![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Levels of Biological Organization |
1. Cells - Smallest unit of life Eg. Blood cell 2. Tissues - A group of cells Eg. Muscle cell 3. Organs - A group of tissues that work together Eg. Heart 4. Organ System - A group of organs Eg. Circulatory system 5. Organism or Individual - A living thing Eg. Mouse, amoeba 6. Population - A group of the same species living together Eg. Deer 7. Community - Made up of several populations Eg. Mice, deer, grass 8. Biome - A large area with its own climate and powerful type of vegetation (made up of communities) Eg. Tundra 9. Biosphere - Region of earth which supports life (made of biomes) |
|
|
Food Chain and Food Web |
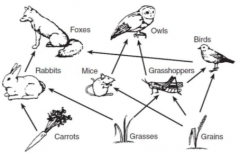
Food Chain - Feeding sequence showing flow of energy Food Web - Many interacting feeding sequences showing flow of energy |
|
|
Ecosystem |
Unit of biosphere with organism interacting with environment |
|
|
Niche |
Interactions of living things with their surroundings |
|
|
Trophic Level |
Feeding level of an organism |
|
|
Scavengers and Decomposers |
Scavengers - Large organisms that consume dead organisms Eg. Vultures Decomposers - Small organisms that break down dead organisms and wasteEg. Fungi |
|
|
The Earth's Spheres |
Atmosphere - Air mass around the earth Lithosphere - Solid part of Earth surface Hydrosphere
- Water covering the Earth
Biosphere - Layer of planet with life
|
|
|
Ecological Pyramids Pyramid of numbers |
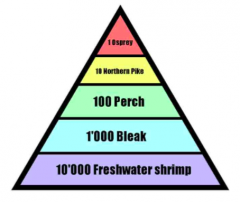
Area of each box proportional to the number of individuals at that trophic level |
|
|
Ecological Pyramids Pyramid of biomass |
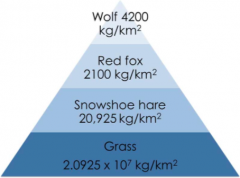
The total mass of organisms at each trophic level |
|
|
Ecological Pyramids Pyramid of energy |
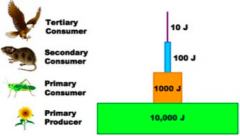
Food energy at each trophic level |
|
|
Laws of Thermodynamics |
- 1st: Energy is not created or destroyed, but changes form - 2nd: Energy tends to become more random (e.g. thermal/heat) |
|
|
Energy Flow in an Ecosystem |
- Sun provides energy for all life - About 70% of light energy from the sun is converted to heat (infrared) energy by hydrosphere and lithosphere - Light energy used for photosynthesis by plants |
|
|
Photosynthesis |
- Light energy is used to make energy-rich sugars Word equation - Carbon dioxide + Water —> Sugar + Oxygen Chemical equation - CO2 + H2O —> C6H12O6 + O2 |
|
|
Cellular Respiration |
- Food is used for energy in plants Word equation Sugar + Oxygen —> Carbon dioxide + Water Chemical equation C6H12O6 + O2 —> CO2 + H2O |
|
|
Abiotic Factors that Affect an Ecosystem Light |
A) Intensity - Plants need certain amount of light for photosynthesis - Saturation intensity: maximum light needed, low in moss, high in sunflower B) Duration - Plants: Photoperiod —> Some plants need lots of light others less - Animals: Controls migration, hibernation, sleep patterns, mating C) Quality - Red and blue light needed for photosynthesis |
|
|
Abiotic Factors that Affect an Ecosystem Temperature |
Plants - Optimum temperature around 30 C - Temperature affects: - Germination (opening of seeds) - Fruit/flower growth - Dormancy in winter |
|
|
Abiotic Factors that Affect an Ecosystem Wind |
Good effects: - Carries plant seeds, pollen, spores, cools Bad effects: - Soil erosion, storm damage, evaporation |
|
|
Habitat |
Space an organism lives in |
|
|
Producers and Consumers |
Producers (Autotrophs) - Makes food from abiotic environment - Self Feeders Consumers (Heterotrophs) - Gets food from biotic environment - Other feeders |
|
|
Primary Consumer and Top Consumer |
Primary Consumer - Trophic level of herbivore Top Consumer - Trophic Level not consumed by others |
|
|
Limits on a Population Biotic Potential |
Maximum population size that can be maintained |
|
|
Limits on a Population Factors that Affect Biotic Potential |
1. Birth potential: # of offspring per birth 2. Capacity for Survival: # of offspring that reaches reproductive age 3. Procreation: # of times a year an organism can reproduce 4. Length of reproductive life: # of years an organism can reproduce for |
|
|
Limits on a Population Environmental Resistance |
Factors decreasing population size |
|
|
Limits on a Population Factors that Control Population Size |
Abiotic - Natural disasters - Chemical pollution - Temperature - Light Biotic - Disease - Predators - Deforestation |
|
|
Limits on a Population Density Dependent and Independent Factors |
Dependant factors - Competition - Predation - Food shortages Independant - Flood - Fire - Drought |
|
|
Zones of Lakes Littoral Zone |
- By shore - Warm - Plants rooted - Lots of light - High oxygen - Lots of organisms |
|
|
Zones of Lakes Limnetic Zone |
- Too deep for plants to root - Moderate temperature - Moderate oxygen - Lots of light - Lots of plankton |
|
|
Zones of Lakes Profundal Zone |
- Cold - Little plant life - Low oxygen - As detritus falls, bacteria uses oxygen to decompose |
|
|
Types of Lakes Oligotrophic |
- Deep - Clear - Cold - Few organisms and nutrients - High oxygen - Eg. Lake Superior |
|
|
Types of Lakes Eutrophic |
- Shallow - Cloudy - Warm - Many organisms and nutrients - Low oxygen - Eg. Lake Erie |
|
|
Eutrophication |
- Build up in nutrients - Life in oligotrophic lake changing into eutrophic lake |
|
|
Human Effects on Lake Ecosystem |
- Commercial fishing - Garbage - Oil spills - Replace natural vegetation - Draining wetlands - Degrading to create deep water for boats |
|
|
Biodiversity |
- Large variety in living things - A greater variety in a food web means greater stability in an ecosystem because it indicates ecosystem is healthy enough to support a variety of species |
|
|
Sustainability |
Fulfilling the needs of the present without degrading the environment so future generations can’t do the same |
|
|
Invasive Species |
- A non-native species brought by purpose or accident to an ecosystem by humans - Eg. Carp |
|
|
Threats to Biodiversity |
- Habitat destruction - Water pollution - Global climate change - Invasive species - Toxins |
|
|
Pests |
- Organisms that people consider harmful - Eg. insects, rodents, weeds |
|
|
Pesticides |
- Insecticides —> Kills insects - Herbicides —> Kills weeds - Fungicides —> Kills molds and fungi - Bactericides —> Kills bacteria |
|
|
Classifications of Species at Risk |
Extinct - Species no longer exists Extirpated - Species no longer exists in a specific area Endangered - Reduced in numbers Threatened - Likely to become endangered if factors risking it’s survival aren’t changed Special Concern - May become threatened or endangered because of combination of factors |
|
|
Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification/Bioamplification |
Bioaccumulation - Build up of toxins inside an organism Biomagnification/Bioamplification - Increase in toxin in organisms with each step of the food chain |
|
|
Toxins / Poisons |
DDT: Insecticide - No serious effect on humans - Results in bird eggshells being very fragile PCB: Transformer coolant - Brain defects, cancer PAH: Petroleum by-product - Cancer Heavy Metal: Pb, Zn, Cu, Hg - Mining by-product - Harm nervous system and reproduction |
|
|
Composition of Soil |
- Minerals - Air - Water - Organic matter |
|
|
Soil Layers |
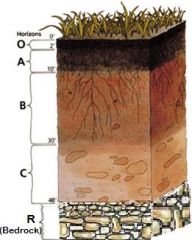
Litter - O - Uppermost layer Dead + decaying leaves and grass Topsoil - A - Below litter - Small particles + humus (decayed materials) Subsoil - B - Many stones - Low organic matter - High minerals Bedrock - C - Rock under soil |
|
|
Weathering |
Rocks get broken apart by wind, glaciers, frost, etc. |
|
|
Soil and Water Surface Water Ground Water |
Soil and Water - Water helps hold the soil in place Surface Water - Precipitation that collects above ground Ground Water - Sits on bedrock |
|
|
Percolation Leaching |
Percolation - Process where water filters through soil Leaching - Nutrients and minerals are drawn down through soil as water is percolating |
|
|
Factors of pH in Soil |
- Nature of rock from which soil was formed - Type of plants that grow and die in soil - Rain of snow that falls |
|
|
Carbon Cycle |
. |
|
|
Water Cycle |
Absorption: - Plants absorb water through their roots Evaporation: - Water vapour evaporates from bodies of water Percolation: - Water is pulled through the soil by gravity Perspiration: - Water is lost through the bodies of animals Precipitation: - Water condenses and falls from clouds Respiration: - Animals lose water as they breathe Runoff/Leaching: - Water drains into bodies of water dissolved material lost by leaching Transpiration: - Water is lost through evaporation from plants |
|
|
Nitrogen Cycle |
Absorption: - Plants absorb nitrates as nutrients Death and Decay: - Animal dies or urinates ammonia Death and Decay: - Plant dies Denitrification: - Bacteria turns nitrates into nitrogen gas Food Chain: - Animal eats plants containing proteins Lightning and Nitrogen Fixing: - Lightning and bacteria fixed into NO3 Nitrogen Fixing: - Bacteria turn nitrites into nitrates Transformation: - Bacteria turns ammonia into nitrites
|

