![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
643 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Nitogen cycle
|
Convert nitrogen into useable forms
- soil bacteria convert nitrogen into ammonium -soil bacteria convert ammonium into nitrate - plants absorb both forms of nitrogen - bacteria converts nitrate back into nitrogen gas into atmosphere - Excess nitrate and ammonium eventually enter the lithosphere - |
Plants- N2- NH4+- NO3-
|
|
|
Water cycle
|
Ice and snow- ground water- run off- ocean water- evaporation - sun - condensation - precipitation
|
|
|
|
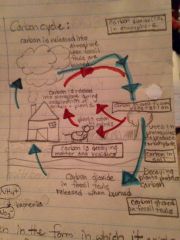
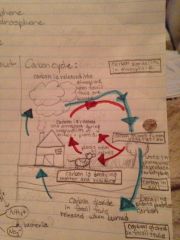
Carbon cycle
|
Carbon released into atmosphere when fossil fuels burned
-carbon stored in vegetation - used in photosynthesis to produce carbohydrates -carbon in soil - decaying plants produce carbon -carbon stored in fossil fuels and released when burned -plants eaton by animals - carbon released into atmosphere during respiration of animals and plants - into vegetation again - |
|
|
|
Phosphorus cycle
|
Stored in lithosphere
-rocks break and phosphate is released into soil -phosphate absorbed by plants through roots - bacteria break down dead organisms releasing phosphate back in soil |
Causes EUTROPHICATION ( deposits of excess nutrients)
Ex. Lake Erie, overgrowth in algae by 30 times upsetting natural balances |
|
|
Abiotic
|
Non-living factors/parts of an ecosystem
|
ex. Water, oxygen, light, nutrients, soil, rock
|
|
|
Biotic
|
Living part of an ecosystem
|
Ex. Animals, plants, bacteria
|
|
|
Symbiosis
|
Interaction between members of 2 different species
|
Fish eating bacteria off of shark
|
|
|
Predation
|
1 organism eats/consumes another organism for food
|
|
|
|
Competition
|
2 or more organisms compete for the same resource
|
|
|
|
Sustainable ecosystem
|
An ecosystem capable of withstanding pressure and giving support to a variety of organisms
|
|
|
|
Sustainable ecosystem
|
An ecosystem capable of withstanding pressure and giving support to a variety of organisms
|
|
|
|
Ecosystem
|
All things interact: all interacting parts of a biological community and its environment
|
|
|
|
Sustainable ecosystem
|
An ecosystem capable of withstanding pressure and giving support to a variety of organisms
|
|
|
|
Ecosystem
|
All things interact: all interacting parts of a biological community and its environment
|
|
|
|
Mutualism
|
An interaction where both organisms benefit
|
Coral and algae ( algae gives coral colour and coral gives algae food)
|
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Restoration Ecology
|
Renewal of degraded ecosystems through human intervention
|
Don Valley Brick Works
- bricks made from crushed rock from quarry - quarry filled, landscaped, 3 ponds water from Mud Creek -stream passes through site, first pond captures sediment carried by current -plants in other 2 ponds filter before it flows in Lake Ontario |
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Restoration Ecology
|
Renewal of degraded ecosystems through human intervention
|
Don Valley Brick Works
- bricks made from crushed rock from quarry - quarry filled, landscaped, 3 ponds water from Mud Creek -stream passes through site, first pond captures sediment carried by current -plants in other 2 ponds filter before it flows in Lake Ontario |
|
|
Restoration Methods
|
- reforestation
- wetland restoration |
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Restoration Ecology
|
Renewal of degraded ecosystems through human intervention
|
Don Valley Brick Works
- bricks made from crushed rock from quarry - quarry filled, landscaped, 3 ponds water from Mud Creek -stream passes through site, first pond captures sediment carried by current -plants in other 2 ponds filter before it flows in Lake Ontario |
|
|
Restoration Methods
|
- reforestation
- wetland restoration |
|
|
|
Biocontrol
|
Introducing a species thats eats off the alien species
|
Controlling alien species
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Restoration Ecology
|
Renewal of degraded ecosystems through human intervention
|
Don Valley Brick Works
- bricks made from crushed rock from quarry - quarry filled, landscaped, 3 ponds water from Mud Creek -stream passes through site, first pond captures sediment carried by current -plants in other 2 ponds filter before it flows in Lake Ontario |
|
|
Restoration Methods
|
- reforestation
- wetland restoration |
|
|
|
Biocontrol
|
Introducing a species thats eats off the alien species
|
Controlling alien species
|
|
|
Chemicals
|
Langara Island
Nesting sea birds and burrowing species -2 alien species of rats - ate birds eggs and nesting( bird pop declined) - poisoning campaign succeeded - ravens and shrews affected by poison -1996 rats eliminated from Island |
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Restoration Ecology
|
Renewal of degraded ecosystems through human intervention
|
Don Valley Brick Works
- bricks made from crushed rock from quarry - quarry filled, landscaped, 3 ponds water from Mud Creek -stream passes through site, first pond captures sediment carried by current -plants in other 2 ponds filter before it flows in Lake Ontario |
|
|
Restoration Methods
|
- reforestation
- wetland restoration |
|
|
|
Biocontrol
|
Introducing a species thats eats off the alien species
|
Controlling alien species
|
|
|
Chemicals
|
Langara Island
Nesting sea birds and burrowing species -2 alien species of rats - ate birds eggs and nesting( bird pop declined) - poisoning campaign succeeded - ravens and shrews affected by poison -1996 rats eliminated from Island |
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Bioremediation
|
Intro to living plants to clean and revegetate soil at toxic sites
|
|
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Restoration Ecology
|
Renewal of degraded ecosystems through human intervention
|
Don Valley Brick Works
- bricks made from crushed rock from quarry - quarry filled, landscaped, 3 ponds water from Mud Creek -stream passes through site, first pond captures sediment carried by current -plants in other 2 ponds filter before it flows in Lake Ontario |
|
|
Restoration Methods
|
- reforestation
- wetland restoration |
|
|
|
Biocontrol
|
Introducing a species thats eats off the alien species
|
Controlling alien species
|
|
|
Chemicals
|
Langara Island
Nesting sea birds and burrowing species -2 alien species of rats - ate birds eggs and nesting( bird pop declined) - poisoning campaign succeeded - ravens and shrews affected by poison -1996 rats eliminated from Island |
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Bioremediation
|
Intro to living plants to clean and revegetate soil at toxic sites
|
|
|
|
Bioaugmentation
|
Use of organism ti add nutrients to depleted soil
|
Clover can replenish nitrogen
|
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Restoration Ecology
|
Renewal of degraded ecosystems through human intervention
|
Don Valley Brick Works
- bricks made from crushed rock from quarry - quarry filled, landscaped, 3 ponds water from Mud Creek -stream passes through site, first pond captures sediment carried by current -plants in other 2 ponds filter before it flows in Lake Ontario |
|
|
Restoration Methods
|
- reforestation
- wetland restoration |
|
|
|
Biocontrol
|
Introducing a species thats eats off the alien species
|
Controlling alien species
|
|
|
Chemicals
|
Langara Island
Nesting sea birds and burrowing species -2 alien species of rats - ate birds eggs and nesting( bird pop declined) - poisoning campaign succeeded - ravens and shrews affected by poison -1996 rats eliminated from Island |
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Bioremediation
|
Intro to living plants to clean and revegetate soil at toxic sites
|
|
|
|
Bioaugmentation
|
Use of organism ti add nutrients to depleted soil
|
Clover can replenish nitrogen
|
|
|
Measuring Biodiversity
|
Canopy fogging, quadrat sampling, transect sampling, netting
|
|
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Restoration Ecology
|
Renewal of degraded ecosystems through human intervention
|
Don Valley Brick Works
- bricks made from crushed rock from quarry - quarry filled, landscaped, 3 ponds water from Mud Creek -stream passes through site, first pond captures sediment carried by current -plants in other 2 ponds filter before it flows in Lake Ontario |
|
|
Restoration Methods
|
- reforestation
- wetland restoration |
|
|
|
Biocontrol
|
Introducing a species thats eats off the alien species
|
Controlling alien species
|
|
|
Chemicals
|
Langara Island
Nesting sea birds and burrowing species -2 alien species of rats - ate birds eggs and nesting( bird pop declined) - poisoning campaign succeeded - ravens and shrews affected by poison -1996 rats eliminated from Island |
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Bioremediation
|
Intro to living plants to clean and revegetate soil at toxic sites
|
|
|
|
Bioaugmentation
|
Use of organism ti add nutrients to depleted soil
|
Clover can replenish nitrogen
|
|
|
Measuring Biodiversity
|
Canopy fogging, quadrat sampling, transect sampling, netting
|
|
|
|
Canopy fogging
|
Low dose of insecticide
Insects fall and collected on screen Keep and observe some insects |
|
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Restoration Ecology
|
Renewal of degraded ecosystems through human intervention
|
Don Valley Brick Works
- bricks made from crushed rock from quarry - quarry filled, landscaped, 3 ponds water from Mud Creek -stream passes through site, first pond captures sediment carried by current -plants in other 2 ponds filter before it flows in Lake Ontario |
|
|
Restoration Methods
|
- reforestation
- wetland restoration |
|
|
|
Biocontrol
|
Introducing a species thats eats off the alien species
|
Controlling alien species
|
|
|
Chemicals
|
Langara Island
Nesting sea birds and burrowing species -2 alien species of rats - ate birds eggs and nesting( bird pop declined) - poisoning campaign succeeded - ravens and shrews affected by poison -1996 rats eliminated from Island |
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Bioremediation
|
Intro to living plants to clean and revegetate soil at toxic sites
|
|
|
|
Bioaugmentation
|
Use of organism ti add nutrients to depleted soil
|
Clover can replenish nitrogen
|
|
|
Measuring Biodiversity
|
Canopy fogging, quadrat sampling, transect sampling, netting
|
|
|
|
Canopy fogging
|
Low dose of insecticide
Insects fall and collected on screen Keep and observe some insects |
|
|
|
Quadrat sampling
|
Square area made of plastic and different species counted
|
|
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Restoration Ecology
|
Renewal of degraded ecosystems through human intervention
|
Don Valley Brick Works
- bricks made from crushed rock from quarry - quarry filled, landscaped, 3 ponds water from Mud Creek -stream passes through site, first pond captures sediment carried by current -plants in other 2 ponds filter before it flows in Lake Ontario |
|
|
Restoration Methods
|
- reforestation
- wetland restoration |
|
|
|
Biocontrol
|
Introducing a species thats eats off the alien species
|
Controlling alien species
|
|
|
Chemicals
|
Langara Island
Nesting sea birds and burrowing species -2 alien species of rats - ate birds eggs and nesting( bird pop declined) - poisoning campaign succeeded - ravens and shrews affected by poison -1996 rats eliminated from Island |
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Bioremediation
|
Intro to living plants to clean and revegetate soil at toxic sites
|
|
|
|
Bioaugmentation
|
Use of organism ti add nutrients to depleted soil
|
Clover can replenish nitrogen
|
|
|
Measuring Biodiversity
|
Canopy fogging, quadrat sampling, transect sampling, netting
|
|
|
|
Canopy fogging
|
Low dose of insecticide
Insects fall and collected on screen Keep and observe some insects |
|
|
|
Quadrat sampling
|
Square area made of plastic and different species counted
|
|
|
|
Transect sampling
|
Using a transect line, a rope or measuring tape which is unrolled within habitat to count at every interval
|
|
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Restoration Ecology
|
Renewal of degraded ecosystems through human intervention
|
Don Valley Brick Works
- bricks made from crushed rock from quarry - quarry filled, landscaped, 3 ponds water from Mud Creek -stream passes through site, first pond captures sediment carried by current -plants in other 2 ponds filter before it flows in Lake Ontario |
|
|
Restoration Methods
|
- reforestation
- wetland restoration |
|
|
|
Biocontrol
|
Introducing a species thats eats off the alien species
|
Controlling alien species
|
|
|
Chemicals
|
Langara Island
Nesting sea birds and burrowing species -2 alien species of rats - ate birds eggs and nesting( bird pop declined) - poisoning campaign succeeded - ravens and shrews affected by poison -1996 rats eliminated from Island |
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Bioremediation
|
Intro to living plants to clean and revegetate soil at toxic sites
|
|
|
|
Bioaugmentation
|
Use of organism ti add nutrients to depleted soil
|
Clover can replenish nitrogen
|
|
|
Measuring Biodiversity
|
Canopy fogging, quadrat sampling, transect sampling, netting
|
|
|
|
Canopy fogging
|
Low dose of insecticide
Insects fall and collected on screen Keep and observe some insects |
|
|
|
Quadrat sampling
|
Square area made of plastic and different species counted
|
|
|
|
Transect sampling
|
Using a transect line, a rope or measuring tape which is unrolled within habitat to count at every interval
|
|
|
|
Netting
|
Mesh nets used to capture birds in terrestrial and fish in aquatic ecosystems
|
|
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Restoration Ecology
|
Renewal of degraded ecosystems through human intervention
|
Don Valley Brick Works
- bricks made from crushed rock from quarry - quarry filled, landscaped, 3 ponds water from Mud Creek -stream passes through site, first pond captures sediment carried by current -plants in other 2 ponds filter before it flows in Lake Ontario |
|
|
Restoration Methods
|
- reforestation
- wetland restoration |
|
|
|
Biocontrol
|
Introducing a species thats eats off the alien species
|
Controlling alien species
|
|
|
Chemicals
|
Langara Island
Nesting sea birds and burrowing species -2 alien species of rats - ate birds eggs and nesting( bird pop declined) - poisoning campaign succeeded - ravens and shrews affected by poison -1996 rats eliminated from Island |
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Bioremediation
|
Intro to living plants to clean and revegetate soil at toxic sites
|
|
|
|
Bioaugmentation
|
Use of organism ti add nutrients to depleted soil
|
Clover can replenish nitrogen
|
|
|
Measuring Biodiversity
|
Canopy fogging, quadrat sampling, transect sampling, netting
|
|
|
|
Canopy fogging
|
Low dose of insecticide
Insects fall and collected on screen Keep and observe some insects |
|
|
|
Quadrat sampling
|
Square area made of plastic and different species counted
|
|
|
|
Transect sampling
|
Using a transect line, a rope or measuring tape which is unrolled within habitat to count at every interval
|
|
|
|
Netting
|
Mesh nets used to capture birds in terrestrial and fish in aquatic ecosystems
|
|
|
|
Hotspots
|
Large # of species in small area
|
Ex. Leitrim Wetlands and Carolinian Canada
|
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Restoration Ecology
|
Renewal of degraded ecosystems through human intervention
|
Don Valley Brick Works
- bricks made from crushed rock from quarry - quarry filled, landscaped, 3 ponds water from Mud Creek -stream passes through site, first pond captures sediment carried by current -plants in other 2 ponds filter before it flows in Lake Ontario |
|
|
Restoration Methods
|
- reforestation
- wetland restoration |
|
|
|
Biocontrol
|
Introducing a species thats eats off the alien species
|
Controlling alien species
|
|
|
Chemicals
|
Langara Island
Nesting sea birds and burrowing species -2 alien species of rats - ate birds eggs and nesting( bird pop declined) - poisoning campaign succeeded - ravens and shrews affected by poison -1996 rats eliminated from Island |
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Bioremediation
|
Intro to living plants to clean and revegetate soil at toxic sites
|
|
|
|
Bioaugmentation
|
Use of organism ti add nutrients to depleted soil
|
Clover can replenish nitrogen
|
|
|
Measuring Biodiversity
|
Canopy fogging, quadrat sampling, transect sampling, netting
|
|
|
|
Canopy fogging
|
Low dose of insecticide
Insects fall and collected on screen Keep and observe some insects |
|
|
|
Quadrat sampling
|
Square area made of plastic and different species counted
|
|
|
|
Transect sampling
|
Using a transect line, a rope or measuring tape which is unrolled within habitat to count at every interval
|
|
|
|
Netting
|
Mesh nets used to capture birds in terrestrial and fish in aquatic ecosystems
|
|
|
|
Hotspots
|
Large # of species in small area
|
Ex. Leitrim Wetlands and Carolinian Canada
|
|
|
Deforestation
|
Clearing forests fir logging or other human uses and never replanting them
|
|
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Restoration Ecology
|
Renewal of degraded ecosystems through human intervention
|
Don Valley Brick Works
- bricks made from crushed rock from quarry - quarry filled, landscaped, 3 ponds water from Mud Creek -stream passes through site, first pond captures sediment carried by current -plants in other 2 ponds filter before it flows in Lake Ontario |
|
|
Restoration Methods
|
- reforestation
- wetland restoration |
|
|
|
Biocontrol
|
Introducing a species thats eats off the alien species
|
Controlling alien species
|
|
|
Chemicals
|
Langara Island
Nesting sea birds and burrowing species -2 alien species of rats - ate birds eggs and nesting( bird pop declined) - poisoning campaign succeeded - ravens and shrews affected by poison -1996 rats eliminated from Island |
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Bioremediation
|
Intro to living plants to clean and revegetate soil at toxic sites
|
|
|
|
Bioaugmentation
|
Use of organism ti add nutrients to depleted soil
|
Clover can replenish nitrogen
|
|
|
Measuring Biodiversity
|
Canopy fogging, quadrat sampling, transect sampling, netting
|
|
|
|
Canopy fogging
|
Low dose of insecticide
Insects fall and collected on screen Keep and observe some insects |
|
|
|
Quadrat sampling
|
Square area made of plastic and different species counted
|
|
|
|
Transect sampling
|
Using a transect line, a rope or measuring tape which is unrolled within habitat to count at every interval
|
|
|
|
Netting
|
Mesh nets used to capture birds in terrestrial and fish in aquatic ecosystems
|
|
|
|
Hotspots
|
Large # of species in small area
|
Ex. Leitrim Wetlands and Carolinian Canada
|
|
|
Deforestation
|
Clearing forests fir logging or other human uses and never replanting them
|
|
|
|
Alien species
|
A species that is accidentally or deliberately introduced into a new location
|
Ex. Zebra mussels
Usually arrive in shipments of food and goods |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Restoration Ecology
|
Renewal of degraded ecosystems through human intervention
|
Don Valley Brick Works
- bricks made from crushed rock from quarry - quarry filled, landscaped, 3 ponds water from Mud Creek -stream passes through site, first pond captures sediment carried by current -plants in other 2 ponds filter before it flows in Lake Ontario |
|
|
Restoration Methods
|
- reforestation
- wetland restoration |
|
|
|
Biocontrol
|
Introducing a species thats eats off the alien species
|
Controlling alien species
|
|
|
Chemicals
|
Langara Island
Nesting sea birds and burrowing species -2 alien species of rats - ate birds eggs and nesting( bird pop declined) - poisoning campaign succeeded - ravens and shrews affected by poison -1996 rats eliminated from Island |
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Bioremediation
|
Intro to living plants to clean and revegetate soil at toxic sites
|
|
|
|
Bioaugmentation
|
Use of organism ti add nutrients to depleted soil
|
Clover can replenish nitrogen
|
|
|
Measuring Biodiversity
|
Canopy fogging, quadrat sampling, transect sampling, netting
|
|
|
|
Canopy fogging
|
Low dose of insecticide
Insects fall and collected on screen Keep and observe some insects |
|
|
|
Quadrat sampling
|
Square area made of plastic and different species counted
|
|
|
|
Transect sampling
|
Using a transect line, a rope or measuring tape which is unrolled within habitat to count at every interval
|
|
|
|
Netting
|
Mesh nets used to capture birds in terrestrial and fish in aquatic ecosystems
|
|
|
|
Hotspots
|
Large # of species in small area
|
Ex. Leitrim Wetlands and Carolinian Canada
|
|
|
Deforestation
|
Clearing forests fir logging or other human uses and never replanting them
|
|
|
|
Alien species
|
A species that is accidentally or deliberately introduced into a new location
|
Ex. Zebra mussels
Usually arrive in shipments of food and goods |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Invasive species
|
A species that can take over the habitat of a native species
|
Ex. Zebra mussels decreased the pop. of crustaceans which lead to a decrease in fish
BALLAST WATERS |
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Restoration Ecology
|
Renewal of degraded ecosystems through human intervention
|
Don Valley Brick Works
- bricks made from crushed rock from quarry - quarry filled, landscaped, 3 ponds water from Mud Creek -stream passes through site, first pond captures sediment carried by current -plants in other 2 ponds filter before it flows in Lake Ontario |
|
|
Restoration Methods
|
- reforestation
- wetland restoration |
|
|
|
Biocontrol
|
Introducing a species thats eats off the alien species
|
Controlling alien species
|
|
|
Chemicals
|
Langara Island
Nesting sea birds and burrowing species -2 alien species of rats - ate birds eggs and nesting( bird pop declined) - poisoning campaign succeeded - ravens and shrews affected by poison -1996 rats eliminated from Island |
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Bioremediation
|
Intro to living plants to clean and revegetate soil at toxic sites
|
|
|
|
Bioaugmentation
|
Use of organism ti add nutrients to depleted soil
|
Clover can replenish nitrogen
|
|
|
Measuring Biodiversity
|
Canopy fogging, quadrat sampling, transect sampling, netting
|
|
|
|
Canopy fogging
|
Low dose of insecticide
Insects fall and collected on screen Keep and observe some insects |
|
|
|
Quadrat sampling
|
Square area made of plastic and different species counted
|
|
|
|
Transect sampling
|
Using a transect line, a rope or measuring tape which is unrolled within habitat to count at every interval
|
|
|
|
Netting
|
Mesh nets used to capture birds in terrestrial and fish in aquatic ecosystems
|
|
|
|
Hotspots
|
Large # of species in small area
|
Ex. Leitrim Wetlands and Carolinian Canada
|
|
|
Deforestation
|
Clearing forests fir logging or other human uses and never replanting them
|
|
|
|
Alien species
|
A species that is accidentally or deliberately introduced into a new location
|
Ex. Zebra mussels
Usually arrive in shipments of food and goods |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Invasive species
|
A species that can take over the habitat of a native species
|
Ex. Zebra mussels decreased the pop. of crustaceans which lead to a decrease in fish
BALLAST WATERS |
|
|
Overexploitation
|
Overuse of a resource until its depleted
|
Ex. Pigeon overhunting lead to extinction
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Restoration Ecology
|
Renewal of degraded ecosystems through human intervention
|
Don Valley Brick Works
- bricks made from crushed rock from quarry - quarry filled, landscaped, 3 ponds water from Mud Creek -stream passes through site, first pond captures sediment carried by current -plants in other 2 ponds filter before it flows in Lake Ontario |
|
|
Restoration Methods
|
- reforestation
- wetland restoration |
|
|
|
Biocontrol
|
Introducing a species thats eats off the alien species
|
Controlling alien species
|
|
|
Chemicals
|
Langara Island
Nesting sea birds and burrowing species -2 alien species of rats - ate birds eggs and nesting( bird pop declined) - poisoning campaign succeeded - ravens and shrews affected by poison -1996 rats eliminated from Island |
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Bioremediation
|
Intro to living plants to clean and revegetate soil at toxic sites
|
|
|
|
Bioaugmentation
|
Use of organism ti add nutrients to depleted soil
|
Clover can replenish nitrogen
|
|
|
Measuring Biodiversity
|
Canopy fogging, quadrat sampling, transect sampling, netting
|
|
|
|
Canopy fogging
|
Low dose of insecticide
Insects fall and collected on screen Keep and observe some insects |
|
|
|
Quadrat sampling
|
Square area made of plastic and different species counted
|
|
|
|
Transect sampling
|
Using a transect line, a rope or measuring tape which is unrolled within habitat to count at every interval
|
|
|
|
Netting
|
Mesh nets used to capture birds in terrestrial and fish in aquatic ecosystems
|
|
|
|
Hotspots
|
Large # of species in small area
|
Ex. Leitrim Wetlands and Carolinian Canada
|
|
|
Deforestation
|
Clearing forests fir logging or other human uses and never replanting them
|
|
|
|
Alien species
|
A species that is accidentally or deliberately introduced into a new location
|
Ex. Zebra mussels
Usually arrive in shipments of food and goods |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Invasive species
|
A species that can take over the habitat of a native species
|
Ex. Zebra mussels decreased the pop. of crustaceans which lead to a decrease in fish
BALLAST WATERS |
|
|
Overexploitation
|
Overuse of a resource until its depleted
|
Ex. Pigeon overhunting lead to extinction
|
|
|
Carrying Capacity
|
Size of population supported by resources in ecosystem/ equilibrium
|
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Greenhouse gases and Greenhouse Effect
|
Atmospheric gases that trap heat from leaving atmosphere
|
Moderate Earth's tempuratures
- Kyoto Protocol |
|
|
Photosynthesis
|
Converting sun energy into food
|
6CO2+6H2O--> C6H12O6+ 6O2
|
|
|
Acid precipitation
|
Fossil fuels are released and burned and gases + water in atmosphere
- falls as rain, sleet, or snow |
Nitrogen and sulfur dioxide= by products
|
|
|
Measuring pH
|
How acidic or basic something is
|
7=neutral, closer to 0=more acidic
|
|
|
Cellular respiration
|
Aerobic condition
- oxygen present |
C6H12O6+6CO2--> 6CO2+6H2O+energy/energy out
|
|
|
Bioaccumulation
|
Ingestion of toxins at a rate faster than eliminated
|
|
|
|
Biomagnification
|
Increase in concentration of a toxin as it moves up trophic levels
|
DDT affected hardness of egg shells so when mother bird sat on eggs for warmth they cracked.
-PCBs |
|
|
Environmental stewardship
|
Idea humans are responsible for looking after property and species
|
|
|
|
Restoration Ecology
|
Renewal of degraded ecosystems through human intervention
|
Don Valley Brick Works
- bricks made from crushed rock from quarry - quarry filled, landscaped, 3 ponds water from Mud Creek -stream passes through site, first pond captures sediment carried by current -plants in other 2 ponds filter before it flows in Lake Ontario |
|
|
Restoration Methods
|
- reforestation
- wetland restoration |
|
|
|
Biocontrol
|
Introducing a species thats eats off the alien species
|
Controlling alien species
|
|
|
Chemicals
|
Langara Island
Nesting sea birds and burrowing species -2 alien species of rats - ate birds eggs and nesting( bird pop declined) - poisoning campaign succeeded - ravens and shrews affected by poison -1996 rats eliminated from Island |
|
|
|
Trophic levels
|
Amount if energy moving from one level to another
|
Producer>primary consumer>secondary consumer> tertiary consumer
10% moves from each level |
|
|
Bioremediation
|
Intro to living plants to clean and revegetate soil at toxic sites
|
|
|
|
Bioaugmentation
|
Use of organism ti add nutrients to depleted soil
|
Clover can replenish nitrogen
|
|
|
Measuring Biodiversity
|
Canopy fogging, quadrat sampling, transect sampling, netting
|
|
|
|
Canopy fogging
|
Low dose of insecticide
Insects fall and collected on screen Keep and observe some insects |
|
|
|
Quadrat sampling
|
Square area made of plastic and different species counted
|
|
|
|
Transect sampling
|
Using a transect line, a rope or measuring tape which is unrolled within habitat to count at every interval
|
|
|
|
Netting
|
Mesh nets used to capture birds in terrestrial and fish in aquatic ecosystems
|
|
|
|
Hotspots
|
Large # of species in small area
|
Ex. Leitrim Wetlands and Carolinian Canada
|
|
|
Deforestation
|
Clearing forests fir logging or other human uses and never replanting them
|
|
|
|
Alien species
|
A species that is accidentally or deliberately introduced into a new location
|
Ex. Zebra mussels
Usually arrive in shipments of food and goods |
|
|
Consumer
|
Cant make own food
|
Ex. Bear, fox, fish
|
|
|
Invasive species
|
A species that can take over the habitat of a native species
|
Ex. Zebra mussels decreased the pop. of crustaceans which lead to a decrease in fish
BALLAST WATERS |
|
|
Overexploitation
|
Overuse of a resource until its depleted
|
Ex. Pigeon overhunting lead to extinction
|
|
|
Carrying Capacity
|
Size of population supported by resources in ecosystem/ equilibrium
|
|
|
|
Exponential growth
|
Accelerating growth thats produces a J shaped curve when its graphed against time
|
|
|
|
Herbivore
|
Eats vegetation
|
Ex. Deer, rabbit
|
|
|
Carnivore
|
Eats meat and animals
|
Ex. Lion
|
|
|
Omnivore
|
Eats both plants and animals
|
Ex. Bear
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
Moves nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex.Mushroom
|
|
|
Scavenger
|
Eats dead things while moving nutrients back to abiotic parts
|
Ex. Vulture
|
|
|
Effects of acid precipitation
|
-forest soils lose valuable nutrients
- increases in metals in soil interferes with nutrient uptake -devastating to aquatic ecosystems |
|
|
|
Exponential growth
|
Accelerating growth thats produces a J shaped curve when its graphed against time
|
Wild turkeys were plentiful until over hunting and DEFORESTATION
|
|
|
Humans and C. C
|
Humans alter carrying capacities
|
|
|
|
Urban sprawl
|
A city's growth as its population increases
|
|
|
|
Intensification
|
Reduces urban sprawl by building up instead of out
|
|
|
|
Parasitism
|
Organism whose niche is dependant on a close association with a larger host organism
|
|
|
|
Ecological niche
|
Abiotic limiting factors and biotic relationships with other species ex brown bat with NO OBSTACLES
|
|
|
|
Ecological niche
|
Abiotic limiting factors and biotic relationships with other species ex brown bat with NO OBSTACLES
|
|
|
|
Bottom up
|
Shortage of plant resource at base causes a decline in higher trophic levels
|
Grasshopper and shrews
|
|
|
Ecological niche
|
Abiotic limiting factors and biotic relationships with other species ex brown bat with NO OBSTACLES
|
|
|
|
Bottom up
|
Shortage of plant resource at base causes a decline in higher trophic levels
|
Grasshopper and shrews
|
|
|
Top down
|
Prey effects the number of predators
|
Rabbits and coyotes
|
|
|
Ecological niche
|
Abiotic limiting factors and biotic relationships with other species ex brown bat with NO OBSTACLES
|
|
|
|
Bottom up
|
Shortage of plant resource at base causes a decline in higher trophic levels
|
Grasshopper and shrews
|
|
|
Top down
|
Prey effects the number of predators
|
Rabbits and coyotes
|
|
|
Dominant species
|
So abundant they have the largest biomass
|
Primary producers
|
|
|
Ecological niche
|
Abiotic limiting factors and biotic relationships with other species ex brown bat with NO OBSTACLES
|
|
|
|
Bottom up
|
Shortage of plant resource at base causes a decline in higher trophic levels
|
Grasshopper and shrews
|
|
|
Top down
|
Prey effects the number of predators
|
Rabbits and coyotes
|
|
|
Dominant species
|
So abundant they have the largest biomass
|
Primary producers
|
|
|
Keystone species
|
Greatly affects pop # and health of an exosystem
|
Sea otters
|
|
|
Ecological niche
|
Abiotic limiting factors and biotic relationships with other species ex brown bat with NO OBSTACLES
|
|
|
|
Bottom up
|
Shortage of plant resource at base causes a decline in higher trophic levels
|
Grasshopper and shrews
|
|
|
Top down
|
Prey effects the number of predators
|
Rabbits and coyotes
|
|
|
Dominant species
|
So abundant they have the largest biomass
|
Primary producers
|
|
|
Keystone species
|
Greatly affects pop # and health of an exosystem
|
Sea otters
|
|
|
Succession
|
The series if changes in an ecosystem thats occurs over time following a disturbance
|
|
|
|
Ecological niche
|
Abiotic limiting factors and biotic relationships with other species ex brown bat with NO OBSTACLES
|
|
|
|
Bottom up
|
Shortage of plant resource at base causes a decline in higher trophic levels
|
Grasshopper and shrews
|
|
|
Top down
|
Prey effects the number of predators
|
Rabbits and coyotes
|
|
|
Dominant species
|
So abundant they have the largest biomass
|
Primary producers
|
|
|
Keystone species
|
Greatly affects pop # and health of an exosystem
|
Sea otters
|
|
|
Succession
|
The series if changes in an ecosystem thats occurs over time following a disturbance
|
Beaver meadow for wolf packs
|
|
|
Ecosystem engineer
|
A species that causes such dramatic change to landscape that it creates a new ecosystem
|
Ex beaver and beaver meadow
|
|
|
Connectivity
|
Connecting between different ecosystems
|
|

