![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
DNA is |
Double stranded and antiparallel |
|
|
What does antiparallel mean |
It means the DNA stands are parallel and identical, but run in opposite directions |
|
|
Define mRNA |
A copy of a gene that codes for a specific polypeptide, and takes it out of the nucleus, to the Ribosomes |
|
|
tRNA |
Carries amino acids to the ribosome |
|
|
rRNA (ribosomes) |
The site of protein translation |
|
|
Differences between DNA and RNA |
DNA forms a double helix whereas RNA is single stranded DNA has A T C G RNA has A U C G DNA has deoxyribose RNA has ribose |
|
|
Basic overview of Central Dogma |
Replication (DNA Polymerase and Helicase) Transcription (RNA Polymerase) Translation (Ribosome, rRNA, tRNA) |
|
|
Function of helicase |
Breaks the hydrogen bonds between complimentary base pairs of DNA (separates the strands) |
|
|
Function of DNA polymerase |
Synthesizing new strands by catalyzing the reactions between free deoxynucleotides and base pairs of the parent strand |
|
|
DNA replication is a ......... process |
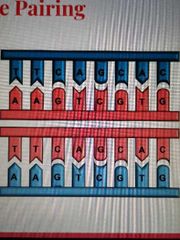
Semi-conservative process One stand will be from the template, one strand will be new |
|
|
Summary of Meselson and Stahl's experiment |
E.coli was cultured in 15N for several generations, and then was moved to a 14N solution abruptly. After several generations, the DNA samples were extracted and analysed. Newly synthesized strands were predicted to have 14N bands. |
|
|
What were the results of Meselson and Stahl's experiment (first replication, second replication) |
After first replication: Molecules had a mix of 15N and 14N After second replication: Previous mix was present, additionally some molecules only had 14N |
|
|
How did the experiment prove the theory of semi-conservative replication? |
It proved the theory because the evidence suggested that newly produced strands from the first replication were used as templates in the second replication |
|
|
What is Polymerase Chain Reaction |
An artificial method of replicating DNA in controlled conditions |
|
|
Define transcription |
The process by which an RNA sequence is formed from DNA |
|
|
Summarize transcription |
1. RNA Polymerase binds to DNA at a start codon 2. RNA Polymerase moves along DNA, separating strands and pairing free nucleotides with complementary bases (A with U, T with A, C with G, G with C) RNA built in 5' to 3' 3. Stop codon is reached 4. RNA separates from DNA, double helix reforms |
|
|
Define translation |
The process by which proteins are synthesized using information coded in mRNA to form a sequence of amino acids |
|
|
tRNA contains.... |
Anticodon - 3 complimentary bases Amino acid attachment site |
|
|
Summarize process of translation |
1. Ribosome (acts as a catalyst) binds to mRNA (moves 5' to 3') 2. Start codon is reached 3. tRNA molecules align according to complimentary base pairing 4. Ribosome catalyses the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids that the tRNA carries 5. Repeats until a stop codon is reached 6. Polypeptide chain is released |

