![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define gene |
Section of DNA that codes for protein, unit of inheritance |
|
|
Define gene expression |
The code of the gene is used to make protein |
|
|
Define chromosomes |
Structure in the nucleus composed of DNA + protein |
|

|

|
|
|
Define junk DNA (Non-coding DNA) |
Section of the chromosomes that doesn't code for a protein |
|
|
Scientists who discovered Structure of DNA |
Watson + Crick |
|
|
What does DNA stand for? |
Deoxyribonucleic Acid |
|
|
Shape of DNA |
Double helix |
|
|
Nitrogenous Bases in DNA |
Adenine (A) - Thymine (T), Guanine (G) - Cytosine (C) |
|
|
Purine Bases |
Adenine, Guanine |
|
|
Pyrimidine Bases |
Thymine, Cytosine |
|
|
Define Complementary Base Pairs |
Each base has a corresponding base. Bases attach to each other by hydrogen bonds |
|
|
Besides the nucleus, in what other cell structures can DNA be found in? |
Chloroplasts + mitochondria |
|
|
5 carbon sugar in DNA |
Deoxyribose |
|
|
Other than nitrogenous bases and sugars, what other structure makes up the DNA nucleotide? |
Phosphate |
|
|
Define DNA Replication |
The production of an identical copy of DNA in the nucleus |
|
|
In what phase of the cell cycle does DNA Replication occur? |
Interphase |
|
|
Draw + Describe DNA Replication |
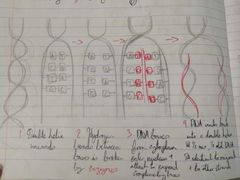
|
|

Label the broader perspective of DNA replication |

|
|
|
Define DNA Profiling (Genetic Fingerprinting) |
Making a unique pattern of a person's DNA to compare with other DNA |
|
|
Applications of DNA Profiling |
- Crime Scenes (forensics) e.g. blood, saliva, semen - Paternity Tests |
|
|
Describe the process of DNA profiling |
1. Cells broken down to release DNA 2. DNA cut into fragments using restriction enzymes 3. Fragments separated based on size using gel electrophoresis 4. Patterns compared |
|
|
Define genetic screening |
Testing DNA for the presence (or absence) of a particular gene or altered gene |
|
|
What does RNA stand for? |
Ribonucleic acid |
|
|
RNA Bases |
Adenine - Uracil Guanine - Cytosine |
|
|
Differences between RNA vs. DNA |
RNA: Single Strand, Contains Uracil, Found in nucleus, cytoplasm + ribosome, Can leave nucleus DNA: Double strand, Contains Thymine, Found in Nucleus, Cannot leave nucleus |
|
|
Define Protein Synthesis |
Making of a protein in the ribosomes |
|
|
Structure of Protein |
Many amino acids joined together by a peptide bond |
|
|
Shape of Protein? |
Folded |
|
|
Define triplet/codon |
Sequences of 3 bases that code for 1 amino acid |
|
|
Function of DNA strand in Protein Synthesis |
Carries code to make protein |
|
|
Define transcription
|
Copying of DNA code on to mRNA in the nucleus
|
|
|
Where in the cell does Transcription occur?
|
Nucleus |
|
|
Where in the cell does Translation occur? |
Ribosome |
|
|
What does m in mRNA stand for?
|
Messenger RNA |
|
|
Composition of rRNA |
rRNA + protein |
|
|
Composition of tRNA |
Anti-codon + amino acid |
|
|
What does the t stand for in tRNA? |
Transfer
|
|
|
What does r in rRNA stand for? |
Ribosomal |
|
|
Describe the process of Protein Synthesis
|
1. DNA carries code to make protein 2. DNA unwinds + enzymes break bonds between bases 3. Transcription occurs (def) as RNA bases attach to complementary bases on one DNA strand 4. RNA polymerase bonds bases together to form mRNA 5. mRNA leaves nucleus + bonds with rRNA in ribosome. DNA strands in nucleus rewind into a double helix. 6. tRNA enters ribosome from cytoplasm 7. tRNA attaches to complementary mRNA codons - beginning at start codon, the series of codons in sequence that will form protein + stopping at stop codon 8. Translation (def) in ribosome occurs as ribosome bonds the amino acids together to form a protein 9. Protein folds into 3D globular shape to give it its function |
|
|
What bonds bases together during Protein Synthesis to form mRNA? |
RNA polymerase |
|
|
What breaks bonds between DNA bases? |
Enzymes |
|
|
Structure of mRNA |
Start codon, series of codons that code for particular protein, stop codon |
|
|
Define Translation |
The production of a protein using the code on RNA
|
|
|
What must the protein do in order to function? |
Fold into 3D globular shape |
|
|
Types of RNA |
Messenger RNA (mRNA), Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and Transfer RNA (tRNA) |
|
|
Function of mRNA |
- Involved in transcription (Copies DNA code in nucleus + carries it to ribosome, Attaches to rRNA) |
|
|
Function of rRNA
|
- Forms ribosome - Bonds with mRNA |
|
|
Function of tRNA |
- Involved in translation (Carries amino acids to the ribosome from cytoplasm, Binds to mRNA w/ complementary anticodon, places amino acids in sequence) |
|
|
Define allele |
Different forms of the same gene |
|
|
What controls characteristics? |
Pairs of alleles |
|
|
Define Locus
|
The position of a gene on a chromosome |
|
|
Define Homozygous |
2 of the same in the pair, both capital or small e.g. BB or bb |
|
|
Define Heterozygous
|
2 alleles are different in the hairs
e.g. Bb |
|
|
Define Genotype |
Genetic makeup i.e. the genes present e.g. Bb, BB or bb |
|
|
Define Phenotype |
Physical appearance e.g. brown hair |
|
|
Define Dominant |
If present, will always show in the phenotype i.e. prevents recessive allele from working e.g. B |
|
|
Define Recessive |
Prevented from working by dominant allele, only shows in phenotype if both alleles are recessive e.g. bb |
|
|
Define F1 Progeny |
Offspring produced |
|
|
Only _______ allele for each ____________ enters ____________ |
One, characteristic, gamete |
|
|
Define Punnett Square |
A grid used to show the ratio of genotypes of the progeny in a genetic cross |
|
|
Types of Genetic Crosses |
Monohybrid, Sex Determination, Incomplete Dominance, Dihybrid, Linked, Sex Linked |
|
|
Define autosomes |
Non-sex chromosomes |
|
|
Define sex chromosomes |
Chromosomes that determine the gender/sex of the individual |
|
|
Sex Chromosomes in Humans |
Females - XX |
|
|
Organisms that have sex chromosomes that are the opposite of humans |
Birds, butterflies and moths Females - XY Males - XX |
|
|
Define Incomplete Dominance in Genetic Crosses
|
When neither allele prevents the other from working i.e. no dominant allele, heterozygous condition shows a different trait e.g. Snapdragon Plants RR - Red rr - White Rr - Pink |
|
|
Father of Genetics |
Gregor Mendel |
|
|
Medel's 1st Law |
Law of Segregation: Inherited characteristics are controlled by a pair of alleles. These alleles separate at gamete formation w/ only one allele being found in each gamete |
|
|
Mendel's 2nd Law |
Law of Independent Assortment When gametes are formed, either of a pair of alleles is equally likely to combine w/ either of another pair of alleles (dihybrid crosses) |
|
|
Define Linkage in relation to genetic crosses |
Genes are located on the same chromosome i.e. they pass on together, they do not show independent assortment |
|
|
Why is linkage significant in genetic crosses? |
Independent assortment results in more variation than linked |
|
|
Define Sex Linkage |
Characteristic is controlled by a gene on the sex chromosome (X) e.g. Colour blindness, haemophilia |
|
|
Why are males more likely to have traits such as colour-blindness, albinism and haemophilia? |
Males only have one allele for colour vision because the Y chromosome is shorter. |
|
|
Why is a boy guaranteed to have a trait such as colour-blindness, albinism and haemophilia if their mother had it? |
Males cannot be carriers |
|
|
Define Pedigree Studies |
Diagrams showing the genetic history of a group related individuals |

