
What does SMART stand for? Explain each word's meaning. |
Specific Same as specificity, must be specific to the individual's aims, abilities, position and sport. Measurable Must be able to measure whether you have achieved your target (e.g decrease the amount of time taken to run the 100m BY 3 SECONDS) Achievable Must be able to achieve your goal, for example, not aiming to run a marathon after running 6 miles twice. Realistic A goal may be achievable, but for it to be realistic a performer must have the resources and availability to complete the training. Time-Bound Setting a deadline stops procrastination, for example: must complete within 6 weeks. |
|
|
What is interval training? |
High intensity periods of work followed by defined periods of rest. Can be made specific to a player's sport. Include rest and recovery. Controlling the amount of rest allows for higher intensity work (FITT). |
|
|
What is continuous training? |
Steady training, where the working heart rate is not very high (intensity), there are no rest periods and a session usually lasts for at least 15 to 20 minutes (time). |
|
|
What is Fartlek training? |
Training that allows an athlete to run at varying speeds, over unmeasured distances, or on different terrain. Fartlek is Swedish for 'Speed Play'. Suitable for most game sports, and very similar to interval training. |
|
|
What is circuit training? What can it be used to improve? |
A set of 6 to 10 exercises performed at stations in an organised pattern. Each exercise is performed for a specified number of repetitions or for a prescribed time before moving on to the next exercise. Can be used to improve elements of HRE or SRF, or improve specific skills. Exercises should be organised by muscle group used, e.g not two arm exercises next to one another. |
|
|
What is weight training? |
Using progressive resistance, by increasing weight or repetitions, to increase muscular strength, muscular endurance, speed, muscle bulk and rehabilitate after illness or injury. |
|
|
What is cross training? What are the three main benefits? |
Using more than one training method. Breaks up the monotony of using a single training method. Helps to reduce the stresses on the body which can result from a single training method. Can be more easily adapted to suit individual needs. |
|
|
What is the safest weight to use in weight training? |
The safest weight to use is about 40 to 50 per cent of the five repetition max (or rep max (RM)). |
|
|
What is the RM? |
RM is the maximum weight a person can lift, so five rep max is the maximum weight a person can lift five times. |
|
|
How many reps per set are commonly used in weight training? |
10 reps per set are commonly used, but can be altered. |
|
|
How long should a single rep last in weight training? |
Weights should be controlled rather than quick (1.5 to 2.0 secs). |
|
|
How long should recovery be between sets and between workouts in weight training? |
Recovery between sets is normally 1-2 minutes. One rest day between workouts. |
|
|
What can interval training be used to improve? Give four sports which may therefore use interval training. |
Speed and muscular endurance. Swimming, athletics, football, hockey. |
|
|
What can continuous training be used to improve? Give three sports which may therefore use continuous training. |
Cardiovascular endurance. Cycling, swimming, marathon running (although cross training is more likely). |
|
|
What can Fartlek training be used to improve? Give three sports which may therefore use Fartlek training. |
Aerobic and anaerobic fitness. Football, netball, hockey. |
|
|
What can circuit training be used to improve? Give four sports which may therefore use circuit training. |
Local muscular endurance, cardiovascular fitness, circulo-respiratory fitness (i.e. the heart, the blood, the blood vessels and the lungs). Any of the HRFs or SREs. Skills circuit can also improve a variety of skills for all sports. Football, boxing, badminton, tennis. |
|
|
What can weight training be used to improve?Give two sports which may therefore use weight training. |
Muscular strength, muscular endurance, speed, muscle bulk and to rehabilitate after illness or injury. Athletics (sprinting, long jump), rugby. |
|
|
What can cross training be used to improve? Give two sports which may therefore use cross training. |
All round fitness, with reduced monotony and stresses on the body from repetition. Sprinters (for power, strength, speed) Racket games, tennis (for speed, muscular endurance). Any sport with a justified answer. |
|
|
How would an experienced marathon runner's fitness session differ from that of a newcomer's? |
The experienced marathon runner would have much longer sessions, with a higher intensity and less rest and recovery, whereas the newcomer would have shorter session with a lower intensity and more rest and recovery to improve their muscles. |
|
|
What are the three main components of a training session? |
Warm-up Main activity Cool-down |
|
|
What is the purpose of a warm-up in a training session? (4 points) |
Prevent injury Improve performance Practise skills before the event/match/game. Prepare psychologically for the event. |
|
|
Describe and explain the three main phases of a warm-up. |
Pulse-Raiser To gradually increase body temperature and heart rate, and improve the exchange of oxygen from haemoglobin. Stretching Static stretching (easy for about 10-15 seconds) and dynamic (ballistic) (bouncing, although not recommended by some coaches). To reduce the risk of injury to muscles. Specific Skills Practise Practising individual shots or skills. |
|
|
What is the purpose of the main activity in a training session? |
To improve the body's fitness in specific areas using a method of training. Could be the main training activity, or the main game/event. |
|
|
What is the purpose of a cool-down in a training session? |
To gradually return the body to its normal resting heart rate and temperature. Most important after an anaerobic training session. Disperses lactic acid to prevent stiffness and soreness in the muscles. |
|
|
What may be included in a typical cool-down? |
10-15 minutes lowering heart rate (may include activities seen in warm-up, such as jogging). 10-15 minutes stretching (or longer) of static stretching (held for around 30-35 seconds). 10-15 minutes relaxation. |
|
|
Name the methods of training which can involve aerobic AND anaerobic respiration. |
Circuit training Cross training Fartlek training |
|
|
Name the methods of training which involve aerobic respiration. |
Continuous training Weight training |
|
|
Name the methods of training which involve anaerobic respiration. |
Interval training |
|
|
What is resting heart rate? |
The number of times that the heart beats per minute (BPM) during rest. |
|
|
What is working heart rate? |
The number of times that the heart beats per minute (BPM) during/immediately after exercise/activity. |
|
|
What is recovery rate? |
The measure of how long it takes for a person's heart rate to return to its resting level after a training session. |
|
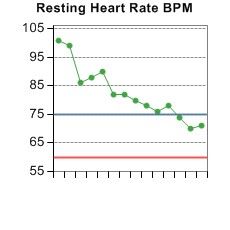
What does this resting heart rate graph show? |
It shows an improvement of cardiovascular fitness, as the amount of blood the heart can pump per beat (stroke volume) has increased, meaning less beats per minute are needed to supply the same amount of blood/oxygen to the muscles. This shows that the heart is stronger and healthier. |
|

At what point on the graph is the performer at their resting heart rate? |
0 minutes and 12 minutes |
|

At what point on the graph is the performer in their anaerobic threshold? |
1 minute |
|

At what point on the graph is the performer in their aerobic threshold? |
Between 1.5 minutes and 5 minutes. |
|

How long is the performer's recovery rate? |
11 minutes (from 1 minute to 12 minutes) |
|

How long is the performer in their target zone (aerobic threshold)? |
3.5 minutes |

