![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
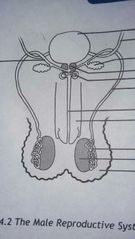
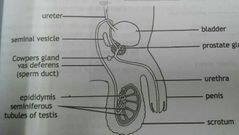
Male reproductive system |
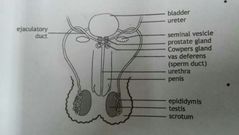
· a pair of testes found in the scrotum · epididymis · vas deferens · ejaculatory duct · urethra · seminal vesicles · prostate gland · Cowper's glands · the penis |
|
|
Testes |
· the male sex organs · they occur in the scrotum which lies outside the abdominal cavity |
|
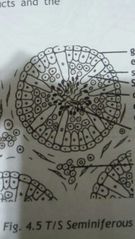
Structure of the testes |

· seminiferous tubules found in each testis · seminiferous tubules are lined by germinal epithelial cells that produce sperm · inside the seminiferous tubules are the cells of Sertoli which are rich in glycogen · glycogen serves as nutrients for the spermatids as tgey develope into sperm · the interstitial cells (called cells of Leydig) are found between the seminiferous tubules · the cells of Leydig excrete testosterone · testosterone is responsible for the male characteristics |
|
|
Spermatogenesis |
The process by which sperm is produced |
|
Tubules responsible for carrying sperm |
· epididymis · vas deferens · ejaculatory ducts · urethra · Accessory Glands |
|
|
Epididymis |
A coiled tube lying outside each testis but within the scrotum. It leads from the seminiferous tubules, stores sperm temporarily and later passes the sperm into the vas deferens |
|
|
Vas deferens |
Carries the sperm from the epididymis into the ejaculatory duct |
|
|
Ejaculatory ducts |
Joins the urethra just after it leaves the bladder. Contraction of the muscular walls of this duct forces semen through the urethra |
|
|
Urethra |
A tube that runs through the penis and opens at the tip of it. It is a common tube for passage of urine and semen |
|
|
Accessory Glands |
(Seminal vesicles, the prostate gland and the Cowper's glands) secrete a fluid which promotes the movement of the sperm and that also provides nutrients |
|
|
Penis |
The external reproductive organ of the male. It is responsible for transferring the sperm to the female. It is made up of spongy tissue which becomes filled with blood, causing the penos to become erect before it is inserted into the female organ |
|
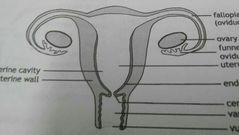
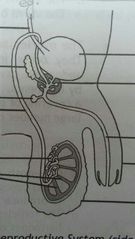
The structure of the female reproductive system |
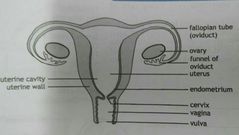
· two ovaries · a fallopian tube leading from each ovary · uterus/womb · vagina/birth canal · vulva/external opening
|
|
|
The ovaries |
The female sex organs. They occur in the lower part of the abdominal cavity and are held in place by ligaments. Each ovary is made of a covering of germinal epithelium cells with a large number of follicles within it |
|
|
Structure of the ovaries |
· the germinal epithelium that produces the follicles · oogenesis takes place within the follicles to produce the ova · the follicles excrete oestrogen and progesterone · when poverty occurs, these hormones becone responsible for the female characteristics |
|
|
Fallopian tubes |
· convey ova from the ovaries to the uterus · the upper part of the fallopian tubes are expanded into ciliated funnels which partially enclose the ovaries · two fallopian tubes open into the uterus · the endometrium (the lining of the uterus) is richly supplied with blood vessels · the cervix extends to the vagina |
|
|
Vagina |
Leads from the uterus to the outside by means of the vulva. During copulation, the penis is placed into the vagina which then releases sperm |
|
|
Changes in puberty |

|

