![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
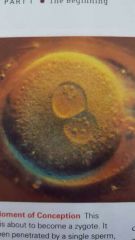
Zygote |
Single cell that forms from the fusing of two gametes, a sperm and an ovum. |
|
|
|
DNA |
Deoxyribonucleic acid; molecule that contains chemical instructions for cells to manufacture various proteins. |
|
|
|
DNA Four Bases |
T- Thymine A- Adenine G- Granite C- Cytosine |
|
|
|
Chromosome |
One of 46 molecules of DNA (23 pairs) that each cell of the body contains. Together, contain all the genes. |
|
|
|
Genes |
Small section of a chromosome; unit for transmission of heredity. Consists of string of chemicals which instruct the cell to manufacture certain proteins. |
|
|
|
Gamete |
A reproductive cell; a sperm or an ovum. Combines with gamete from other sex to form a zygote. |
|
|
|
Allele |
Any of the possible forms in which a gene for a particular trait can occur. |
|
|
|
Polymorphic |
"Many forms"; genes that have various alleles. |
|
|
|
single-nucleotide polymorphism |
Genes that have various alleles with each variation being: "single-nucleotide polymorphism". (abbreviated SNP) |
|
|
|
Genotype |
Organisms entire genetic inheritance, or genetic potential. |
|
|
|
Phenotype |
The observable characteristics of a person, including appearance, personality, intelligence, and all other traits. |
|

