![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Long-run Costs |
Period long enough for all inputs to become variable. |
|
|
|
Calculation for Total Cost (TC) |
TC = TVC |
Long-run |
|
|
Decisions Business Must Make |
• What must the scale of production be: decide how many units to produce to minimise cist of production.
• Where should the business be located: Factors that influence: nature of product; infrastructure required; target market. • Which production technique should be used: Direct impact of long-run cost of production. Eventually influence profitability. |
|
|
|
Economies of scale |
When inputs are increased and production increase by more than the % increase in inputs. |
|
|
|
Long-run Average Cost (LRAC) |

• Vary based on economies of scale that a business experiences.• Economies of Scale: LRAC decreases as Q increases• Constant Costs: LRAC remains constant as Q increases• Diseconomies of Scale: LRAC increases as Q increases |
|
|
|
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility |
As Q consumed increases, satisfaction attained decreases. |
|
|
|
Reasons for Economies of Scale |
• Specialisation of resources. • Technology advanced equipment. • Improvement in organisation eg. assembly-line production. |
|
|
|
Total Revenue (TR) |
Total value of sales of business or producer. |
|
|
|
Calculation for TR |
TR = Price × Q sold |
|
|
|
Average Revenue (AR) |
If AR = Market price, then the product is homogeneous. |
|
|
|
Calculation for AR |
AR = TR/Q sold |
|
|
|
Marginal Revenue (MR) |
Change in TR if one additional unit of a product is sold. |
|
|
|
Calculation for MR |
MR = (Change in TR)/(Change on Q sold) |
|
|
|
Accounting Profit (or total profit) |
The difference between TR from sales and total explicit costs. |
|
|
|
Explicit Costs |
Payments of money that have been made for the factors of production and other inputs that are used in the production process. |
|
|
|
Normal Profit |
• Minimum return that is required by the owners of a business in order for them to continue with the business. • This profit should be large enough to justify the continuation of the business. • Normal profit is the remuneration for entrepreneurship. • It included in the TC of production. |
|
|
|
Economic Profit |
Extra profit (additional to the money that is allocated to the entrepreneurship as a factor of production) that a business makes on a specific transaction. |
|
|
|
Draw MR/MC Graph |
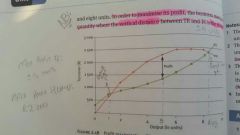
|
|
|
|
Draw MR/MC Graph |

|
|

