![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What determines species distributions? |
Physical environment to tolerance limits to biotic interaction; food, predators, competitors, parasites, diseases. |
|
|
What are the fundamental types of terrestrialcommunities? |
Biomes are the major types of terrestrial vegetation. Each biome is characterized by a specific type of vegetation that is determined by the regional climate |
|
|
AbioticFactors Determining the Geographic Rangegoogle.com/GIAG2.crl |
Climate is a key component of the physical environment; Temperature & Precipitation Soils |
|
|
LatitudinalVariation in Temperature |
Driven by the angle of the sun rays relative to theEarth surface |
|
|
SeasonalVariation in Temperatures |
Driven by the tilt of the Earth’s axis relative to theSun |
|
|
LatitudinalVariation in Precipitation |
Driven by the global air circulation Atmospheric circulation: Hadley cells Mid-latitude desertification: World’s largest deserts are around 30° N & S |
|
|
LocalVariation in Precipitation driven by? |
Driven by major landscape features (e.g., mountainrain shadow) one side moist other side dry. |
|
|
EcologicalFiltering Occurs when? |
Occurs when abiotic or biotic factors limit theexistence of species in a community |
|
|
Ecological Filtering Abiotic Filters? |
Abiotic filters: Environmental conditions & Limiting resources |
|
|
Ecological Filtering biotic Filters? |
Biotic filters: Competition , Predation & Parasitism |
|
|
How can disturbance function as an ecological filter? |
Disturbance can function as an ecological filter (byremoving a species) or influence other ecological filters (altering limitingresources) |
|
|
DistributionDepends on Evolutionary History What types? |
Geological history Historical shifts in climate Phylogenetic history |
|
|
Geological History |
Continental drift Glaciation (formation of the Bering Land Bridge) |
|
|
Phylogenetic history |
Species and their descendants have geographicaldistributions |
|
|
Typesof Terrestrial Communities: Large Scale |
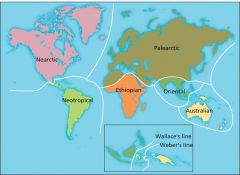
Biogeographic realms: Determined by evolutionary history, geologicalconnections, and regional climate |
|
|
Typesof Terrestrial Communities: Small Scale |
Biomes: ecosystemscharacterized by specific types of vegetation Plant species may be different in the same biomes indifferent geographical regions Deciduous forests in Europe vs. N. America orrainforests in Asia vs. S. America |
|
|
Biomes |
Tundra, Conifer Forest, Temperate Deciduous Forest, Temperate Grassland, Mediterranean Shrubland, Desert, Tropical Savanna, Tropical Rainforest. |
|
|
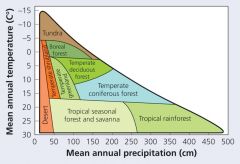
Determining factors of Biomes. |
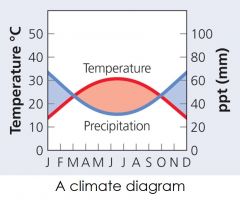
Climate factors(temperature and precipitation) are the maindeterminants of biome plant life |
|
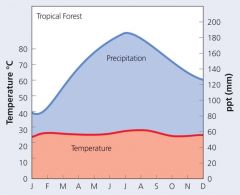
Rainforest Features |
Leaf morphology toprevent water accumulation Epiphytic habit Trunk buttresses Shallow root system |
|
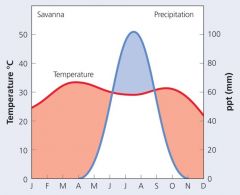
TropicalSavanna Features |
Deciduous habit (↓water loss duringthe dry season) Grasses regrow from roots (↑growth after fire) Thorns and spines (protection from grazers) |
|
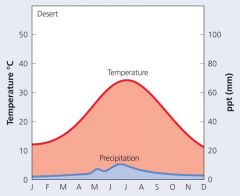
Desert Features |
Allelopathy (↓competitionfor water) Reduced leaves (↓water loss) Hairy leaves (↑shade, ↓wind) |
|
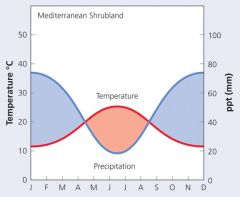
Mediterranean Shrubland Feature |
Flammable oils (promotefires to ↓competition) Resprout from roots(after fire) Hard, needle-like leaves w/few stomata (↓water loss)?`@ |
|
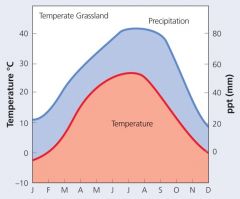
TemperateGrassland Feature |
Deep root systems
Quick regrowth from roots Meristem underground (prevent damage from grazing orfire) High silica content (↓grazing) |
|
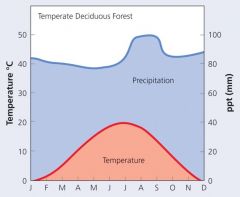
TemperateDeciduous Forest Feature |
Deciduous habit (↓waterloss during winter dormancy) Broad leaves to capture sunlight Thick bark to protect from cold Understory plants flower in the spring before canopy develops |
|
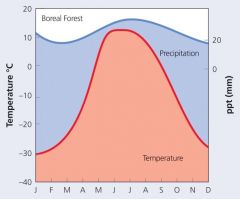
BorealForest Feature |
Evergreen habit(↑photosynthesis) Needle-like leaves (↓water loss and snow retention) Dark color (↑heat absorption) Drooping branches to shed excess snow |
|
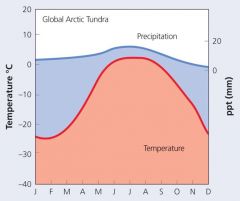
ArcticTundra Feature |
Small, low-growingplants Shallow root system (permafrost) Dark color (↑heat absorption) Hairy stems & leaves (↓water loss) Growth in clumps (protection from the wind and cold) |
|
|
Biomesare Linked to Climate Patterns |
|

