![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define ecosystem |
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment. |
|
|
Define ecology |
The branch of biology that deals with the relations of organisms to one another and to their physical surroundings. |
|
|
Define Biotic |
relating to or resulting from living things, especially in their ecological relations. |
|
|
Define abiotic |
Non living things |
|
|
Define predation |
Is where one species eats another. |
|
|
Define Commensalism |
Where a species benefits from another species. |
|
|
Define Mutualism |
When two species benefit from each other. |
|
|
Define parasitism |
The parasite lives off of the host, harming it and possibly causing death of the host |
|
|
Define Competition |
Two different species are fighting for the same resources. |
|
|
Define producer |
A organism that serves as a source of food for other organisms in a food chain. |
|
|
Define consumer |
A organism that feeds on other organisms in a food chain. |
|
|
Define Decomposer |
an organism, especially a soil bacterium, fungus, or invertebrate, that decomposes organic material. |
|
|
What's a food chain? |
A series of organisms each dependent on the next as a source of food. food. |
|
|
What's a food web? |
a system of interlocking and interdependent food chains. |
|
|
What's population? |
In genetics a population is a group of interbreeding individuals of the same species, which is isolated from other groups. |
|
|
What's carrying capacity? |
The carrying capacity of a biological species in an environment is the maximum population size of the species that the environment can sustain indefinitely, given the food, habitat, water, and other necessities available in the environment |
|
|
What's limiting factors? |
In ecology, common limiting factor resources are environmental conditions that limit the growth, abundance, or distribution of an organism or a population of organisms in an ecosystem. |
|
|
What's species diversity? |
Species diversity is the number of different species that are represented in a given community. |
|
|
What is watershed? |
an area or ridge of land that separates waters flowing to different rivers, basins, or seas. |
|
|
What is sustainability? |
refers to the capacity of the biosphere to meet the needs of the present generation, without hindering future generations from being able to meet their needs. This means using our natural resources wisely in the short-term so that these resources are available in the long-term. |
|
|
What is fragmentation? |
the process or state of breaking or being broken into small or separate parts. |
|
|
What is equilibrium? |
a state in which opposing forces or influences are balanced. |
|
|
What is biodiversity? |
the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem. |
|
|
What is extripated? |
root out and destroy completely. |
|
|
What is succession? |
is the gradual process by which ecosystems change and develop over time. Nothing remains the same and habitats are constantly changing. There are two main types of succession, primary and secondary. |
|
|
Water vs. Terrestrial |
Almost all the habitats found in the world can be put into two major habitats; aquatic and terrestrial. Aquatic ecosystems are found in water .Terrestrial animals are the animals who live on land for most or all of their life span. ... Water plants do not have roots and do not have woody or stiff trunks. |
|
|
3 Key things for a ecosystem |
Producers,consumers, decomposers. |
|
|
What's the 5 Biotic interactions in an ecosystem? |
Predation,commensalism,mutualism,parasitism,competetion. |
|
|
Carbon cycle |

|
|
|
Water cycle |
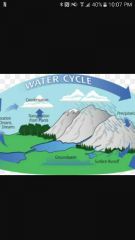
|
|
|
Nitrogen cycle |
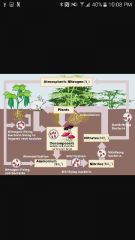
|
|
|
Alge bloom |
Fertilizer gets washes away by heavy rain, gets into river. Causes alge to grow like wildfire and then once it has no food left, dies. As it rots it sucks air out of the water. Killing the species in the river. |
|
|
Why and how are water sheds important? |
Drains surface water and storm water to run off drain into other bodies of water. |
|
|
What is biosphere? |
the regions of the surface, atmosphere, and hydrosphere of the earth (or analogous parts of other planets) occupied by living organisms. |
|
|
What is a lithosphere? |
the rigid outer part of the earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle. |
|
|
What is a hydrosphere? |
All the waters on the earth's surface, such as lakes and seas, and sometimes including water over the earth's surface, such as clouds. |
|
|
What is atmosphere? |
the envelope of gases surrounding the earth or another planet. |

