![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
84 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Medicinal Chemistry |
Influence of chemical structure on biological acitvity |
|
|
|
Desolvation |
Removal of water molecules from polar regions of drug |
|
|
|
Removal of water molecules from polar regions of a molecule |
desolvation |
|
|
|
6 Noncovalent interactions (strongest to weakest) |
Ionic H-bond Van der Waals Dipole-dipole Ion-dipole Induced dipole |
|
|
|
interaction between quaternary ammonium ion and aromatic ring |
induced dipole |
|
|
|
example of induced dipole interaction |
interaction between quaternary ammonium ion and aromatic ring |
|
|
|
Alkanes are stable under what 5 conditions? |
ambient aqueous acidic basic heat |
|
|
|
How are alkanes usually excreted? |
unchanged |
|
|
|
Which location does CYP450 react with which type of aliphatic molecules?? |
Terminal or adjacent Carbon of Hydrocarbon chain |
|
|
|
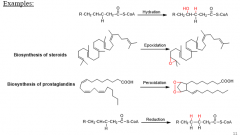
alkenes have what that results in what? |
double bond geometric isomers |
|
|
|
which type(s) of noncovalent interactions do alkanes experience? |
Van der Waals |
|
|
|
Which type(s) of noncovalent interactions do alkenes experience? |
weak dipole |
|
|
|
What reactions are alkenes vulnerable to? |
oxidation peroxidation epoxidation reduction hydration |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
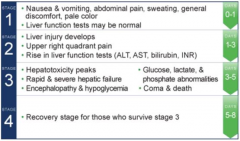
|
|
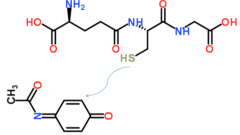
|
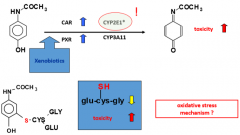
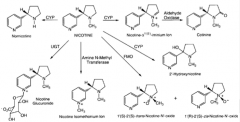
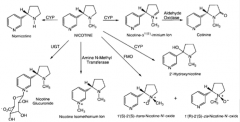
glutathione n-acetyl cysteine |
|
|
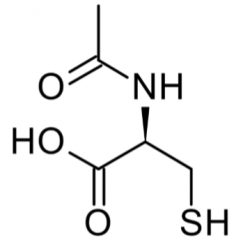
|
n-acetyl cysteine |
|
|
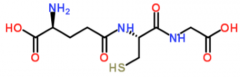
|
glutathione |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
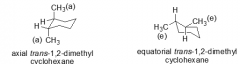
Which is lower energy? axial-trans equatorial-trans |
equatorial trans |
|
|
|
What isomer variants are generated by polysubstitution? |
cis and trans |
|
|
|
How many carbons does a ring need for conformational isomers? |
6+ |
|
|
|
What are the variations of conformational isomerism? |
boat and chair |
|
|
|
Axial vs equatorial is a product of |
polysubstitution and conformational isomerisms |
|
|
|
how are cycloalkanes similar to alkenes? |
both can have geometric isomers |
|
|
|
aromatic hydrocarbons are vulnerable to which type of metabolic rxn? |
aromatic hydroxylation |
|
|
|
description of the mechanism of aromatic hydroxylation |
electrophilic |
|
|
|
Aromatic hydroxylation may involve which reaction mechanism as an intermediary? |
epoxidation |
|
|
|
epoxidation may be an intermediate mechanism for this type of reaction |
aromatic hydroxylation |
|
|
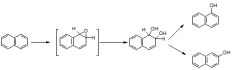
|
aromatic hydroxylation via epoxidation |
|
|
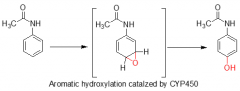
|
aromatic hydroxylation |
|
|
|
describe the geometric conformation of aromatic hydrocarbons |
flat |
|
|
|
aromatic hydrocarbons experience which noncovalent interaction(s)? |
Van der Waals induced dipole |
|
|
|
Noncovalent interaction(s) experienced by halogenated hydrocarbons: |
van=der waals |
|
|
|
what "strengths" do halogenated hydrocarbons have over regular hydrocarbons? what "advantage" does this result in? |
Higher chemical stability not readily excreted by kidney Longer half life |
|
|
|
These funx groups are Permanent dipoles |
alcohols |
|
|
|
How can alcohols be structured to be more water-soluble? |
hydroxyl near center of molecule |
|
|
|
alcohols with hydroxyls far from th molecular center are.... |
less water soluble |
|
|
|
This type of funx group forms strong H-bonds because..... |
Alcohols permanent dipoles |
|
|
|
Which alcohol(s) are stable against oxidases? |
tertiary |
|
|
|
Tertiary alcohols are stable against what? |
oxidases |
|
|
|
Which funx group(s) is/are mildly acidic? |
phenols |
|
|
|
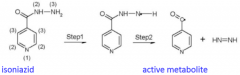
pKa of Phenol |
9.96 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
What metabolic rxn is most common for phenols? |
G and S conjugation |
|
|
|
CYPs perform which rxn(s) on Phenols? |
oxidation hydroxylation |
2 |
|
|
Methylation is a metabolic rxn that can happen to which funx group(s)? |
phenols |
|
|
|
Phenols can experience which metabolic rxn(s)? |
oxidation/hydroxylation methylation G and S conjugation |
3 types |
|
|
Ether general structure |
ROR |
|
|
|
ROR is what? |
Ether |
|
|
|
Ethers experience which noncovalent interaction(s)? |
weak H-bonding |
|
|
|
Solubility of these functional groups can be described as weak in water: |
Ethers |
|
|
|
The solubility of ethers can be described as: |
poor in water |
|
|
|
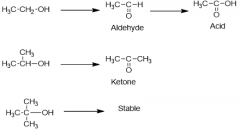
Noncovalent Interaction(s) experienced by Aldehydes and Ketones: |
H-bond to water |
|
|
|
Reduction of these functional group(s) produce alcohols: |
ketones aldehydes |
2 |
|
|
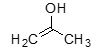
Enol is produced by resonance of a: |
ketone |
|
|
|
A resonance of a ketone could be described as an: |
enol |
|
|
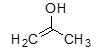
form of acetone |
enol |
|
|
|
Ethers are metabolized by which rxn(s)? |
none |
|
|
|
These functional groups are generally excreted unchanged |
ethers alkanes |
|
|
|
What physiochemical effects can occur from the addition of an amine? |
solubilization as a free base or salt of an amine binding site |
3 |
|
|
Addition of this functional group(s) can solubilize a drug by which means? |
amine acts as free base or salt of amine |
1 2 |
|
|
Amines experience which noncovalent interaction(s)? |
H-bonding steric effects |
|
|
|
Substitution with which agents decrease the basicity of amines? |
oxidizing groups aromatic rings |
|
|
|
What reacts to form quaternary ammonium salts? |
amines and acid |
|
|
|
Amines can under go these metabolic rxn(s) |
dealkylation deamination conjugation |
3 |
|
|
Monoamine oxidaze and diamine oxidase perform this metabolic rxn |
deamination |
|
|
|
metabolic deamination is catalyzed by the following enzyme(s) |
MAO DAO |
|
|
|
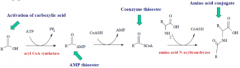
Carboxylic acids undergo the following metabolic reaction(s) |
G conjugation oxidation of beta C by coenzyme A |
2 applies to fatty acids |
|
|
Fatty acids are described molecularly as |
carboxylic acid with aliphatic tail |
|
|
|
carboxylic acid with aliphatic tail |
fatty acid |
|
|
|
Fatty acids undergo which metabolic rxn by which cofactor? |
oxidation by coenzyme A |
on beta carbon |
|
|
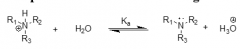
Functional derivative(s) of carboxylic acids |
esters amides |
2 |
|
|
Esters and amides are functional derivatives of which type(s) of functional groups? |
Carboxylic acids |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
very strong acids like mineral acids |
sulfonic acids |
|
|
|
sulfonic acids experience these type(s) of noncovalent interactions |
ion-dipole with water |
|
|
|
Sulfonamides are in what state |
solid form |
|
|
|
Solubility of sulfonamides can be described as: |
insoluble |
|
|
|
Solubility of thioethers can be described as: |
lipophilic |
|
|
|
These funx groups are produced from metabolism of thioethers |
sulfoxides/sulfones |
|
|
|
Sulfoxides and sulfones are products of: |
Thioethers |
|
|
|
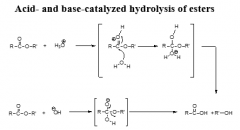
esterases |
|

