![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
172 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Bond connecting Nucleotide? |
phosphodiester |
|
|
Three parts of a nucleotide? |
-phosphate -sugar -base |
|
|
What is different on each nucleotide? |
base |
|
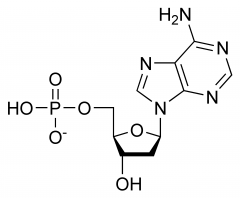
|
Adenine |
|
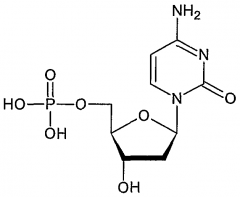
|
cytosine |
|
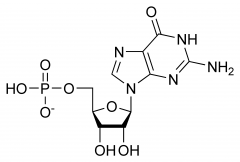
|
Guanosine |
|
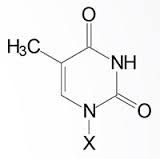
|
Thymine |
|
|
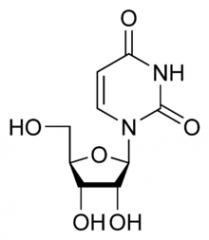
Uracil |
|
|
Which nucleotides are purines? |
A and G |
|
|
Which nucleotides are pyrimidines? |
C, T and U |
|
|
How many rings does a purine have? |
2 |
|
|
how many rings does a pyrimidine have? |
1 |
|
|
How does the numbering scheme for nucleotides progress and in what direction? |
n-1 - n - n+1 - n+2 - GOES 5 TO 3 |
|
|
Sugar for RNA? |
ribose |
|
|
Sugar for DNA? |
deoxyribose |
|
|
length of H-bond between A-T (NH-O)? |
2.8A |
|
|
length of H-Bond of A-T (N-HN)? |
3.0A |
|
|
length of H-bond of G-C (O-HN)? |
2.9A |
|
|
length of H-Bond of G-C (NH-N)? |
3.0A |
|
|
What forms the double helix? |
nucleotide pairing |
|
|
Where does base pairing in B-DNA occur? |
between two complimentary strands (intermolecular) |
|
|
Where does base pairing in A-DNA occur? |
between complimentary regions of one strand (intramolecular) |
|
|
What stabilizes tRNA tertiary structure? |
non WC base pairs |
|
|
interactions that are important for stability of double helix? |
-base pairing -base stacking |
|
|
What can shift A-DNA to B-DNA? |
dehydration |
|
|
why is DNA a polymer? |
-leads to more diversity -only need one enzyme to link |
|
|
What are heterocyclic rings? |
have more than just carbon |
|
|
Where is the glycosil bond? |
between nitrogen of base and carbon of sugar |
|
|
What charge density makes a good H-bond Donor? |
>0.19 |
|
|
What charge density makes a good H-bond acceptor? |
<-0.45 |
|
|
How do you get H-bond capabilities from a atom? |
add contribution from sigma and pi electrons |
|
|
Characteristics of H-bonds?> |
-electrostatic -20X weaker than covalent bonds -can bend and stretch |
|
|
What does a positive charge density mean? |
e deficient -good hydrogen bond donor |
|
|
what does a negative charge density mean? |
e rich atom -good H-bond acceptor |
|
|
pseudo dyad symmetry? |
flip bases over, glycosyl bond is superimposed |
|
|
how far awaya are bases due to stacking of bases? |
3.4 A |
|
|
does base stacking support dipole dipole interactions? |
no |
|
|
What forces cause base stacking? |
-dipole induced dipole -van der waals -hydrophobic interactions |
|
|
Which form of helice is more stable? why? |
A form -has intra and interstrand stacking |
|
|
What does Y stand for? |
pyrimidine |
|
|
What does R stand for> |
Purines |
|
|
What is the shape of a nucleotide? why? |
planar -pi bonds |
|
|
WHat is a gauche angle? |
30 to 90 -30 to -90 |
|
|
what angle is syn? |
-90 to 90 |
|
|
what angle is anti? |
90 to 270 |
|
|
what angle is cis? |
-90 to 90 |
|
|
what angle is trans/ |
90 to 270 |
|
|
What is a nucleoside? |
base and sugar |
|
|
What is a nucleotide? |
base, sugar and phosphate |
|
|
what is the preferential conformation of glycosyl bond? |
anti |
|
|
What stabilizes anti conformation? |
H-bond between O5' and C8 (R) or C5/C6 (Y) |
|
|
What is chi? |
glycosyl bond torsion angle |
|
|
what is the preferred torsion angle for gamma? |
Gauche + |
|
|
Why do sugars not have all ring atoms in the same plane? |
energetically unfavorable because eclipsed |
|
|
What is a twist? |
sugar pucker with 2 atoms out of plane |
|
|
What is an envelope? |
sugar pucker with one atom out of plane |
|
|
what is an endo pucker? |
atom is on same side of 5' C |
|
|
what is an endo pucker? |
atom is on opposite side of 5' C |
|
|
What form is C3' endo? |
A form |
|
|
what form is C2' endo? |
B form |
|
|
What is P? |
pseudo rotation angle |
|
|
C3' endo phosphate distance? |
5.9A |
|
|
C2' endo phosphate distance? |
7.0 A |
|
|
how many bp/turn in A form? |
11 |
|
|
how many bp/turn in B form? |
10 |
|
|
WHat is a stable RNA tetra loop? |
CGUCGG CGNRAG |
|
|
what does lechateliers principle say? |
a reaction will achieve equilibrium |
|
|
What does an increase in base stacking cause? and how is it used? |
a decrease in absorbance -determines if ds or ss |
|
|
what is Tm? |
midpoint of melting curve |
|
|
what does two state model mean> |
all or nothing binding |
|
|
what si the equilibrium constant for initiation? |
less than 1 |
|
|
What can shift the euilibrium to ds? |
increased salts |
|
|
What does he Tm increase for each factor of 10 for salt? |
10-20 C |
|
|
what can you get from a melting curve? |
Keq do to all or nothing model |
|
|
what is f and what can ut be used for? |
fraction of bases paired determine concentration |
|
|
what percent of base pairing is needed to have irreversible melting? |
75% |
|
|
how do proteins recognize DNA> |
sequence and structure |
|
|
What forces stabilize protein and nucleic acid interactions? |
electrostatics hydrophobics polarity |
|
|
How can B-DNA recognize protein in the major groove? |
-2'C -H-bond A and D from bases |
|
|
How can B-DNA recognize protein in the minor groove? |
H-bond A and D |
|
|
How can A-DNA recognize protein in the major groove? |
2'OH -H-bond A and D |
|
|
how do proteins recognize A form ds RNA? |
shape |
|
|
how do proteins typically reconize DNA? |
alpha helixs in major grooves |
|
|
What is direct readout? |
dna is recognized by H-bonds, nonpolar groups, water mediated interactions in the grooves |
|
|
indirect readout? |
effects of sequence on helical parameters |
|
|
which is more stable 5-R-Y-3 or 5-Y-R-3 ? why? |
5-R-Y-3 -better overlap of pi electrons and polar groups |
|
|
What is a common sequence that accommodates a high propeller twist? |
Adenine runs |
|
|
what is a common structure of protein that recognizes DNA? |
alpha turn helix |
|
|
what does a negative roll around y axis do? |
opens major groove |
|
|
what do propeller twists have? |
narrowed minor groove |
|
|
What is an EMSA? |
gel shift assay to determine protein free DNA affinity |
|
|
What information can you get from an EMSA? |
Dfree and DP |
|
|
What is the free energy of DNA protein interaction with Kd = 10^-9 to 10^-13M? |
-13 to -18 kcal/mol |
|
|
What is the Kd of RNA protein interaction
|
10^-6 to 10^-12M?
|
|
|
What is the Kd of protein protein interaction? |
10^-6 to 10^-9 antibody antigen =10^-17 |
|
|
What is the Kd of nonspecific DNA protein interaction? |
10^-6 |
|
|
What form is double stranded RNA? |
always A form |
|
|
What is coaxial stacking? |
base stacking at the interface of RNA helices |
|
|
What are the names of the four parts of tRNA? |
acceptor stem Dloop Tloop anticodon loop |
|
|
WHat are the two edges of a purine? |
hogsteen N7 and N6 watson crick N3 and N6 |
|
|
What are the two edges of a pyrimidine? |
watson crick N3 and N4 C-H edge C5 and N4 |
|
|
what are non-WC base pairs in RNA 3D structure? |
modified base pairs unpaired in 2ndary structure conserved in all tRNAs |
|
|
what is intercalation? |
interstrand stacking |
|
|
What does intercalation need? |
extra room for base to insert |
|
|
What must tRNA interact with? |
-codon -aminoacyl tRNA synthetase -elongation factors peptidyl transferase |
|
|
what indicates hoogsten edge? |
N7 |
|
|
what sugar pucker allows intercalation? |
C2 endo |
|
|
how do negatively charged sidechains interact? |
helices coaxial stacking using magnesium |
|
|
what is a ribose zipper? |
H-bond between 2' OH of ribose of one helix and 2'OH and 2 O of pyrimidine (3N of Purine) |
|
|
What is a A minor motiff? |
minor groove minor groove interactions |
|
|
WHat are other methods to determine structure other than crystals? |
-phylogenetic -genetic -biochemical -computer |
|
|
What is phylogenetic methods? |
look for covariance between RNAs of similar function |
|
|
Problems with phylogenetic studies? |
-need conserved sequences -cant predict non-WC |
|
|
WHat do biochemical structure methods do? |
use enzymes or chemicals to alter the RNA |
|
|
WHat do you use to create hydroxyl radicals? |
fenton reaction |
|
|
what is used to probe structure? |
hydroxyl radical |
|
|
What are the two methods to determine where the bichemical reaction occured? |
-sequencing end labeled RNA -primer extension |
|
|
How can you predict the free energy of a duplex? |
adding the free energy of each base pair in the duplex |
|
|
what do you need to determine free energy of a single base pair in a duplex? |
look at that base pair and its neighbor |
|
|
What is a dot plot? |
judges reliance of computer prediction |
|
|
WHere do most sequence specific protein RNA interactions occur? |
unpaired secondary structure |
|
|
Where do most ribozymes catalyze reactions? |
other RNA -phosphodiester bond |
|
|
Why is the phosphodiester bond of RNA more reactive than DNA? |
2' OH |
|
|
What O does base catalyzed hydrolysis attack? why? |
P-O5' =sn2 mechanism |
|
|
how does P-O3' cleavage occur? |
use a nucleophile not within RNA |
|
|
What part of the tRNA does the 30S ribosome recognize? |
anticodon |
|
|
What part of the tRNA does the 50S ribosome recognize? |
amino acid stem |
|
|
What are the three binding sites of a ribosome? |
A, P, E |
|
|
how does the petide bond form in the ribosome? |
lone pair on amino group in A-site attacks carbon ester in P-site |
|
|
What is used to translocate tRNA in the ribosome? |
GTP |
|
|
What inhibits peptidyl transferase? |
puromycin |
|
|
what catalyzes peptide formation? |
peptidyl transferase |
|
|
What are the proteins in a ribosome for? |
helping hold structure |
|
|
What groove is the amino group of A in? |
major |
|
|
What groove is N7 of A in? |
major |
|
|
What groove is C4 of T in? |
major |
|
|
What groove is C6 of G in? |
major |
|
|
What groove is amino group of G in? |
minor |
|
|
What groove is H-bond donation for C and G in? |
minor |
|
|
What regions of RNA are conserved in a phylogenetic study? |
ssRNA |
|
|
Where can sequence specific interactions of RNA occur? |
-where major groove is widened by -mismatches, loops, or disruptions |
|
|
what is altered in a protein-RNA complex? |
-RNA -protein |
|
|
what do rybozymes act on? |
-RNA substrate (themselves or another RNA) |
|
|
where do most ribozymes catalyze reactions? |
phosphodiester bond |
|
|
Why is RNA more reactive than DNA? |
2' OHq |
|
|
what reaction cleaves phosphodiester? |
transestrification |
|
|
Which P-O is cleaved in a base catalyzed reaction? |
P-O5' |
|
|
What acts as a nucleophile in a P-O5' cleavage? |
2' OH |
|
|
What is the mechanism of P-O5' cleavage and wy? |
SN2, its inline |
|
|
What is the product of a P-O5' cleavage? |
3'-Phosphate and 2'-Phosphate -5' OH |
|
|
How does P-O3' cleavage occur? |
nucleophile comes from somewhere else |
|
|
How can enzymes catalyze reactions at phosphodiester bonds? |
use His as general acid or base |
|
|
What are the products of a P-O3' cleavage? |
-3' Hydroxyl -5' phosphate |
|
|
What is an example of a self cleaving ribozyme and by what mechanism does it react? |
hammerhead ribozyme -P-O5' cleavage |
|
|
Where do hammerhead ribozymes naturally occur? |
viroids |
|
|
how to hammerhead ribozymes replicate RNA? |
-rolling circle replication followed by strand synthesis and cleavage |
|
|
How are ribozymes similar to catalysts? |
can turnover |
|
|
What are group 1 introns? |
ribozymes |
|
|
How do group 1 introns work? |
3' OH of separate guanine attacks P-O5' |
|
|
what do circular nucleotide strands do on a denaturing gel? |
run slower |
|
|
What is required by many ribozymes for catalysis? |
metal ions -Mg!!! -Mn |
|
|
Why are metals needed by ribozymes? |
-structural -catalysis |
|
|
what do group 1 introns require? |
Mg |
|
|
Where are group 1 introns found? |
invertebrates |
|
|
what is the nucleophile in group 2 introns? |
2' OH of adenosine |
|
|
what is formed during group 2 intron splicing? |
lariats loop |
|
|
which P-O is broken during group 2 intron splicing? |
P-O3' |
|
|
What are snRNPs and what do they do? |
splisosome -catalyze mRNA splicing |
|
|
what do snRNAs do for splisosomes? |
base pair to intron to direct proteins to specific sites |
|
|
Where is the adenosine in group 2 introns that acts as a nucleophile? |
domain 6 |
|
|
Where is the metal coordinating site in group 2 introns? |
domain 5 |
|
|
what is intercalation? |
special form of interstrand stacking |

