![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Types of ring opening reactions, epoxides |
Acid/enzyme catalyzed Nucleophilic |
|
|
Reagent to reduce epoxides to alcohols |
LiAlH4 |
|
|
oxirane synthesis from olefins |
Uses peroxy acids, proceeds through butterfly intermediate |
|
|
Common names for the three types of aliphatic 3-membered heterocycles |
N-containing: ethylenimine O-containing: ethylene oxide/epoxide S-containing: ethylene sulfide/episulfide |
|
|
Examples of epoxides in our system |
Vitamin K epoxide (cofactor in reaction of descarbosy-prothrombin to prothrombin)
Squalene epoxide (precursor to cholesterol) |
|
|
Strain in three-membered rings makes protons more _____ |
acidic b/c increased s-character in bonds |
|
|
Methods of aziridine synthesis |
From animoalcohol with thionyl chloride or sulfuric accid
From azide and alkene
From epoxide (stereochemical inversion) |
|
|
Description of MAPK's |
Evolutionarily conserved enzymes connecting cell surface receptors to critical regulatory targets within cells |
|
|
MAPK stands for |
Mitogen activated protein kinase |
|
|
Types of MAPKs in mammalian cells |
1. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1/2) 2. c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK1/2/3) 3. p38 kinases (p38alpha/beta/gamma/delta) 4. ERK5 (big MAPK/BMK) 5. ERK3s (ERK3/4) 6. ERK7s (ERK 7/8)
|
|
|
Common features of MAPKs |
1. Proline-targeted serine/threonine kinases
2. Activation occurs on phosphorylation of two residues in kinase activation loop
3. regulated through tree-tiered cascade of protein phosphorylation |
|
|
MAPK regulation cascade |
mitogen --> MAP3K (MAPK kinase kinase) --> MAP2K (MAPK kinase kinase) --> MAPK |
|
|
Processes MAPKs are involved with, for example |
Transcription Cell cycle regulation apoptosis
|
|
|
RSK stands for |
Ribosomal s6 kinase |
|
|
MSK stands for |
Mitogen- and stress- activated protein kinase |
|
|
Signaling cascade in response to mitogens |
Mitogens -->
MEK1/2 -->
ERK1/2 -->
RSK 1-4 (cell survival, proliferation), MNK 1/2 (mRNA translation), MSK1/2 (nuclear response to stress) |
|
|
Signaling cascade in response to stress cytokines |
Stress cytokines -->
MEK3/6 -->
p38 -->
MNK1 (mRNA translation), MSK1/2 (nuclear response to stress), MK2,3,6 (mRNA stability) |
|
|
MAPKs are regulated by |
interactions with substrates via docking motifs, scaffold proteins, subcellular localization, phosphatases |
|
|
Reason why MEK is a dual-specificity kinase |
two amino acid residues are on the target protein |
|
|
Examples of docking motifs that regulate MAPKs |
D motif, DEF motif |
|
|
CD domain stands for |
Common Docking domain |
|
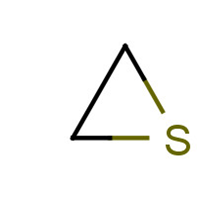
|
Common name: ethylene sulfide, episulfide
Systematic name: thiirane |
|
|
Relative reactivity of oxirane and thiirane |
Both highly reactive, but oxirane is more reactive (because more strained) |
|
|
Reactions of thiirane |
1.nucleophilic ring opening 2. Oxidation by NaIO4 or peroxy acid, yields alkene and SO
|
|
|
Thiirane synthesis methods |
1. from 2-chloroethyl mercaptan, with base 2. from 2-hydroxyethane thiol, with COCl2 (phosgene) |
|
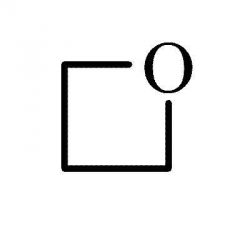
|
Common name: trimethylene oxide
Systematic name: oxetane |
|
|
Relative reactivity: oxetane to oxirane |
Similar reactivity, but oxirane is faster |
|
|
Reactions of oxetanes |
1. acid-catalyzed opening to 1,3-diol 2. Lewis acid-catalyzed polymerization |
|
|
Methods of oxetane synthesis |
1. cyclization of 1,3-diol with base and SO2R 2. Paterno Buchi Reaction (cycloaddition of alkene and carbonyl) |
|
|
Scientist who discovered penicillin |
Alexander Fleming |
|
|
Taxol contains this type of aliphatic heterocycle |
Oxetane |
|
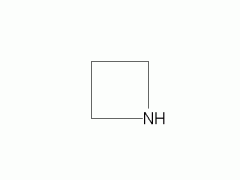
|
Azetidine |
|
|
Beta lacatam mechanism |
Bind to penicillin binding protein |
|
|
How do bacteria get resistance to beta lactams? |
Beta lactamase hydrolyzes amide bond |
|
|
Solution to beta lactam resistance |
use suicide inhibitor that binds to beta lactamase |
|
|
Differences between THF and diethyl ether |
Oxygen in THF is less sterically hindered, increasing its solvation and making it more H2O soluble |
|
|
What does alpha-substitution with a carbonyl do to THF? |
1. Changes it to gamma lactone
2. Makes it very unstable - very prone to acid or base hydrolysis |

