![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

The structure of the nucleus |

· Nuclear membrane: a double membrane that is continous with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) · Nucleoplasm: a jelly-like fluid which contains free nucleotide bases · Nucleoulus: a dark body tgar manufactures and contains ribosomal RNA · Chromatin network: tangled threads that occur throughout the nucleoplasm. When cells divide the network condenses to form chromosomes |
|
|
Functions of the nucleus |
· The control center for all activities in the cell · Chromosomes carry hereditary characteristics from cell to cell and from parent to child |
|
|
The structure of nucleic acids |
· Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids · Both types of nucleic acids are made up of monomers called nucleotides · Each nucleotide is made up of a: ° Nitrogenous base ° Sugar portion (ribose or deoxyribose) ° Phosphate portion |
|
|
Kinds of DNA |
· Nuclear DNA - Found within the nucleus. Together with histones, it makes up chromosomes · Extra-nuclear DNA - DNA found outside the nucleus · Chloroplastic DNA -DNA found in the chloroplasts · Mitochondrial DNA/mtDNA - DNA found in the mitochondria (helps us trace our ancestors) |
|
|
Function of Nuclear DNA |
· Controls the structure and functioning of the cell by controlling the synthesis of proteins
· Transmits hereditary characteristics from parent to child |
|
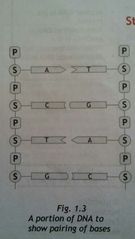
Structure of DNA |
· Made up of monomers called nucleotides · The sugar it has is deoxyribose · Has adenine, guanine (purines), and cystosine, thymine (pyrimidines) · The sugar molecule becomes attached to the phosphate ion of another by sugar-phosphate bonds · There are two complementary base pairs: ° Cytosine and guanine ° Adenine and thymine · The nitrogenous bases are held together with weak hydrogen bonds · DNA makes a double helix
|
|
|
What are the purines? |
Adenine and guanine |
|
|
What are the pyrimidines? |
Cytosine and thymine |
|
|
What holds the nitrogenous bases together? |
Weak hydrogen bonds |
|
|
The shape of DNA |
Double helix |
|
|
Genes |
· A small section of DNA that carries the genetic code for the formation of particular traits and proteins |
|
|
Non-coding DNA |
· Sections of DNA that do not carry code for proteins or any other characteristic |
|
|
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) |
Found in the ribosomes in the cytoplasm of the cell |
|
|
Messenger RNA (mRNA) |
Found in the nucleus but moves out of the nucleus and attaches to ribosomes in the cytoplasm later |
|
|
Transfer RNA (tRNA) |
Found in the cytoplasm of the cell |
|
|
Functions of RNA |
All three types play an important role in protein synthesis |
|
|
The structure of RNA |
· single-stranded · uncoiled · the sugar is ribose · thymine is replaced by uracil · shorter chains |
|
|
Differences between DNA and RNA |

|

