![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the minimum data required for pregnancy records? |
1) Cow ID. 2) Fertility data- calving date and services. 3) Veterinary data- fertility treatments, problems 4) Future actions- Service, PD. |
|
|
What must we do with data recorded for fertility? |
Analyse is every 3-6 months. Report written and talk about it face to face. |
|
|
What things to be look at on a routine herd health visit? |
1) Post natal checks- 21 days after calving. 2) NSB/ONO 3) PD 4) Cows with abnormal cycles. 5) Failure to concieve |
|

When do we perform a PNC and why? |
21 days after calving. Ensure uterus involuted and no endometritis. Vaginal and rectal exam. Do at risk cows- RFM, abortions, prolapse, dystocia cases. |
|
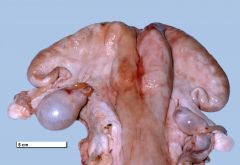
What is considered a cow thats NSB/ONO? What exam to we carry out? |
>42 days after the VWP and no observed oestrous. >63 days post calving and no service. > No visible heat 2-3 weeks after a fertility treatment. Rectal exam to examine the ovaries for cysts |
|
|
What is the aim of the PD ? |
TO detect negative cows and get them presented for re-insemination. |
|
|
When should PD's be carried out? |
30 days for ultrasound. 42-60 days for manual. 60 days post service as 5-10% cows loose the calf at day 30-60= early embryonic deaths. |
|
|
At what point post calving is a cow considered to be abnormally cycling? What is considered an abnormal cycle? |
>42 DAYS post calving. 19-24 day cycle. |
|
|
What is considered a repeat breeder? |
Not pregnant after 3 services. |
|
|
Reason for poor oestrus (heat) detection? |
1) Poor expression of signs of heat by the cow. 2) Poor detection of heat by the farmer. |
|
|
On average how long do dairy cows show signs of oestrus? |
Only 7-10 hours. |
|
|
What measures suggest a problem with oestrus detection on the farm? |
1) If non service oestrus events recorded, a long calving to 1st oestrus interval (aim for 45 days) 2) Long calving to first service interval aim for 42 days. 3) Poor pregnancy rates after PD. 4) Poor heat detection/ submission rates. 5) Heat detection analysis |
|
|
What are cow factors influencing oestrus signs? |
1) Energy balance. 2) Lameness 3) General health 4) Reproductive tract 5) Calving difficulties. 6) RFM 7) Uterine involution 8) Uterine infection. |
|
|
What are environmental factors influencing expression of oestrus signs? |
1) Temp 2) Ventilation. 3) Footing. 4) Grouping.W |
|
|
What are people factors influencing oestrus detection? |
1) Knowledge of heat signs. 2) Heat checks per day. 3) Length of time observed. 4) Who is doing the check 6) Records |
|
|
How can we maximise cows showing signs of oestrus? |
1) Have adequate loafing area space- avoid overcrowding. 2) Non slip floor. 3) Minimise stress in summer with good ventilation. 4) Minimise NEB/BCS loss in early lactation. 5) Minimise social stress- min group changes, adequate trough space. 6) Lame cows treated promptly. 7) Reduce diseases like RFM, endometritis and cystic ovarian disease |
|
|
What is the ideal heat observation frequency and length of each observation? |
Ideally 3 times a day for 20-30 minutes. 6am. 2pm 10pm Do when cows undisturbed |
|
|
What things are essential to detecting heat? |
Cow ID. Records. |
|

What are the benefits of tail paint as an aid to heat detection? Cons? |
Simple. Cheap. Effective. Cons: can wash off in bad weather, false positives |
|
|
Name some heat mount detectors, how do they work? Pros and cons? |
Kamars, place on top of cows spine above pelvis, detects when a cow mounted. False positives. |
|
|
Downfall of using a teaser animal? |
Disease, cost and hassle of keeping a bull |
|
|
Pro of using a natural service bull for heat detection? |
Attract cows in oestrus. Sweeper after AI. |
|
|
What is the principal around using a pedometer for heat detection? |
Cows activity increases 4 fold during oestrus. Attach to neck or leg. |
|
|
When would a pedometer give false positives? |
Movement of social groups. Foot trimming. Turnout |
|
|
What is a test on milk for oestrus? |
Milk progesterone as will be low in oestrus. |
|
|
What is the effect of NEB on cow fertility? |
Negatively impacts her fertility for 2-3 months. A loss of 3/4 of a BCS unit is enough to do it.W |
|
|
What syndromes are caused by NEB in the cow? |
1) Ovarian cyst disease. 2) Prolonged anoestrus. 3) Weak/silent signs of bulling. 4) Early embryonic death. 5) Poor conception rates. 6) Poor PD |
|
|
Pros of on farm AI? |
Cost effective. Better AI timing. |
|
|
Cons of on farm AI? |
Technique.
Quality control. Pressure on staff. |
|
|
Why is dairy cow fertility declining? |
1) Larger herds 2) More cows per staff member. 3)Less farm labour. 4) Less time available for oestrus detection. 5) Poorer nutritional management of high yielders. |

